MySQL Database Architectures - MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet 2021-11
- 1. MySQL Database Architectures Disaster Recovery Solutions Introducing MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Kenny Gryp MySQL Product Manager
- 2. Safe Harbor Statement The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purpose only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied up in making purchasing decisions. The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle's product remains at the sole discretion of Oracle. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 2 / 55
- 3. IT Disasters & Outages: Primary Causes On-site power failure is the biggest cause of significant outages Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 3 / 55
- 4. IT Disasters & Outages: Costs are Rising Over half who had experienced an outage costing more than $100,000. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 4 / 55
- 5. 5-hour computer outage cost us $150 million. The airline eventually canceled about 1,000 flights on the day of the outage and ground an additional 1,000 flights over the following two days. Millions of websites offline after fire at French cloud services firm. The fire is expected to cost the company more than €105 million. Tens of thousands of passengers were stranded in cities around the world due to cancellation of about 130 flights and the delay of 200. Millions of bank customers were unable to access online accounts. The bank took almost 2 days to recover and get back to normal functioning. IT Disasters and Outages: Examples Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 5 / 55
- 6. Past, Present & Future Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 6 / 55
- 7. Setting up Replication topology was usually done manually, taking many steps including user management, restoring backups, configuring replication... MySQL only offered the technical pieces, leaving it up to the user to setup an (always customized) architecture Even required other software ... bringing lot's of work for DBA's and experts, who spent their time automating and integrating their customized architecture 'Past' - Manual Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 7 / 55
- 8. RPO = 0 RTO = seconds (automatic failover) 2016 - MySQL InnoDB Cluster MySQL Group Replication: Automatic membership changes, network partition handling, consistency... MySQL Shell to provide a powerful interface that helps in automating and integrating all components InnoDB CLONE to automatically provision members, fully integrated in InnoDB MySQL Router MySQL Server Present - Solutions! Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 8 / 55
- 9. RPO != 0 RTO = minutes (manual failover) 2020 - MySQL InnoDB Replicaset 'classic', 'asynchronous' Replication based Solution, fully integrated MySQL Shell MySQL Router MySQL Server Present - Solutions! Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 9 / 55
- 10. Concepts - RTO & RPO RTO: Recovery Time Objective How long does it take to recover from a single failure RPO: Recovery Point Objective How much data can be lost when a failure occurs Types of Failure: High Availability: Single Server Failure, Network Partition Disaster Recovery: Full Region/Network Failure Human Error: Little Bobby Tables Business Requirements Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 10 / 55
- 11. MySQL InnoDB Cluster & MySQL InnoDB ReplicaSet are solutions implemented to meet various High Availability requirements. Introducing MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet, which is one of the key options to meet Disaster Recovery requirements. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 11 / 55
- 12. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 12 / 55
- 13. High Availability (Failure Within a Region) RPO = 0 RTO = seconds (automatic failover) Disaster Recovery (Region Failure) RPO != 0 RTO = minutes or more (manual failover) No write performance impact Features Easy to use Familiar interface and usability mysqlsh, CLONE, ... Add/remove nodes/clusters online Router integration, no need to reconfigure application if the topology changes MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet One or more REPLICA MySQL InnoDB Clusters attached to a PRIMARY MySQL InnoDB Cluster Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 13 / 55
