Notes - Radiation Electromagnetic
- 2. Light A common term for electromagnetic radiation, which travels in space as waves. The human eye can only sense a limited range of all the various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. We only “see” visible light.
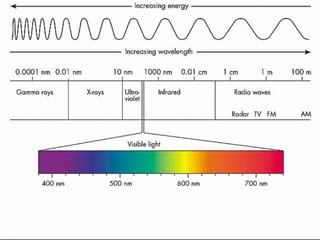
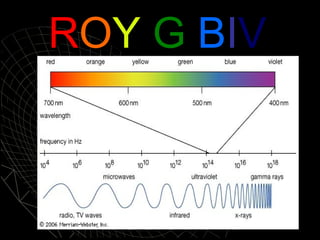
- 3. Electromagnetic Radiation includes: (largest to smallest) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Radio Microwaves Infrared (IR) Visible light Ultraviolet (UV) X-rays Gamma
- 5. Examples of uses UV – (black light). Some animals, including birds, reptiles, and insects such as bees, can see into the near ultraviolet. Many fruits, flowers, and seeds stand out more strongly from the background in ultraviolet wavelengths as compared to human color vision.
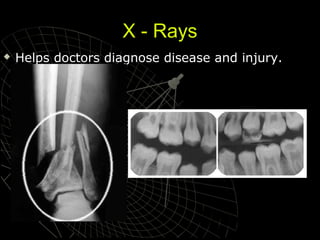
- 7. X - Rays Helps doctors diagnose disease and injury.
- 8. Radio Waves Your favorite radio station, TV, entertainment, communication.
- 9. Gamma rays Used for the treatment of cancer Radiation therapy detects the gamma radiation Gamma-ray Image with stowaways
- 10. Question: How does this (Electromagnetic Radiation) relate to astronomy? Stars, planets, and gas in space emit electromagnetic radiation. Each element in the Periodic table has it own unique wavelength and frequency. Knowing its wavelength and frequency, we are able to determine color and composition of stars, planets, ect…
- 11. Truck going through Radiation Portal Monitor
- 12. The Moon as seen in gamma rays by the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. Surprisingly, the Moon is actually brighter than the Sun at gamma ray wavelengths.
- 13. Click here Electromagnetic Radiation in Astronomy
- 14. Electromagnetic radiation is classified by its wavelengths (distance from peak to peak).
- 15. Red light has longer wavelengths than blue light.
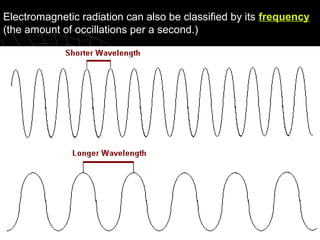
- 16. Electromagnetic radiation can also be classified by its frequency (the amount of occillations per a second.)
- 17. Electromagnetic radiation travel at the speed of light.
- 18. ROY G BIV
- 19. What is the Doppler Effect? Change in the wave frequency that occurs when energy moves toward or away from an observer or object, such as sound or light.
- 20. What is a “red shift?” The process of galaxies moving AWAY from Earth, resulting a in a longer wavelength.
- 21. What is a “Blue Shift?” The process of galaxies moving toward Earth, resulting in a shorter wavelength.
- 22. Why are these “shifts” important in studying our universe? Observations show that most galaxies are moving away from us, thus proving that the universe is expanding (BIG BANG THEORY). Can provide information about incoming objects (asteroids).
Editor's Notes
- {}