Nutrition in Animals, Class 7, Science Chapter-2
- 1. CHAPTER - 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Class 7 Science
- 2. 1) Animal nutrition :- The mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation in the body is called nutrition. Animals get their food directly or indirectly from plants. Animal nutrition:-includes nutrient requirement, mode of taking food and its utilisation in the body. 2) Different ways of taking food :- Name of animal Kind of food Mode of feeding Snail Grass Chewing Ant Insects Scrapping Eagle Flesh Swallowing Humming bird Nectar Sucking Lice Blood Sucking Mosquito Blood Sucking Butterfly Nectar Siphoning/Sucking House fly Decaying matter Brewing
- 3. Chewing Swallowin g Chewing Scrapping Sucking Sucking/ Siphoning
- 5. 2.Digestion:-The process by which complex food substances are broken down into simpler substances is called digestion. Digestion Complex Substances Simpler Substances NUTRIENTS AND THEIR SIMPLER SUBSTANCES. 1.Carbohydrates Glucose 2.Fats Fatty Acids 3.Protiens Amino Acids
- 6. 1.1.Digestion in humans: Digestion System Involves:- Ingestion Digestion Absorption Assimilation Egestion Process of taking of food in the body. Breaking down of food into simpler Substances. Absorption of digested food by Villi. Transportation of absorbed food to the cells. Removal of waste excreta.
- 7. 1.2) Digestion in humans :- The main parts of the alimentary canal are :- Oesophagus (Food pipe), Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Buccal Cavity(Mouth) Anus
- 8. 1.4.The mouth and buccal cavity :- Food is taken into the body through the mouth. In the mouth the food is broken down into smaller pieces by the teeth. The mouth has salivary glands which secrete saliva. The tongue helps to mix the food with saliva and swallow the food. The saliva breaks down starch into sugars. Starch Sugar Saliva
- 9. Tongue :- The tongue helps to mix the food with saliva and swallow the food. The tongue has taste buds to detect different tastes of food. The different regions of the tongue detect different tastes
- 10. Teeth :- There are four types of teeth. They are incisors, canines, permolars and molars. Incisors :- help in biting and cutting the food. Canines :- help in piercing and tearing the food. Premolars and molars :- help in chewing and grinding the food.
- 11. Name Upper Jaw Lower Jaw Total Incisors 4 4 8 Canine 2 2 4 Premolars 6 6 12 Molars 4 4 8 --- --- total 32
- 12. 1.5.OESOPHAGUS :- Long Canal to transported food toward Stomach, called Food pipe. Paristalis :-Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
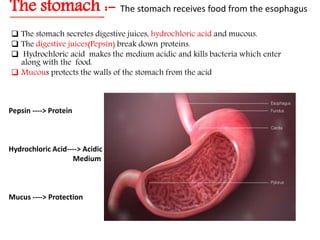
- 13. The stomach :- The stomach receives food from the esophagus The stomach secretes digestive juices, hydrochloric acid and mucous. The digestive juices(Pepsin) break down proteins. Hydrochloric acid makes the medium acidic and kills bacteria which enter along with the food. Mucous protects the walls of the stomach from the acid Pepsin ----> Protein Hydrochloric Acid----> Acidic Medium Mucus ----> Protection
- 14. 1.6.Liver and pancreas:- Liver produce Bile Juice that are stored in bladder called Gall Bladder. Bile Juice breaks down fats. Pancreas secretes Pancreatic juice and helps to digest Proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Liver and Pancreas shared a common duct. The liver is the largest gland in the body.
- 15. 1.7.The small intestine :- The small intestine is a long coiled tube about 9m long in adult human. It receives secretions from liver and pancreas. It also secretes digestive juices. The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which breaks down carbohydrates and proteins. The intestinal juice completes the digestion of starch into glucose, fats into fatty acid and glycerol and proteins into amino acids.
- 16. 1.8. Absorption of digested food in the small intestine:- The digested food is absorbed by the walls of the small intestine. This process is called absorption. The small intestine has several finger like projections called villi having blood vessels. The villi helps to increase the surface area for absorption. The absorbed materials are carried by the blood to the different parts of the body and used by the body. This is called assimilation. The undigested food then passes into the large intestine.
- 17. 1.9.The large intestine :- The large intestine is wider and shorter than small intestine. It is about 1.5 metres in length. Large intestine absorbs water and some salts from the undigested food material. The remaining waste passes into the rectum and remains there as semi- solid faeces(Potty). The faecal matter is removed through the anus from time-to-time. This is called egestion
- 18. 2. Digestion in grass eating animals(Ruminants) :- Grass eating animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a separate part of the stomach called rumen. Examples:- Cow Sheep Goat
- 19. 2.Digestion in grass eating animals(Ruminants) :- Ruminants quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen. The food that is partly digested and is called cud. Then the cud is brought back to the mouth in small lumps and chewed. This process is called rumination. The chewed food then passes into a sac like structure between the small intestine and large intestine called Caecum. The cellulose in the grass is digested with the help of some bacteria.
- 20. 3. Feeding and digestion in amoeba :- Amoeba is a single celled organism found in pond water. The cell has a cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus. The cytoplasm has many bubble like vacuoles. The cell has finger like projections called pseudopodia or false feet which helps it to move and capture food. When amoeba comes near food particle, pseudopodia is produced around the food particle. The food particle is trapped in a food vacuole. In the food vacuole the food is digested by digestive enzymes and absorbed. The undigested waste is then sent out by the vacuole.
- 21. Animal nutrition includes nutrient requirement, mode of intake of food and its utilisation in the body. The human digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and secretory glands. It consists of the (i) buccal cavity (ii) oesophagus (iii) stomach (iv) small intestine (v) large intestine ending in rectum and (vi) anus. The main digestive glands which secrete digestive juices are (i) the salivary glands, (ii) the liver and (iii) the pancreas. The stomach wall and the wall of the small intestine also secrete digestive juices. The modes of feeding vary in different organisms. Nutrition is a complex process involving: (i) ingestion, (ii) digestion, (iii) absorption, (iv) assimilation and (v) egestion. Summary:-
- 22. ----The End----