NBSintro2013
- 1. How can digital technologies improve organizational performance?
- 2. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER •LHST works with senior managers to leverage networks, processes and technology to enhance individual and corporate performance. • The client portfolio in the ICT industry includes Microsoft, Apple, Ernst & Young, France Telecom, HP, IBM, Oracle and SAP . •The work with the IT industry in Europe has included fifty partner and customer conferences, a dozen case studies, and various marketing support activities. Prof. Lee SCHLENKER, Professeur ESC Pau- EMLYON Managing Director, LHST Web : www.leeschlenker.com Objectives Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 3. 3 Focus Improve Knowledge Leverage Measure Process Centric ? ? ? ? ? Social Networks ? ? ? ? ? Search ? ? ? ? ? Mobility ? ? ? ? ? Objectives Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 4. http//:newcastlemba.com • Course slides • Recommended reading • Course deliverables • Student input Objectives Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 5. A curation page – 20 percent An written case study– 50 percent A video presentation– 30 percent Objectives Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 6. What Morgan called « the management of meaning » ©2010 LHST sarl Intro Perspective MirrorValue Deliverables • What does enterprise IT mean? • What are you trying to improve? • What do you need to learn? • What does better mean? • How do you measure success? Focus Improve Knowledge Leverage Measure
- 7. • Economic transformation: The transformation from a manufacturing- based economy to a services-based economy now underway throughout the developed world will accelerate. • One World of Business. Political and economic dynamics are forging a single global market, a global workforce, global customers, partners, and suppliers. • Always On, Always Connected. The challenges of the “always on, always connected” world will be converting information into insights; managing time and staying focused on high priority tasks • The Transparent Organization. The systems that make organizations more agile also make them more accountable. • NetGen Meets Baby Boom. Workers who will be delivering the innovations and productivity growth of tomorrow, this technology not only won’t come as a surprise, it will be a positive expectation. • Competing for Talent in a Shrinking Workforce: Because demographics show an aging, shrinking workforce in most of the developed world over the next 50 years, maximizing the productivity of the workers that are available is critical. Intro Perspective MirrorValue Deliverables
- 8. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER • Globalization : the increasingly circulation of information across borders. • Technical progression: the transformation of communication « atoms to bits » • Economic integration: vertical and horizontal integration to profit from economies of scale • Social innovation: human attempts to create new forms of expression • Multitasking : individual efforts to use multiple communication platforms Henry JenkinsIntro Perspective MirrorValue Deliverables
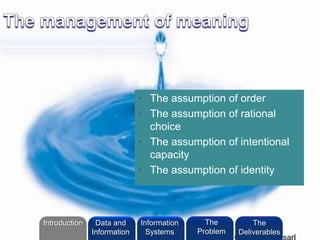
- 9. • The assumption of order • The assumption of rational choice • The assumption of intentional capacity • The assumption of identity ©2010 LHST sarl Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 10. • Study the fundamentals of an Information System • Analyze the constraints and possibilities of « structured » information • Explore how the potential links between an IS and innovation • Analyze the potential value of digital transformation Objectives Information Systems The Internet Data and Information The Problem The Challenges
- 11. What is the link between data and action? • Understanding the implications between « structured » and « unstructured data » • Analyzing the difference between the data and reality • Understanding how the data fits together • Exploring the difference between data and action Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 12. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER • From an objective point of view, information refers to date in context that conveys meaning to an individual. • From a subjective point of view, we could suggest that it’s the individual’s perspective of the data that implies meaning. • Given these definitions what meaning do Wikileaks, Facebook or Whatapp have? Assane, The Conversation Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 13. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER • Structured data refers to data that can be easily represented in textual/numeric form and stored in a database. • Structured data is often logically organized around a data model or data object. • Such models permit companies to compare and aggregate data in databases, datamarts and data warehouses. Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 14. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER • Data is considered « non-structured » if we can’t predefine its attributes and store it in a table or data base • Examples of this kind of data include press clippings, videoclips, and songs • In reality, this data isn’t « non-structured » - its just that its attributes involve « complex » relationships http://ean.marie.gouarne.online.fr/bi.html Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 15. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER What meaning do we attach to the data? Frame Cloud Figure (s) Oracle Antonello da Messina Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
