MySQL Replication — Advanced Features / Петр Зайцев (Percona)
- 1. © 2017 Percona1 Peter Zaitsev, CEO Advanced MySQL Replication Features Highload++ Moscow, Russia November 8, 2017
- 2. © 2017 Percona2 In This Presentation Few Words about Replication & Availability MySQL Replication Timeline Advanced MySQL Replication Options
- 3. © 2017 Percona3 Few Words about Replication
- 4. © 2017 Percona4 Replication Having Multiple Copies of the data, updated with changes
- 5. © 2017 Percona5 Why Replication Availability Scalability Performance
- 6. © 2017 Percona6 Availability Service Stays up when component fails
- 7. © 2017 Percona7 Availability via Redundancy Have more than one system Works well for stateless systems Is not enough for databases
- 8. © 2017 Percona8 Availability via Replication Redundant Computing Resource Paired with Replicated Data
- 9. © 2017 Percona9 Component Failure • Total Crash • Process Crash • Stall/Unresponsive • Consistency Issues Node Failures • Single Network Port Failures • Network Device Failures • Partitions • Complicated Failures Network Failures
- 10. © 2017 Percona10 Scalability with Replication Scales Reads Does not Scale Writes very well Data Distribution is needed for scaling writes
- 11. © 2017 Percona11 Performance Reduce response time by maintaining replica closer to user Better Performance Through avoiding resource saturation
- 12. © 2017 Percona12 Replication in MySQL A brief Time Line
- 13. © 2017 Percona13 MySQL Replication MySQL 3.23 • Initial Statement Replication Implemented MySQL 4.0 • Split IO Thread and SQL Thread MySQL 5.1 • Row and Mixed replication modes supported MySQL 5.6 • Per Database Parallel Replication • GTID Support MySQL 5.7 • General Parallel Replication • Multi-Source Replication • Group Replication / MySQL Innodb Cluster
- 14. © 2017 Percona14 Galera Based Replication Technology Similar to MySQL Group Replication but more mature Available for MySQL, Percona, MariaDB Alternative Track
- 15. © 2017 Percona15 Replication in MariaDB Is not 100% Same as in MySQL Different GTID Implementation Different parallel replication Not instrumented in the same way Number of features became available in MariaDB Earlier Not covering MariaDB in this Presentation
- 16. © 2017 Percona16 Advanced Replication
- 17. © 2017 Percona17 What is Basic Replication ? Statement Replication Replication of the Full Database Using Binary Log Position Single Tier Topology Single Thread Asynchronous Write to Single Master Keep Slave Meta-Data Data in Files Master-Slave- Replication Manual Failover & Traffic Management
- 18. © 2017 Percona18 Statement vs Row Replication •STATEMENT •ROW •MIXED Configured on the Master as binlog_format
- 19. © 2017 Percona19 How Rows are Logged ? •Full •Minimal •Noblob binlog_row_image
- 20. © 2017 Percona20 Missing Seeing Queries ? Also Log Query For informational Purposes binlog_rows_query_log_events Off by Default
- 21. © 2017 Percona21 Replication of Full Database Full Replication Most Simple for Troubleshooting and Recovery Can replicate only portions of the database Can add additional data to the slaves
- 22. © 2017 Percona22 Replication Filering • Binlog_do_db • Binlog_ignore_db On the Master (writing binary log) • Replicate_do_db • Replicate_ignore_db • Replicate_wild_do_table • Replicate_wild_ignore_table On the Slave
- 23. © 2017 Percona23 Position Identification By Binary Log Position •File: mysql- bin.000003 •Position: 73 By GTID •3E11FA47-71CA- 11E1-9E33- C80AA9429562:23
- 24. © 2017 Percona24 What is in GTID ? GTID = source_id:transaction_id Source_id is Server_uuid of Originating Server Always Preserved on the Slaves Track which transactions executed mysql.gtid_executed table (5.7) + binlog
- 25. © 2017 Percona25 GTID Benefits and Drawbacks Automatic Position Discovery Easy Slave Promotion Discovery of Missed Transactions Pain in the Ass with Manual Troubleshooting
- 26. © 2017 Percona26 Replication Topologies Single Tier Master-Slave Bi-Directional Tree Ring Directed Graph
- 27. © 2017 Percona27 Options For Complicated Topologies •Store copy of applied statements in local binlog •Disabled by default until MySQL 8 Log_slave_updates
- 28. © 2017 Percona28 Parallel Replication Single Thread Replication is typical limiting factor Parallel Replication for multiple Databases since 5.6 Parallel Replication for same table since 5.7
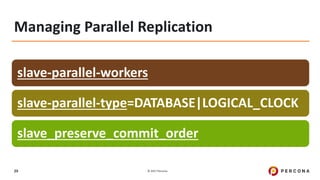
- 29. © 2017 Percona29 Managing Parallel Replication slave-parallel-workers slave-parallel-type=DATABASE|LOGICAL_CLOCK slave_preserve_commit_order
- 30. © 2017 Percona30 Asynchronous Replication Default in MySQL There is no guaranty of Timeliness “Replication Lag” can be days… and weeks Support for Semi-Synchronous Replication Support for Virtually Synchronous Group Replication
- 31. © 2017 Percona31 Sync or Async Synchronous Replication Asynchronous Replication
- 32. © 2017 Percona32 Synchronous Replication Data “Persisted” on Target Server Guarantees No Data Loss if Source server fails Conflicts can be easily prevented Expensive
- 33. © 2017 Percona33 Persistence in terms of Durability – In case of original node loss, can date be recovered? Visibility – Is data visible by reads going to secondary node Both Required for truly synchronous replication
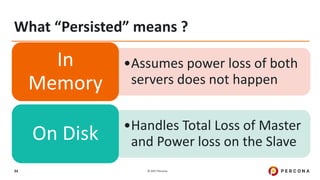
- 34. © 2017 Percona34 What “Persisted” means ? •Assumes power loss of both servers does not happen In Memory •Handles Total Loss of Master and Power loss on the SlaveOn Disk
- 35. © 2017 Percona35 Asynchronous Replication Anything not Synchronous Many different variants exist!