- 14. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet - 3 Datacenters Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 14 / 55
- 15. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet - Not every Cluster has to be 3 nodes Each replica is a MySQL InnoDB Cluster that can have 1-9 members. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 15 / 55
- 16. Replication Enhancements Features in replication that made ClusterSet possible: 8.0.22: Automatic connection failover for Async Replication Channels 8.0.23: Automatic connection failover for Async Replication Channels using Group Replication 8.0.24: Make skip-replica-start a global, persistable, read-only system variable. 8.0.26: Group Replication Member actions (configurable super_read_only on PRIMARY member) 8.0.26: Specify the UUID used to log View_change_log_event 8.0.27: Asynchronous Replication Channel configuration automatically follows the PRIMARY member Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 16 / 55
- 17. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Configuration Commands Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 17 / 55
- 18. Create MySQL InnoDB Cluster Start with setting up a regular MySQL InnoDB Cluster: mysqlsh> c root@localhost:3331 mysqlsh> sql create schema sbtest; mysqlsh> bru = dba.createCluster("BRU") mysqlsh> bru.addInstance('localhost:3332') mysqlsh> bru.addInstance('localhost:3333') mysqlsh> bru.status() Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 18 / 55
- 19. Create ClusterSet mysqlsh> clusterset = bru.createClusterSet('clusterset') A new ClusterSet will be created based on the Cluster 'BRU'. - Validating Cluster 'BRU' for ClusterSet compliance. - Creating InnoDB ClusterSet 'clusterset' on 'BRU'... - Updating metadata... ClusterSet successfully created. Use ClusterSet.createReplicaCluster() to add Replica Clusters to it. <ClusterSet:cluster> Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 19 / 55
- 20. Check ClusterSet Status mysqlsh> clusterset.status() { "clusters": { "BRU": { "clusterRole": "PRIMARY", "globalStatus": "OK", "primary": "127.0.0.1:3331" } }, "domainName": "clusterset", "globalPrimaryInstance": "127.0.0.1:3331", "primaryCluster": "BRU", "status": "HEALTHY", "statusText": "All Clusters available." } Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 20 / 55
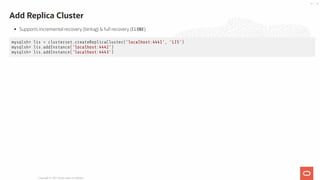
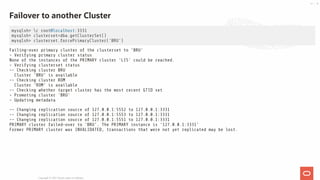
- 21. Add Replica Cluster Supports incremental recovery (binlog) & full recovery (CLONE) mysqlsh> lis = clusterset.createReplicaCluster('localhost:4441', 'LIS') mysqlsh> lis.addInstance('localhost:4442') mysqlsh> lis.addInstance('localhost:4443') Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 21 / 55
- 22. mysqlsh> clusterset.status() mysqlsh> bru.status() mysqlsh> lis.status() { "clusters": { "BRU": { "clusterRole": "PRIMARY", "globalStatus": "OK", "primary": "127.0.0.1:3331" }, "LIS": { "clusterRole": "REPLICA", "clusterSetReplicationStatus": "OK", "globalStatus": "OK" } }, "domainName": "clusterset", "globalPrimaryInstance": "127.0.0.1:3331", "primaryCluster": "BRU", "status": "HEALTHY", "statusText": "All Clusters available." } Or, to get everything in one command: mysqlsh> clusterset.status({extended:1}) Check ClusterSet Status Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 22 / 55
- 23. mysqlsh> rom = clusterset.createReplicaCluster( 'localhost:5551', 'ROM') mysqlsh> rom.addInstance('localhost:5552') mysqlsh> rom.addInstance('localhost:5553') mysqlsh> rom.status() mysqlsh> clusterset.status() { "clusters": { "ROM": { "clusterRole": "REPLICA", "clusterSetReplicationStatus": "OK", "globalStatus": "OK" }, "BRU": { "clusterRole": "PRIMARY", "globalStatus": "OK", "primary": "127.0.0.1:3331" }, "LIS": { "clusterRole": "REPLICA", "clusterSetReplicationStatus": "OK", "globalStatus": "OK" } }, "domainName": "clusterset", "globalPrimaryInstance": "127.0.0.1:3331", "primaryCluster": "BRU", "status": "HEALTHY", "statusText": "All Clusters available." } Add second Replica Cluster Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 23 / 55
