Natural enemies2
- 1. Natural Enemies “ Friends of the Farmer” A presentation about natural pest control practices Adapted from IFOAM Training Manual on Organic Farming In the Tropics Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network
- 2. Topics To Cover Ecology of Pests and Diseases ( insect populations, life cycles, impacts of pesticides ) Promoting Natural Enemies ( their uses, characteristics, managing ) Bio-Control (releasing natural enemies, using bacteria, fungus and viruses) Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network i
- 3. Ecology of Pests and Diseases What is Ecology??? “ Study of relationships between organisms and their environment” Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 1
- 4. Ecology of Pests and Diseases Insect POPULATIONS are the problem, not individual insects. Different ecological factors can determine whether an insect population will become a “pest” or maintain in balance with the crop. Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 2
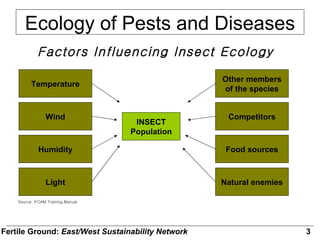
- 5. INSECT Population Temperature Wind Humidity Light Other members of the species Competitors Food sources Natural enemies Ecology of Pests and Diseases Factors Influencing Insect Ecology Source: IFOAM Training Manual Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 3
- 6. Who is the pest (identify which insect is causing the damage) What type of pest (burrower, leaf chewer, sap sucker, etc.) Where is the damage (i.e., leaves, stalk, roots) When is the pest attacking the crop (in the spring, summer, before/after rain, when crop ripens) Why is the pest attacking (to lay eggs, larvae feeding) Ecology of Pests and Diseases Important considerations! Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 4
- 7. Ecology of Pests and Diseases Pupa Egg Mass Life Cycle of rice yellow stem borer ( Scirpophaga incertulas ) Larva (5 stages) Adult Moths Common Life Cycle Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 5
- 8. Ecology of Pests and Diseases When pest populations are abundant there is more food for predator insects (increase in predator population) When the pest populations are low there is less food for the predators (decrease in predator populations) Therefore, pest and predator insect populations are always in equilibrium The Predator Prey Relationship Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 6
- 9. Ecology of Pests and Diseases What do you think happens when you use a pesticide that kills ALL insects, including the beneficial, predator insects ??? = Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 7 Pesticide Use
- 10. Ecology of Pests and Diseases Negative Impacts of Pesticides: Return of pest populations due to elimination of natural enemies - phenomenon known as Resurgence Development of insecticide-resistant pest populations - pesticide no longer kills the pest! Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 8
- 11. Ecology of Pests and Diseases Source: IFOAM Training Manual Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 9
- 12. Promoting Natural Enemies Uses and Characteristics of Natural Enemies Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 10 Pathogens (fungi, bacteria or viruses) Predators (spiders, lady beetles, syrphid flies) Parasitoids (wasps or flies) Nematodes (tiny soil dwelling worms)
- 13. Promoting Natural Enemies Managing Natural Enemies Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 11 Source: IFOAM Training Manual
- 14. Bio-Control Releasing Natural Enemies Source: IFOAM Training Manual Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 12
- 15. Bio-Control Why Use Biological Control??? It is based on the understanding that living systems are complex and vary (pesticides are formulated, and do not accommodate for variations) releasing natural enemies can be done before crop pests become a problem (keeping the populations in check), or when the pest becomes a problem (has versatility) Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 13
- 16. Example of Bio-Control Use of Trichogramma to control the tomato fruitborer The tiny black wasps (Trichogramma brasiliensis) search the eggs of the tomato fruitborer to lay their own eggs into them. Instead of a fruitborer larva, a tiny wasp emerges out of the egg. Trichogramma is harmless to the tomato plant. It is mass reared and can be released into the field on “trichocards”, containing several thousand parasitoid eggs. In India, a trichocard containing 20,000 parasitoid eggs costs only Rs.20 to 30 (≈ US$ 0,5). Stages of the Tomato Fruitborer lifecycle Eggs Adult Pupa Larvae Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 14
- 17. Photo Credits Slide One www.goldenacregarden.com/.../beneficial.htm thailand.ipm-info.org/bt/Bt_Basics.htm savanna.lternet.edu/gallery/kbs/KBS_Ha_eating_SBA Slide Two riddimmaker.smugmug.com/keyword/ladybug Slide Three http://www.ramsar.org/pictures/wwd2004-india-keoladeo1.jpg http://community.iexplore.com/photos/journal_photos/misty-morning-in-binsar.jpg www.abroadviewmagazine.com/.../def_land.html Slide Five IFOAM Training Manual Slide Seven http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/IPM/stemborers/image31.jpg http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/IPM/stemborers/image29.jpg http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/IPM/stemborers/image33.jpg http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/IPM/stemborers/image32.jpg Slide Nine http://www.fao.org/ag/icons/19463.jpg http://www.indiatravelogue.com/images1/wildlife/grasshopper.jpg Slide Ten http://whatsthatbug.com/images/aphids_closeup.jpg thailand.ipm-info.org/images/natural_enemies/... Slide Eleven IFOAM Training Manual Slide Twelve www.hampshirecam.co.uk/ws04/spider.jpg www.dpw.wageningen-ur.nl/.../parasitoid.jpg 80.194.73.68/.../Portals/2/Images/Fungi.jpg http://www.entomology.wisc.edu/mbcn/nema.jpg Slide Thirteen IFOAM Training Manual Slide Fourteen IFOAM Training Manual Slide Fifteen http://www.uoguelph.ca/research/news/articles/2005/June/aphid_biocontrol.shtml http://www.biofac.com/Fruit___Vegetables/bobbybro.JPG Slide Sixteen http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/ricedoctor_mx/Seed_and_Grain_Symptoms/image18.gif Slide Seventeen www.mpg.de/.../Web_Pressebild.jpeg Fertile Ground: East/West Sustainability Network 15