- 36. © 2017 Percona36 Asynchronous Properties •What happens with Persistence ? •What happens with Visibility ? Commit on Master
- 37. © 2017 Percona37 Persistence Uncommitted Data on Master Committed Data on Master Data in Slave’s memory Data on Slave’s Disk (log)
- 38. © 2017 Percona38 Visibility •Phantom Reads Results be visible by concurrent sessions before acknowledgement •No Phantom Reads Results can’t be visible by concurrent sessions
- 39. © 2017 Percona39 Semi-Synchronous Replication in MySQL • Both on Master and SlavePlugin Required • INSTALL PLUGIN rpl_semi_sync_master SONAME 'semisync_master.so';Master • INSTALL PLUGIN rpl_semi_sync_slave SONAME 'semisync_slave.so';Slave
- 40. © 2017 Percona40 Semi-Sync Replication Options Master: rpl_semi_sync_master_enabled Master: rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout Master: rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point=AFTER_SYNC|AFTER_COMMIT Master: rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_for_slave_count Slave: rpl_semi_sync_slave_enabled
- 41. © 2017 Percona41 Where Do We Write ? Single Master Multi-Master
- 42. © 2017 Percona42 Single Master All writes go to the single node One way replication stream Simple No Conflicts Replication aware Application or Connector
- 43. © 2017 Percona43 Active-Passive Master-Master Replication is bi-directional Only one Master can be written at the same time Essentially Single Master if configured well Minefield if not configured well
- 44. © 2017 Percona44 Multiple Active Masters Can write to multiple masters Replication is multi-directional More Complicated Possibility of Conflicts
- 45. © 2017 Percona45 MySQL Replication Multi-Master Recipe for problems with Async/SemiSync Replication Design Application to Avoid Conflicts MySQL Group Replication PXC/Galera Based Solutions
- 46. © 2017 Percona46 Multi-Master with MySQL Replication auto_increment_offset auto_increment_increment slave_exec_mode=idempotent
- 47. © 2017 Percona47 Replication Position information Master_info_repository=FILE|TABLE Relay_log_info_repository=FILE|TABLE Sync_master_info Sync_relay_log_info Relay_log_recovery Less Problem with GTID Replication
- 48. © 2017 Percona48 Master Slave Replication ? Most Commonly Used Variant MySQL Group Replication is other Option Percona XtraDB Cluster/Galera - Community Alternative
- 49. © 2017 Percona49 MySQL Group Replication Overview Inspired by Galera Ideas (and Success) Built on top of standard MySQL Replication Available as Plugin for MySQL 5.7 Considered GA but really very early product
- 50. © 2017 Percona50 Difference from MySQL Replication No Master/Slave but Group Membership Transactions are committed when they are certified by majority of nodes (Paxos) Does not accept writes if there is no Quorum Flow Control to prevent unlimited replication lag Nodes encountering inconsistency leave the cluster Conflict Detection and Resolution (or avoidance) Simple FailOver
- 51. © 2017 Percona51 MySQL Group Replication - Writes By Default configures itself as Single Primary Can configure to allow writes to any node
- 52. © 2017 Percona52 MySQL Group Replication Limitations No Automated node Provisioning Manual Recovery of failed nodes No way (yet) to ensure node does not read stale data
- 53. © 2017 Percona53 MySQL Innodb Cluster
- 54. © 2017 Percona54 Failover and Traffic Management How do we Re-Configure Replication if Master Crashes ? How do we Makes Sure Application uses Right Master ? How do we get Slave used by Application ?
- 55. © 2017 Percona55 Making MySQL Replication Better MHA MySQL Failover Orchestrator
- 56. © 2017 Percona56 Orchestrator Screenshot
- 57. © 2017 Percona57 Traffic Management Solutions • Not Immediate, Does not handle existing connectionsDNS • TCP/IP Port level. Does not understand MySQL ProtocolHAProxy • Like HA Proxy in the CloudElastic Load Balancer (etc) • Currently very basicMySQL Router • Proprietary SolutionsMaxScale, ScaleArc • MySQL Protocol Aware 100% Open Source Proxy Solution for MySQLProxySQL
- 58. © 2017 Percona58 We integrate ProxySQL with PXC High Availability Multiplexing (Connection Pooling) Caching Read/write Splitting Easy Configuration with proxysql-admin Can run in dedicated writer and load balanced mode
- 59. © 2017 Percona59 Dedicated shared ProxySQL 5 9 application server 1 application server 2 application server 3 PXC node 1 PXC node 2 PXC node 3 ProxySQL
- 60. © 2017 Percona60 ProxySQL on application side application server 1 application server 2 application server 3 PXC node 1 PXC node 2 PXC node 3 6 0 ProxySQL ProxySQL ProxySQL
- 61. © 2017 Percona61 ProxySQL at PMM
- 62. © 2017 Percona62 SAVE THE DATE! CALL FOR PAPERS OPENING SOON! www.perconalive.com April 23-25, 2018 Santa Clara Convention Center
- 63. © 2017 Percona63
- 64. DATABASE PERFORMANCE MATTERS Database Performance MattersDatabase Performance MattersDatabase Performance MattersDatabase Performance MattersDatabase Performance Matters