- 24. Router Integration Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 24 / 55
- 25. Configure your application to connect to a local MySQL Router to connect to the ClusterSet. Router Integration Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 25 / 55
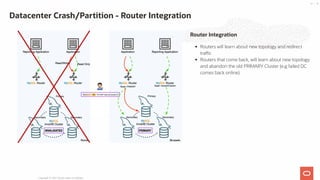
- 26. Router Target Modes: follow the PRIMARY cluster Writes & Reads go to the PRIMARY Cluster connect to the configured target cluster When target cluster is not PRIMARY: only read traffic is open writes will be denied when target cluster is PRIMARY write port opens Features: Configurable per Router instance Configuration can be changed ONLINE in mysqlsh Deploy 2 types of routers: target PRIMARY to send writes to PRIMARY define target cluster to keep read traffic local INVALIDATED clusters can still be used for read traffic (configurable) Router Integration Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 26 / 55
- 27. Router Integration - 3DC Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 27 / 55
- 28. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Router Integration Commands Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 28 / 55
- 29. Bootstrap Router Same as MySQL InnoDB Cluster & MySQL InnoDB ReplicaSet $ sudo mysqlrouter --bootstrap root@localhost:3331 --user=mysqlrouter $ sudo systemctl start mysqlrouter $ sudo tail -f /var/log/mysqlrouter/mysqlrouter.log Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 29 / 55
- 30. Changing Router Configuration Options Change the target_cluster: mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('instance-....com::system', 'target_cluster', 'ROM') mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('instance-....com::system', 'target_cluster', 'BRU') mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('instance-....com::system', 'target_cluster', 'LIS') mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('instance-....com::system', 'target_cluster', 'primary') target_cluster is also configurable during mysqlrouter --bootstrap with --conf-target-cluster or --conf-target-cluster-by-name Change the invalidated_cluster_policy: When the target_cluster cluster is invalidated, should it still accept reads, knowing that they will be stale reads or should all traffic be dropped? mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('instance-....com::system', 'invalidated_cluster_policy', 'accept_ro') mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('instance-....com::system', 'invalidated_cluster_policy', 'drop_all') Change the default setting for routers: mysqlsh> clusterset.setRoutingOption('target_cluster', 'LIS') Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 30 / 55
- 31. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Managing Commands Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 31 / 55
- 32. Change PRIMARY member in PRIMARY cluster mysqlsh> bru.setPrimaryInstance('localhost:3332') Setting instance 'localhost:3332' as the primary instance of cluster 'BRU'... Instance '127.0.0.1:3331' was switched from PRIMARY to SECONDARY. Instance '127.0.0.1:3332' was switched from SECONDARY to PRIMARY. Instance '127.0.0.1:3333' remains SECONDARY. WARNING: The cluster internal session is not the primary member anymore. For cluster management operations please obtain a fresh cluster handle using dba.getCluster(). The instance 'localhost:3332' was successfully elected as primary. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 32 / 55
- 33. Change PRIMARY member in REPLICA cluster mysqlsh> lis.setPrimaryInstance('localhost:4442') Setting instance 'localhost:4442' as the primary instance of cluster 'LIS'... Instance '127.0.0.1:4442' was switched from SECONDARY to PRIMARY. Instance '127.0.0.1:4443' remains SECONDARY. Instance '127.0.0.1:4441' was switched from PRIMARY to SECONDARY. WARNING: The cluster internal session is not the primary member anymore. For cluster management operations please obtain a fresh cluster handle using dba.getCluster(). The instance 'localhost:4442' was successfully elected as primary. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 33 / 55