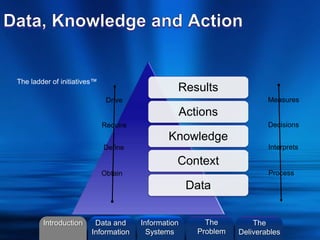
- 16. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER Results Actions Knowledge Context Data Process Interprets Decisions Measures Obtain Define Require Drive The ladder of initiatives™ Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
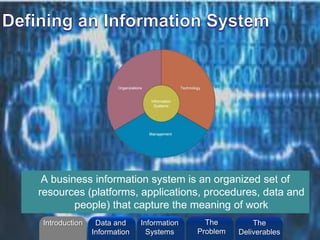
- 17. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER A business information system is an organized set of resources (platforms, applications, procedures, data and people) that capture the meaning of work Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 18. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER To help us understand the motivations, experience and objectives of the internal and external clients of the organization ROI Real time data ... Stockholders Competition “made in” “made by” ... The State Peu de barrières d’entrée Acquisitions, OPA... Partners Loyalty Real costs ... Clients The Enterprise Mobility Empowerment ... Employees Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 19. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 20. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
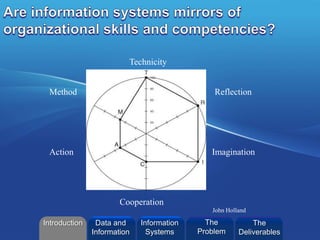
- 22. ©2013 L. SCHLENKER Technicity Reflection Imagination Cooperation Method Action John Holland Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 23. • Nicolas Carr compares IT to previous tech revolutions such as railroads and electricity. In what ways is IT different? • What proof can you offer that information technology in business no longer provides competitive advantage? • Does the pervasiveness of IT mean there will be less innovation now? • Hasn't competitive advantage come from unique use of the technology, not just from the technology itself? What examples can you give? • Do recent advances in Cloud Computing and Mobile Applications confirm or contradict Nicolas Carr's claims? Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 24. Digital Transformation 1. Everyone Will Have the Web 2. The Browser Will Be the Operating System 3. Business Will Live in the Cloud 4. Everything Will Be Social 5. Software Will Eat the World Marc Andreessen Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 25. Work (productivity) • Harder, better, faster… • Mechanized productivity • Knowledge productivity • Continuous Productivity Steven Sinofsky Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 26. • Ordered domain: Known causes and effects. • Ordered domain: Knowable causes and effects. • Un-ordered domain: Complex relationships. Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 27. Grading Scale The marks in this module will be based upon contributions in three areas : • Curation: 20 possible points based on the quality of each individual student’s on-line and in-class participation • Design your School case study: 50 possible points based on the number and quality of the story. • Webcast: 30 possible points based on the quality the presentation of your perspective • Total points possible: 100 http://www.newcastlemba.com Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 28. Written assignment • How can a business school become an idea factory? • The vision - how can a phygital space promote your theme? The design - what types of equipment (furniture, supplies, technologies, and decorations) will support this vision. The events - which specific events (conferences, workshops, coffee breaks, etc.) will be held in the Idea Factory to encourage the exploration and appropriation of your theme? The guests - which specific skills and competences (deep thinking, deep reading, visioning, project management....) will the Factory develop? The results - how do you recommend evaluating the results of your vision (participant comments, usage, number of ides produced...)? Total points possible: 50 Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
- 29. Can you make a difference? • Individual assignment • What have you learned from your case? • Themes : trends, convergence, fragmentation • Delivery: video analysis • Evaluation criteria : personalization, insight, dissonance • Length : minimum four minutes • Exploring digital intermediation Total points possible: 30 Introduction Information Systems The Problem Data and Information The Deliverables
Editor's Notes
- Zynga, Skype, Instagram, Groupon, Foursquare and Pinterest