motivation required by human beings to do anything
- 1. Organizational Behavior Individual Process and Behavior Topic - Motivation
- 2. Flow of Presentation Introduction of topic – Theories of Motivation Content Theory- Maslow’s need hierarchy theory ERG theory Herzberg theory Process Theory- Vroom’s expectancy theory Porter Lawler Model Contemporary Theory- Equity theory
- 3. Meaning Motivation refers to the forces within a person that affect his direction, intensity and persistence of voluntary behavior. Motivation is the set of forces that causes people to engage in one behavior rather than some alternative behavior. Eg.1- Students who stay up all night to ensure that their term papers are the best they can be, Eg.2- Sales people who work on Saturdays to get ahead, and doctors who make follow-up phone calls to patient to check on their condition are all motivated people.
- 4. Objective The objective of motivation is to motivate people to behave in way that are in the organization ‘s best interest. Importance Manager strive to motivate people in the organization to perform at high levels.it means getting them to work hard, to come to work regularly and to make positive contribution to the organization’s mission . But job performance depends on ability and environment as well as motivation.
- 5. Importance Cont.… This relationship can be stated as follows: Performance= M+A+E M= motivation, A= Ability and E= Environment To reach high level of performance, an employee must want to do job well(Motivation) Must be able to do the job effectively(Ability) And must have the material, resources, equipment and information to do the job(Environment). A deficiency in any one of these areas hurts performance.
- 6. Needs Hierarchy Theory Content Theory Needs Hierarchy Theory • Maslow arranged five needs in a hierarchy • Satisfaction-progression process • People who experience self- actualization desire more rather than less of this need • Not much support for Maslow’s theory Self- Actualization Esteem Belongingness Safety Physiological
- 7. ERG Theory Needs Hierarchy Theory ERG Theory • Alderfer’s model has three sets of needs • Adds frustration-regression process to Maslow’s model • Somewhat more research support than Maslow’s theory Self- Actualization Esteem Belongingness Safety Physiological Growth Relatedness Existence
- 8. Frederick Herzberg Theory Late 1950’s and early 1960’s by interviewing 200 accountants and engineers- When they felt especially satisfied and motivated by their jobs and times when they felt dissatisfied and demotivated? In a content analysis , the words , phrases and sentences used by respondents are analyzed and categorized according to their meanings. To his surprise , Herzberg found that entirely different set of factor were associated with the two kinds of feeling about work- e.g. ‘ low pay’ is a source of dissatisfaction instead ‘High pay’ would not be as a source of satisfaction and motivation.
- 9. Frederick Herzberg Theory Herzberg theory is known as dual/two factor theory consist Motivation – Hygiene theory. Herzberg observed that motivation is that factor which presence give satisfaction, but their absence do not lead to dissatisfaction. Hygiene factors are those factor whose absence led to dissatisfaction but their presence do not satisfy the people.
- 10. Frederick Herzberg Theory Motivation factor Challenging work Opportunities to receive recognition Promotion/Growth in the job Sense of personal achievement Chance to take over new responsibilities Hygiene factor Company policy & administration Poor working conditions Salary Job security Quality of supervision Interpersonal relationship
- 11. Innate(Natural) Drives Theory Drive to Bond Drive to Learn • Need to form relationships and social commitments • Basis of social identity • Need to satisfy curiosity and resolve conflicting information • Basis of self-actualization Drive to Defend • Need to protect ourselves • A reactive (not proactive) drive • Basis of fight or flight Drive to Acquire • Need to take/keep objects and experiences • Basis of hierarchy and status
- 12. Learned Needs Theory Some needs are learned, not innate Need for achievement Desire for challenging and somewhat risky goals, feedback, recognition Need for affiliation Desire to seek approval, conform, and avoid conflict Try to project a favorable self-image Need for power Desire to control one’s environment Personalized versus socialized power
- 13. Is Money a Motivator? • Intrinsic(Essential) vs. Extrinsic Motivation • Edwin Locke: “If you think money doesn’t matter, stop paying your employees and see how long they continue coming to work.”
- 14. What about Recognition Programs? • Recognition is about singling people out, making them feel “above the crowd” • How many employees can you “single out?”
