Monocots and dicots
- 1. Differences Between Monocots and Dicots Presented by Crystal Salinas
- 2. Agenda Angiosperm- two classes 1. Monocots 2. Dicots Differences between monocots and dicots Identify plants and place them in the two groups
- 3. What are they? Angiosperm - Flowering plants. First appearing at least 110 million years ago from an unknown gymnosperm ancestor, flowering plants have risen to dominance in most of the world's floras. Angiosperms are divided in to two groups: monocot and dicot.
- 4. What are they? Monocotyledons (Monocots) – These plants have specific characteristics that class them as such. Some examples are: – Palms – Grasses – Orchids – onions
- 6. What are they? Dicotyledons (Dicots) – Dicots also have special characteristics. Some examples of Dicots are: – Oaks – Roses – Mustards – Cacti – sunflowers
- 8. Comparison of Plants Monocot is on the left – Oat plant Dicot is on the right – Bean plant Notice the difference in the two plants
- 9. Vascular Bundle of Monocots In monocots, the vascular bundles in the stem cross section are usually scattered or more complex of an arrangement as compared to dicots.
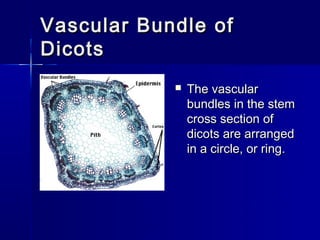
- 10. Vascular Bundle of Dicots The vascular bundles in the stem cross section of dicots are arranged in a circle, or ring.
- 11. Types of Monocots and Dicots
- 12. Review 1. What are three different characteristics that make monocots and dicots different? 2. Are all plants with monocot characteristics monocots? 3. What are some plants that are classified as monocots? 4. What are some plants that are classified as dicots?
- 13. THE END