Music of Africa Q2
- 1. Music of Africa Prepared by: Jetlee Cumbe
- 2. M u s I c
- 6. Music and dance are also important to religious expression and political events.
- 7. Others are work related or social in nature, while many traditional societies view their music as entertainment.
- 9. African traditional music is largely functional in nature, used primarily in ceremonial rites
- 10. basically interlocking structural format, due mainly to its overlapping and dense texture as well as its rhythmic
- 11. Its many sources of influence have produced such varied styles and genres as the following
- 12. Some types of African Music Afrob eat Apal a Axe Jive Jit Kwassa Kwassa Juju Marabi
- 13. Afrobeat A term used to describe the fusion of West African with black American music.
- 14. Apala A musical genre from Nigeria in the Yoruba tribal style to wake up the worshippers after fasting during the Muslim holy feast of Ramadan. Percussion instrumentation includes the rattle (sekere), thumb piano (agidigbo), bell (agogo), and two or three talking drums.
- 15. Axe A popular musical genre from Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. It fuses the Afro-Caribbean styles of the marcha, reggae, and calypso.
- 16. Jit A hard and fast percussive Zimbabwean dance music played on drums with guitar accompaniment, influenced by Mbira-based guitar styles.
- 17. Jive A popular form of South African music featuring a lively and uninhibited variation of the jitterbug, a form of swing dance
- 18. Juju is a popular music style from Nigeria that relies on the traditional Yoruba rhythms, where the instruments in Juju are more Western in origin. A drum kit, keyboard, pedal steel guitar, and accordion are used along with the traditional dun-dun (talking drum or squeeze drum).
- 19. Kwassa Kwassa A dance style begun in Zairein the late 1980’s, popularized by Kanda Bongo Man. In this dance style, the hips move back and forth while the arms move following the hips.
- 20. Marabi A South African three-chord township music of the 1930s-1960s which evolved into African Jazz. Possessing a keyboard style combining American jazz, ragtime and blues with African roots
- 21. Activity 1: Music 1. What are the purpose of music in Africa?
- 22. Review
- 23. Afrob eat Apal a Axe Jive Jit Kwassa Kwassa Juju Marabi
- 24. Kwassa Kwassa A dance style, which the hips move back and forth while the arms move following the hips.
- 25. Afrobeat A term used to describe the fusion of West African with black American music.
- 26. Apala A musical genre from Nigeria in the Yoruba tribal style to wake up the worshippers after fasting during the Muslim holy feast of Ramadan.
- 27. Jive A popular form of South African music featuring a lively and uninhibited variation of the jitterbug, a form of swing dance
- 28. Axe A popular musical genre from Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. It fuses the Afro- Caribbean styles of the marcha, reggae, and calypso.
- 29. Latin American music with the Influnce of Africa music
- 30. Reggae Jamaican musical style Influence of Island’s traditional mento music Offbeat Rhythm
- 31. Salsa Cuban, Puerto Rico, and Colobmbian dance music
- 32. Samba Brazilian Musical Genre and dance style Lively and rhythmical beats Timed dance – set of dances
- 33. Soca Soul of Calypso Calypso and Indian Musica Calypso - Afro-carribean musuc
- 34. Were Muslim music often performed as a wake up call for early breakfast and prayers during Ramadan celebrations.
- 36. REVIEW
- 37. Samba It is a Brazilian Musical Genre and dance style which also a timed dance.
- 39. Reggae It is a Jamaican musical style with the Influence of Island’s traditional mento music and Offbeat Rhythm
- 40. Were Muslim music often performed as a wake up call for early breakfast and prayers during Ramadan celebrations.
- 41. Salsa A Cuban, Puerto Rico, and Colombian dance music
- 46. Balafon Rattles Agogo Atingting kon Slit drum Djembe Shekere Rasp
- 47. BalafonThe balafon is a West African xylophone. It is a pitched percussion instrument with bars made from logs or bamboo
- 48. Balafon
- 50. Rattles Rattles are made of seashells, basketry, animal hoofs, horn, and wood, metal bells, cocoons, palm kernels, or tortoise shells. These rattling vessels may range from single to several objects that are either joined or suspended in such a way as they hit each other
- 51. Rattles
- 52. agogo •The agogo is a single bell or multiple bells that had its origins in traditional Yoruba music and also in the samba baterias (percussion) ensembles.
- 53. agogo The agogo may be called “the oldest samba instrument based on West African Yoruba single or double bells.” It has the highest pitch of any of the bateria instruments
- 54. agogo
- 55. Atingting kon These are slit gongs used to communicate between villages. They were carved out of wood to resemble ancestors and had a “slit opening” at the bottom.