- 34. Switchover - Changing PRIMARY Cluster - setPrimaryCluster() mysqlsh> clusterset.setPrimaryCluster('LIS') Switching the primary cluster of the clusterset to 'LIS' - Verifying clusterset status -- Checking cluster BRU - Cluster 'BRU' is available -- Checking cluster ROM - Cluster 'ROM' is available -- Checking cluster LIS - Cluster 'LIS' is available - Refreshing replication account of demoted cluster - Synchronizing transaction backlog at 127.0.0.1:4442 - Updating metadata - Updating topology -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:3331 to 127.0.0.1:4442 -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:3333 to 127.0.0.1:4442 -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:3332 to 127.0.0.1:4442 - Acquiring locks in replicaset instances -- Pre-synchronizing SECONDARIES -- Acquiring global lock at PRIMARY & SECONDARIES - Synchronizing remaining transactions at promoted primary - Updating replica clusters -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:5552 to 127.0.0.1:4442 -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:5553 to 127.0.0.1:4442 -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:5551 to 127.0.0.1:4442 Cluster 'LIS' was promoted to PRIMARY of the clusterset. The PRIMARY instance is '127.0.0.1:4442' Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 34 / 55
- 35. Failover to another Cluster mysqlsh> c root@localhost:3331 mysqlsh> clusterset=dba.getClusterSet() mysqlsh> clusterset.forcePrimaryCluster('BRU') Failing-over primary cluster of the clusterset to 'BRU' - Verifying primary cluster status None of the instances of the PRIMARY cluster 'LIS' could be reached. - Verifying clusterset status -- Checking cluster BRU Cluster 'BRU' is available -- Checking cluster ROM Cluster 'ROM' is available -- Checking whether target cluster has the most recent GTID set - Promoting cluster 'BRU' - Updating metadata -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:5552 to 127.0.0.1:3331 -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:5553 to 127.0.0.1:3331 -- Changing replication source of 127.0.0.1:5551 to 127.0.0.1:3331 PRIMARY cluster failed-over to 'BRU'. The PRIMARY instance is '127.0.0.1:3331' Former PRIMARY cluster was INVALIDATED, transactions that were not yet replicated may be lost. Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 35 / 55
- 36. Removing a Cluster from the ClusterSet mysqlsh> clusterset.removeCluster('LIS') Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 36 / 55
- 37. ClusterSet Scenarios Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 37 / 55
- 38. When there is newly elected PRIMARY member in a cluster Works on failures in PRIMARY and REPLICA clusters Automatic Handling of InnoDB Cluster state changes Asynchronous replication is automatically reconfigured after primary change PRIMARY Cluster PRIMARY member Crash/Partition Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 38 / 55
- 39. When there is newly elected PRIMARY member in a cluster Works on failures in PRIMARY and REPLICA clusters Automatic Handling of InnoDB Cluster state changes Asynchronous replication is automatically reconfigured after primary change PRIMARY Cluster PRIMARY member Crash/Partition - Automatic! Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 39 / 55
- 40. When there is newly elected PRIMARY member in a cluster Works on failures in PRIMARY and REPLICA clusters Automatic Handling of InnoDB Cluster state changes Asynchronous replication is automatically reconfigured after primary change REPLICA Cluster PRIMARY member Crash/Partition - Automatic! Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 40 / 55
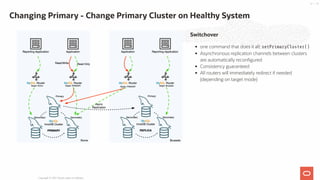
- 41. Switchover one command that does it all: setPrimaryCluster() Asynchronous replication channels between clusters are automatically reconfigured Consistency guaranteed All routers will immediately redirect if needed (depending on target mode) Changing Primary - Change Primary Cluster on Healthy System Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 41 / 55
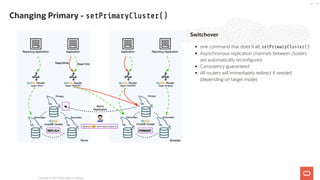
- 42. Switchover one command that does it all: setPrimaryCluster() Asynchronous replication channels between clusters are automatically reconfigured Consistency guaranteed All routers will immediately redirect if needed (depending on target mode) Changing Primary - setPrimaryCluster() Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 42 / 55
