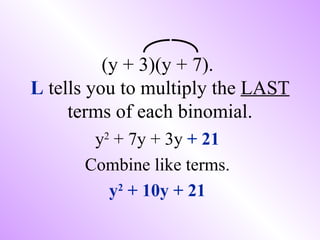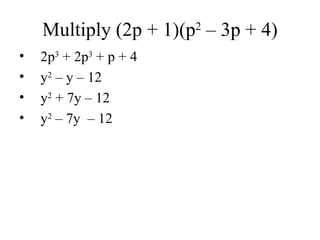Multiplying polynomials
- 1. Objective The student will be able to: multiply two polynomials using the FOIL method, Box method and the distributive property. SOL: A.2b Designed by Skip Tyler, Varina High School
- 2. There are three techniques you can use for multiplying polynomials. The best part about it is that they are all the same! Huh? Whaddaya mean? It’s all about how you write it…Here they are! 1)Distributive Property 2)FOIL 3)Box Method Sit back, relax (but make sure to write this down), and I’ll show ya!
- 3. 1) Multiply. (2x + 3)(5x + 8) Using the distributive property, multiply 2x(5x + 8) + 3(5x + 8). 10x2 + 16x + 15x + 24 Combine like terms. 10x2 + 31x + 24 A shortcut of the distributive property is called the FOIL method.
- 4. The FOIL method is ONLY used when you multiply 2 binomials. It is an acronym and tells you which terms to multiply. 2) Use the FOIL method to multiply the following binomials: (y + 3)(y + 7).
- 5. (y + 3)(y + 7). F tells you to multiply the FIRST terms of each binomial. y2
- 6. (y + 3)(y + 7). O tells you to multiply the OUTER terms of each binomial. y2 + 7y
- 7. (y + 3)(y + 7). I tells you to multiply the INNER terms of each binomial. y2 + 7y + 3y
- 8. (y + 3)(y + 7). L tells you to multiply the LAST terms of each binomial. y2 + 7y + 3y + 21 Combine like terms. y2 + 10y + 21
- 9. Remember, FOIL reminds you to multiply the: First terms Outer terms Inner terms Last terms
- 10. The third method is the Box Method. This method works for every problem! Here’s how you do it. Multiply (3x – 5)(5x + 2) 3x -5 Draw a box. Write a polynomial on the top and side of a box. It does not 5x matter which goes where. This will be modeled in the next problem along with +2 FOIL.
- 11. 3) Multiply (3x - 5)(5x + 2) First terms: 15x2 3x -5 Outer terms: +6x Inner terms: -25x Last terms: -10 5x 15x2 -25x Combine like terms. 15x2 - 19x – 10 +2 +6x -10 You have 3 techniques. Pick the one you like the best!
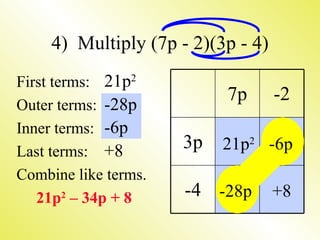
- 12. 4) Multiply (7p - 2)(3p - 4) First terms: 21p2 7p -2 Outer terms: -28p Inner terms: -6p Last terms: +8 3p 21p2 -6p Combine like terms. 21p2 – 34p + 8 -4 -28p +8
- 13. Multiply (y + 4)(y – 3) • y2 + y – 12 • y2 – y – 12 • y2 + 7y – 12 • y2 – 7y – 12 • y2 + y + 12 • y2 – y + 12 • y2 + 7y + 12 • y2 – 7y + 12
- 14. Multiply (2a – 3b)(2a + 4b) • 4a2 + 14ab – 12b2 • 4a2 – 14ab – 12b2 • 4a2 + 8ab – 6ba – 12b2 • 4a2 + 2ab – 12b2 • 4a2 – 2ab – 12b2
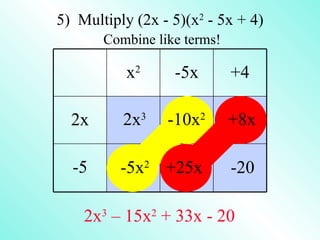
- 15. 5) Multiply (2x - 5)(x2 - 5x + 4) You cannot use FOIL because they are not BOTH binomials. You must use the distributive property. 2x(x2 - 5x + 4) - 5(x2 - 5x + 4) 2x3 - 10x2 + 8x - 5x2 + 25x - 20 Group and combine like terms. 2x3 - 10x2 - 5x2 + 8x + 25x - 20 2x3 - 15x2 + 33x - 20
- 16. 5) Multiply (2x - 5)(x2 - 5x + 4) You cannot use FOIL because they are not BOTH binomials. You must use the distributive property or box method. x2 -5x +4 2x 2x3 -10x2 +8x Almost done! Go to -5 -5x2 +25x -20 the next slide!
- 17. 5) Multiply (2x - 5)(x2 - 5x + 4) Combine like terms! x2 -5x +4 2x 2x3 -10x2 +8x -5 -5x2 +25x -20 2x3 – 15x2 + 33x - 20
- 18. 2 Multiply (2p + 1)(p – 3p + 4) • 2p3 + 2p3 + p + 4 • y2 – y – 12 • y2 + 7y – 12 • y2 – 7y – 12