Overview prolog
- 1. An Overview of Prolog 1
- 2. What is Prolog Prolog is a powerful language for AI and non- numerical programming Stands for programming in logic Centered around a small set of basic mechanisms, including: Pattern matching Tree-based data structuring Automatic back tracking Well suited for problems that involves structured objects and relations between them. 2
- 3. Chapter One: Introduction to Prolog 1. Defining relations by facts 2. Defining relations by rules 3. Recursive rules 4. How Prolog answers questions 5. Declarative and procedural meaning of programs 3
- 4. Chapter one: 1. Defining relations by facts 2. Defining relations by rules 4
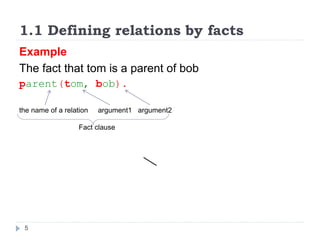
- 5. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 5 Example The fact that tom is a parent of bob parent(tom, bob). the name of a relation argument1 argument2 Fact clause
- 6. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 6 The family tree is defined by the following Prolog program: parent(pam, bob) parent(tom, bob) parent(tom, liz) parent(bob, ann) parent(bob, pat) parent(pat, jim) This program consists of six clauses. Each clause declares one fact about parent relation (particular instance of the parent relation) * a relation is the set of all its instances
- 7. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 7 When the program communicated to Prolog system, Prolog can be posed some questions about the parent relation: Is bob a parent of pat? ?- parent(bob, pat) Prolog answer: True ?- parent(liz, pat) Prolog answer: No solutions ?- parent(tom, pat) Prolog answer: No solutions tom bob ann pat jim liz pam
- 8. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 8 Who is liz’s parent? ?- parent(X, liz) Prolog answer: X = tom Who are bob’s children? ?- parent(bob, X) Prolog answer: X = ann. X = pat. tom bob ann pat jim liz pam
- 9. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 9 Find X and Y such that X is a parent of Y. ?- parent (X, Y). Prolog answers: X = pam. Y = bob. X = tom. Y = bob. X = tom. Y = liz. X = bob. Y = ann. X = bob. Y = pat. X = pat. Y = jim. tom bob ann pat jim liz pam
- 10. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 10 Who is a grandparent of jim? Who is the parent of jim? Assume that this is Y Who is the parent of Y? Assume that this is X ?- parent(Y, jim), parent (X, Y) Prolog answer: X = bob Y = pat • Changing the order of the requirements will affect the result. ?- parent(X, jim), parent (Y, X) Prolog answer: X = pat. Y = bob. ?- parent(X, jim), parent (X, Y) Prolog answer: X = pat. Y = jim. √ x x
- 11. 1.1 Defining relations by facts 11 Do ann and pat have a common parent? Who is a parent X of ann? Is X a parent of pat? ?- parent (X, ann), parent(X, pat) Prolog answer: X = bob tom bob ann pat jim liz pam
- 12. 1.2 Defining relations by rules 12 We can add the information on the sex of the people that occur in the parent relation: female(pam). male(tom). male(bob). female(liz). female(pat). female(ann). male(jim). male and female are unary relations, whereas parent is a binary relation. Gender(pam, female). Gender(tom, male). Gender(bob, male). tom bob ann pat jim liz pam
- 13. 1.2 Defining relations by rules 13 Let us introduce the offspring relation (inverse of parent) offspring(liz, tom). offspring(bob, tom). ... The logical statement is: For all X and Y, Y is an offspring of X if X is a parent of Y offspring(Y, X) :- parent(X, Y). Rule clause tom bob ann pat jim liz pam Fact caluses
- 14. 1.2 Defining relations by rules 14 There is an important difference between facts and rules: Facts is something that is always, unconditionally, true parent(tom, liz). Rules specify things that are true if some condition is satisfied. Rules have: Condition part (right-hand side) = body Conclusion part (left-hand side) = head offspring(Y, X) :- parent(X, Y). head body
- 15. 1.2 Defining relations by rules 15 Questions Is liz an offspring of tom? ?- offspring(liz, tom). Prolog answer: True How Prolog answer this question using the rule: Offspring(Y, X) :- parent(X, Y). Prolog answer: True
- 16. 1.2 Defining relations by rules 16 How to express: Mother relation Grandparent relation Sister relation in Prolog?
Editor's Notes
- offspring(bob, pam). offspring(ann, bob). offspring(pat, bob). offspring(jim, pat).