- 43. Failover to another Cluster one command to invalidate the PRIMARY cluster and promote a new PRIMARY cluster: forcePrimaryCluster() other REPLICA clusters replication will be reconfigured Split Brain Warning local Routers that cannot connect to other clusters will not learn about new topology if datacenter is network partitioned, it will continue to operate as PRIMARY Datacenter Crash/Partition Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 43 / 55
- 44. Failover to another Cluster one command to invalidate the PRIMARY cluster and promote a new PRIMARY cluster: forcePrimaryCluster() other REPLICA clusters replication will be reconfigured Split Brain Warning local Routers that cannot connect to other clusters will not learn about new topology if datacenter is network partitioned, it will continue to operate as PRIMARY Datacenter Crash/Partition - forcePrimaryCluster() Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 44 / 55
- 45. Router Integration Routers will learn about new topology and redirect traffic Routers that come back, will learn about new topology and abandon the old PRIMARY Cluster (e.g failed DC comes back online) Datacenter Crash/Partition - Router Integration Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 45 / 55
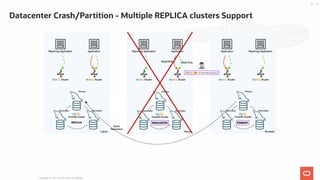
- 46. Datacenter Crash/Partition - Multiple REPLICA clusters Support Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 46 / 55
- 47. Router Integration When GR is offline: network partition no quorum full cluster lost (e.g. power outage) Failover to another Cluster one command to invalidate the PRIMARY cluster and promote a new PRIMARY cluster: forcePrimaryCluster() Router instances will follow PRIMARY (depending on target mode) Group Replication Crash/Partition Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 47 / 55
- 48. Router Integration When GR is offline: network partition no quorum full cluster lost (e.g. power outage) Failover to another Cluster one command to invalidate the PRIMARY cluster and promote a new PRIMARY cluster: forcePrimaryCluster() Router instances will follow PRIMARY (depending on target mode) Group Replication Crash/Partition - forcePrimaryCluster() & Router Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 48 / 55
- 49. MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet - Restrictions Requires Server, Router & Shell version 8.0.27 or higher Only works with Single Primary mode in InnoDB Cluster Asynchronous replication between clusters, not semi-sync (use a single cluster spread across regions if RPO=0) Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 49 / 55
- 50. Business Requirements Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 50 / 55
- 51. Concepts - RTO & RPO RTO: Recovery Time Objective How long does it take to recover from a single failure RPO: Recovery Point Objective How much data can be lost when a failure occurs Types of Failure: High Availability: Single Server Failure, Network Partition Disaster Recovery: Full Region/Network Failure Human Error: Little Bobby Tables Business Requirements Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 51 / 55
- 52. MySQL InnoDB Cluster RPO = 0 RTO = Seconds MySQL InnoDB ReplicaSet RPO != 0 RTO = Minutes+ (manual failover) 👍🏽 Best write performance 👎🏼 Manual failover High Availability - Single Region Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 52 / 55
- 53. RPO = 0 RTO = Seconds 👍🏽 Multi-Region Multi-Primary 👎🏼 3 DC 👎🏼 Requires very stable WAN 👎🏼 Write performance affected by latency between dc's Disaster Recovery - Multi Region MySQL InnoDB Cluster Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 53 / 55
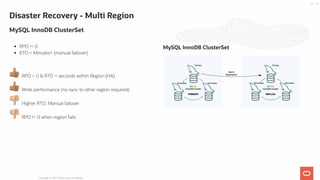
- 54. RPO != 0 RTO = Minutes+ (manual failover) 👍🏽 RPO = 0 & RTO = seconds within Region (HA) 👍🏽 Write performance (no sync to other region required) 👎🏼 Higher RTO: Manual failover 👎🏼 RPO != 0 when region fails MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Disaster Recovery - Multi Region MySQL InnoDB ClusterSet Copyright @ 2021 Oracle and/or its affiliates. 54 / 55