Multimedia tools (sound)
- 2. Introduction • Sound is one of the most important element of multimedia. • It is meaningful “speech” in any language, from a whisper to a scream. • It can provide the listening pleasure of music, the startling accent of special effects or the ambience of a mood setting background. • Sound is the terminology used in the analog form, and the digitized form of sound is called as audio.
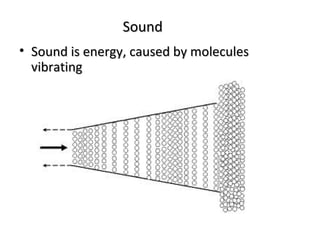
- 4. Power of Sound • When something vibrates in the air is moving back and forth it creates wave of pressure. • These waves spread like ripples from pebble tossed into a still pool and when it reaches the eardrums, the change of pressure or vibration is experienced as sound. • Acoustics – the branch of physics studies sound. • Unit to measure Sound is decibels (db). • A decibel measurement is actually the ration between a chosen reference point on a logarithmic scale and level that is experienced. • Logarithmic scale is also used to measure earthquakes
- 5. Power of Sound • Sound is energy, just like waves breaking on a sandy beach • Too much volume can permanently damage the delicate receiving mechanism behind your eardrums. • The perception of loudness is dependent upon the frequency or pitch of the sound • At low frequencies, more power is required to deliver the same perceived loudness as for a sound at the middle or higher frequency ranges.
- 6. Sound • Sound is energy, caused by molecules vibrating
- 7. Cello Piano
- 8. Multimedia Sound Systems • Macintosh or windows operating system uses sound to make alert signal. • System uses beep and warning sounds are available with the operating system. • They provide several sounds for the system alert. • In windows system sound are WAV files and they are found on windowsMedia subdirectory. • Windows makes use of WAV files as the default file format for audio and Macintosh systems use SND as default file format for audio.
- 9. Cont… Macintosh Windows Sound Recorders for Windows Both Macintosh and Windows PC platform have the default sound.
- 10. Sound conversion Basic Effects
- 11. Capture & Playback of Digital Audio Air pressure variations Digital to Analogue Convert Converter s back into DAC Captured via voltage microphone Signal is converted into binary Analogue (discrete form) to Digital ADC 0101001101 Air pressure Converter 0110101111 variations
- 12. Recording Audio Files Recording Audio Files on the pc Uses either: ii. Microphone connect microphone to the microphone port and record using sound recorder
- 13. Recording Audio Files i. CD-ROM Drive Move music files from CD to hard drive or; Play the cd and then record using the sound recorder. ii. Line-in pressing play on the audio source, which is connected to the computer’s audio line-in socket. Record using the sound recorder. Line in port on the pc Audio cable
- 14. Digital Audio • Digital audio is created when a sound wave is converted into numbers – a process referred to as digitizing. • It is possible to digitize sound from a microphone, a synthesizer, existing tape recordings, live radio and television broadcasts, and popular CDs. • You can digitize sounds from a natural source or prerecorded.
- 15. Cont…
- 16. Cont… • Digital audio - data are stored in the form of samples point. • Samples represent the amplitude (or loudness) of sound at a discrete point in time. • Quality of digital recording depends on the sampling rate, the number of samples point taken per second (Hz). High Sampling Rate Samples stored in digital form waveform Low Sampling Rate
- 17. Digital Sampling 1 second
- 18. Digital Sampling
- 19. Digital Audio • There are three sampling frequencies most often used in multimedia are 44.1 kHz, 22.05 kHz and 11.025 kHz. – The higher the sampling rate, the more the measurements are taken (better quality). – The lower the sampling rate, the lesser the measurements are taken (low quality). • The number of bits used to describe the amplitude of sound wave when sampled, determines the sample size.
- 20. Digital Audio • The value of each sample is rounded off to the nearest integer (quantization).
- 21. Digital audio • If the amplitude is greater than the intervals available, clipping of the top and bottom of the wave occurs.
- 22. Cont… • The quality of your audio is based on the quality of your recording and not the device on which your end user will play the audio, so digital audio is device independent. High Sampling Low Sampling Rate Rate
- 23. Cont… o Quality factors for digital audio file : 1. Sampling Rate 2. Sample Size (resolution) the number of bits used to record the value of a sample in a digitized signal. Sampling Rate Sample size
- 24. Making digital audio files • Crucial aspects of preparing digital audio files are: – Balancing the need for sound quality against available RAM and hard disk resource. – Setting appropriate recording levels to get a high-quality and clean recording.
Editor's Notes
- Oscillation- repetitive variation