- 56. Atingting kon In certain cases, their sound could carry for miles through the forest and even across water to neighboring islands. A series of gong “languages” were composed of beats and pauses, making it possible to send highly specific messages
- 58. Slit drums The slit drum is a hollow percussion instrument. Although known as a drum, it is not a true drum but is an idiophone. It is usually carved or constructed from bamboo or wood into a box with one or more slits in the top
- 59. Slit drums
- 60. Djembe The West African djembe (pronounced zhem-bay) is one of the best-known African drums is. It is shaped like a large goblet and played with bare hands. The body is carved from a hollowed trunk and is covered in goat skin.
- 61. Djembe These drums are played using hands or sticks or both; and sometimes have rattling metal and jingles attached to the outside or seeds and beads placed inside the drum. They are sometimes held under the armpit or with a sling.
- 62. Djembe
- 63. Shekere The shekere is a type of gourd and shell megaphone from West Africa, the gourd.
- 64. Shekere
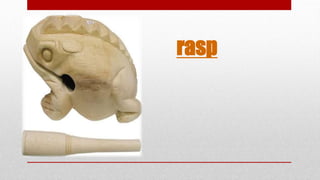
- 65. Rasp A rasp, or scraper, is a hand percussion instrument whose sound is produced by scraping the notches on a piece of wood (sometimes elaborately carved) with a stick, creating a series of rattling effects
- 66. rasp
- 67. Review………..
- 68. Balafon Rattles Agogo Atingting kon Slit drum Djembe Shekere Rasp
- 69. Slit drums
- 70. rasp
- 71. Balafon
- 72. Djembe
- 73. ATINGTING KON
- 74. Agogo
- 75. shekere
- 76. rattles
- 77. Membranophones
- 78. Membranophones Are instruments, usually drums, which have vibrating animal membranes.
- 79. Body percussion Africans frequently use their bodies as musical instruments. Aside from their voices, where many of them are superb singers,
- 80. Body percussion the body also serves as a drum as people clap their hands, slap their thighs, pound their upper arms or chests, or shuffle their feet.
- 81. Talking drum The talking drum is used to send messages to announce births, deaths, marriages, sporting events, dances, initiation, or war.
- 82. Talking drum Sometimes it may also contain gossip or jokes. It is believed that the drums can carry direct messages to the spirits after the death of a loved one
- 83. Lamellophone
- 84. One of the most popular African percussion instruments is the Lamellaphone, which is a set of plucked tongues or keys mounted on a sound board
- 85. It is known by different names according to the regions such as mbira, karimba, kisaanj, and likembe.
- 86. Mbira (hand piano or thumb piano) - The thumb piano or finger xylophone is of African origin and is used throughout the continent.
- 87. Mbira It consists of a wooden board with attached staggered metal tines (a series of wooden, metal, or rattan tongues), plus an additional resonator to increase its volume. It is played by holding the instrument in the hands and plucking the tines with the thumbs, producing a soft plucked sound PLAY 2
- 88. Chordophone
- 89. Musical bow The musical bow is the ancestor of all string instruments. It is the oldest and one of the most widely-used string instruments of Africa. It consists of a single string attached to each end of a curved stick, similar to a bow and arrow. The string is either plucked or struck with another stick, producing a percussive yet delicate sound
- 90. Musical bow
- 91. Lute The lute, originating from the Arabic states, is shaped like the modern guitar and played in similar fashion. It has a resonating body, a neck, and one or more strings which stretch across the length of its body and neck. The player tunes the strings by tightening or loosening the pegs at the top of the lute’s neck. West African plucked lutes include the konting, khalam, and the nkoni.
- 92. Lute
- 93. Kora The kora is Africa's most sophisticated harp, while also having features similar to a lute. Its body is made from a gourd or calabash. A support for the bridge is set across the opening and covered with a skin that is held in place with studs. The leather rings around the neck are used to tighten the 21 strings that give the instrument a range of over three octaves
- 94. KORA
- 95. Zither The zither is a stringed instrument with varying sizes and shapes whose strings are stretched along its body. Among the types of African zither is the raft or Inanga zither from Burundi, the tubular or Valiha zither from Malagasy, and the harp or Mvet zither from Cameroon.
- 96. Zither
- 97. Zeze The zeze is an African fiddle played with a bow, a small wooden stick, or plucked with the fingers. It has one or two strings, made of steel or bicycle brake wire.
- 98. Zeze
- 99. Aerophone
- 100. Flutes Flutes are widely used throughout Africa and either vertical or side-blown. They are usually fashioned from a single tube closed at one end and blown like a bottle
- 102. Horns Horns and trumpets, found almost everywhere in Africa, are commonly made from elephant tusks and animal horns.
- 103. HORNS
- 104. Trumpets African trumpets are made of wood, metal, animal horns, elephant tusks, and gourds with skins from snakes, zebras, leopards, crocodiles and animal hide as ornaments to the instrument
- 105. Trumpets
- 106. Trumpets