N5 mod2 formulation_aims_objectives
- 1. Mod 2: Formulations of Aims and Objectives Chapter 2 in textbook (p.29 – 35) Normally question 2 in Exam (15 points) Combination of long and short questions
- 2. 2.1 FORMULATION OF AIMS AND OBJECTIVES AIM: The term aim (or goal) refers to long-term intentions not defined in specific terms or a specific time frame. See textbook on p. 29 – 2.1 2
- 3. OBJECTIVE: P.29 An objective refers to a specific intention (short-term)to be achieved within a definite time-frame. “In the next semester I will pass N5” 3
- 4. AIMS & OBJECTIVES (TABULATED) AIMS • Long term intentions • Not defined in specific terms • Not in a specific time frame • “One day I want to be a successful business man.” OBJECTIVES • Short term intentions • Specific intention / defined specifically • Definite time frame • “This semester I want to pass N5 Management Comm 4
- 5. 5
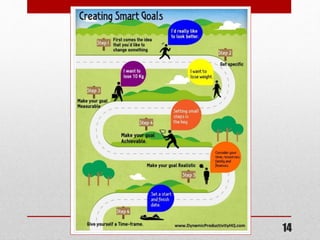
- 6. 2.2 Aspects of determining aims and objectives ( p.29) If I want to determine aims and objectives I need to involve the following aspects: • Establish the purpose of the exercise • Why must I do it? (Lose weight for my wedding) • Implement the process (How to get there?) • Do something about your goal. Follow logical steps to do so. See example of this on p.30 (table) 6
- 7. 2.2.2 Implementing the process Procedures • Identify problem • Formulate problem • Determine possible result • Determine time available • Relevant factors (positive or negative) on effort • Decide on Plan of Action • Set time limit • Set criteria • Monitor results • Put it in writing • Decide on feedback Applied example • I am overweight • I am 10kg overweight • Silky outfit – student dance • Dance is in 12 weeks • Birthday party of friend (eat too much) Exam – bad appetite • Balanced meals & exercise • 10 weeks • 500g per week • Weigh myself every Friday • Note pad on wall • Mother & best friend 7
- 8. 8
- 9. 2.3 Evaluate aims and objectives (p.30) Must be • Valid (worthwhile and relevant). They must be: • Interesting and challenging • Consistent with and conducive to one’s personal values • Consistent with and conducive to the policies and procedure of the organisation of which one is a member • Feasible (realistic, achievable, practical and workable) • Can only be determined once they have been formulated. See example on p.31 9
- 10. Feasibility of objective? Objectives can only be determined once they have been formulated specifically • I want to lose some weight • I want to lose 10kg in 2 weeks • I want to lose 10kg in 15 weeks • Vague, generalised, an aim rather than an objective • Unrealistic, unfeasible • Realistic, feasible and achievable 10
- 12. SMART OBJECTIVE • Specific: clearly formulated in terms of the desired result • Measurable: in terms of quantity and/or quality • Attainable: realistic, achievable, practical and workable • Relevant: worthwhile and in best interest of the individual as well as the organisation of which he/she is a member • Traceable (tangible/time-frame): whether it allows progress to be monitored in terms of realistic or valuable feedback. See applied example on page 31 12
- 13. Smart Objectives • Specific • Measurable • Attainable • Relevant • Traceble • Clearly formulated in terms of the desired result • In terms of quantity and/or quality • Realistic and achievable • Worthwhile and in best interest of the individual as well as the organisation of which he/she is a member • whether it allows progress to be monitored in terms of realistic or valuable feedback. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. 2.4 Time Management (p.32) How is success measured? Is it linked to time? • Why is time important? (2.4.1) • “Time is money” in the world of business • Time spent unnecessarily on one project, is time wasted, could be used on another project • Doing it at the right times also saves – or even makes – money • It is more sensible to clean out your desk on a Friday than on a busy day when you have urgent matters that need attention. 15
- 16. Time management (p.33) • Evaluation of time spent (2.4.2) Categorise it into: • Those activities really necessary vs. those that should be excluded • Those completed within a realistic period of time vs those on which time was wasted • Those performed at the appropriate time vs. those that should have been done at another time (prioritise) • Those that could have been done equally well by someone else. (delegation) • Planning time (2.4.3) Rate each task in terms of: • Importance • Most suitable time for performing it 16
- 17. Time Control Techniques (p.34 – 2.4.3.1) • Diaries (daily, weekly, monthly planning) • Week and year planners • Wall charts and desk pads • Delegation • Assigning task to sub-ordinates – why would you do that? • Self-control 17
- 18. Guidelines for better time utilisation – 2.4.3.2 (p.35) • Prioritise goals • Identify and dispose of time-wasters • Telephone calls, pop-ins, procrastination paper organisation, daily planning, distractions caused by colleagues • Employ time utilisation techniques (see p.34) • Set a time schedule • Evaluate your time spent 18
- 19. 19