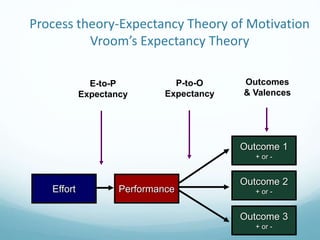
- 15. E-to-P Expectancy P-to-O Expectancy Outcomes & Valences Outcome 1 + or - Effort Performance Outcome 3 + or - Outcome 2 + or - Process theory-Expectancy Theory of Motivation Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
- 16. Increasing E-to-P Expectancy • Train employees • Select people with required competencies • Provide role clarification • Provide sufficient resources • Provide coaching and feedback
- 17. Increasing P-to-O Expectancy • Measure performance accurately • Describe outcomes of good and poor performance • Explain how rewards are linked to past performance
- 18. Increasing Outcome Valences • Ensure that rewards are valued • Individualize rewards • Minimize counter valent outcomes
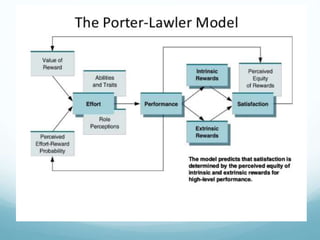
- 19. The Porter and Lawler Model Porter & Lawler exploded the complex relationship between Motivation, Satisfaction and Performance. Acc to them performance is a function of 03 important factors,viz; if employee wants to perform, must be motivated. motivation does not work alone it requires abilities and skills as well. must have the required knowledge of the job.
- 21. Significance of Porter and Lawler Model Put the right person on the right job; Match abilities and trait of individual to the requirements of the job. Make sure the employee understand their role properly.
- 22. Equity Theory of Motivation Proposed by:- J Stacy Adams Argument:- Job performance and satisfaction is the degree of equity or inequity that people perceive in their work situation.
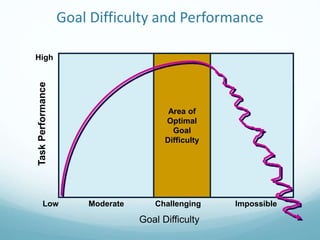
- 24. Goal Difficulty and Performance High Task Performance Low Moderate Challenging Impossible Area of Optimal Goal Difficulty Goal Difficulty
- 25. Goal Setting Maps to Expectancy Theory Specific Relevant Challenging Task Effort Task Performance Feedback Participation Commitment Outcome 1 + or - E-to-P Expectancy P-to-O Expectancy Outcomes & Valences Outcome 3 + or - Outcome 2 + or -
- 26. Theory X & Y of Motivation Proposed by : - Douglas McGregor Theory relates to the Assumptions of Manager about human Natures towards their employees.
- 27. Theory X Assumptions People are naturally lazy. Will avoid work responsibility. They are concerned with only job security. People inherently dislike work. People must be coerced or controlled to do work to achieve objectives. People prefer to be directed.
- 28. Outcome With these assumptions in mind , theory X states that in order for manager to motivate their employee they must use coercion and punishment to ensure that they achieve the goal of the organization. Where as Maslows hierarchy is concerned with fulfilling the needs of the employee, theory X concerns itself with using the threat of removing the factors that fulfill those needs.
- 29. Example:- Instead of using salary increases and job safety to motivate employee, Theory X would use the threat of job loss and salary cuts to motivate employees. Over a period of time managers will soon find themselves unable to effectively motivate employees.
- 30. Theory Y Assumptions People view work as being as natural as play and rest. They exercise self direction and control towards achieving objectives they are committed to People learn to accept and seek responsibility.
- 31. Characteristics of Effective Feedback Effective Feedback Specific Relevant Timely Credible Sufficiently frequent
- 33. Summary • There are a variety of theories which may be useful in helping understand employee behavior • No two employees are the same; being an effective supervisor requires figuring out what makes individual employees tick • Goal Setting isn’t much of a theory; it’s more of a method or technique. However, it tends to work in most jobs where performance can be accurately measured
- 34. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- Satisfaction leads to improved performance, later found very low positive relation between satisfaction and performance