Part b
0 likes594 views
The document presents several financial plans and decision making approaches to determine the best course of action for a company given uncertain future conditions. Plan 1 uses Maximax, Maximin, Minimax Regret, Hurwicz, Expected Opportunity Loss, Expected Value, and Expected Value of Perfect Information approaches to analyze options to expand, maintain status quo, or sell the business. Plan 2 uses probability distributions and random numbers to simulate stock price changes and calculate average prices under different scenarios.
1 of 5




Recommended
Ma



MaRutuja Chudnaik The document discusses various financial ratios used to analyze the financial performance of Tata Steel Limited for the years 2004 and 2003. It provides the formulas and calculations for current ratio, quick ratio, stock to working capital ratio, and other key ratios. The ratios analyzed include profitability, liquidity, leverage, efficiency, and return measures.
Chan chee m ang tp021569



Chan chee m ang tp021569Jessica Allison In the modernisation era, it is all about Globalisation in the international business context. With the rise in Globalisation resulted the increase level of international business activities and yet led to the rise of exchange rate events. Exchange rate is the price of a country’s currency expressed in another country’s currency or the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another and this has to be taking into consideration by Multinational Corporations like Blades Inc. as the Thai based entertainment retailer In another word, appreciation of exchange rate for one Dollar in terms of one Baht (fixed rate) would result in depreciation of the value of Baht. The changes in exchange rates are determined by the factors of changes in interest rates, inflation, trade balance, political stability, internal harmony, high degree of transparency in the conduct of leaders and administrators, general state of economy, and quality of governance. The exchange rate is considered as the vital factor of any country’s economy and indication of the financial health.
Bm045 3-3-smgt tp021569 3rd question



Bm045 3-3-smgt tp021569 3rd questionJessica Allison The document discusses critical success factors of low-cost carriers (LCCs) globally and in India. It analyzes the performance of LCCs in India and reasons for their failure. It then provides strategic options to make Indian LCCs economically viable.
For LCCs globally, key success factors discussed include WestJet's 7 domains attractiveness model, culture of employee empowerment, and low-cost model. AirAsia utilizes absolute cost advantage through low costs per seat and distribution costs.
In India, LCCs saw growth but faced challenges like employee shortage, low regional connectivity, rising fuel costs, declining yields from competition, and infrastructure gaps. Strategic options suggested for Indian LCCs include re
Tsm



TsmJessica Allison The document provides a non-financial and financial plan for Louis Vuitton (LV). It summarizes LV's history, products, target markets, competition, and marketing strategies. Key points include LV targeting wealthy customers globally, particularly in growing Asian markets; threats from counterfeiting and substitute luxury brands; maintaining exclusivity through limited distribution and high prices; and focusing on brand image over sales promotions.
Resm presentatn 2



Resm presentatn 2Jessica Allison This document presents a study on the effects of workplace layout and symbolism on job performance among employees in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. It outlines the objectives and hypotheses of the study, which aim to examine relationships between workplace characteristics and job performance. The significance of the study is discussed, noting gaps in existing Malaysian research. Limitations and key terms are also defined. The proposed methodology will profile respondents, assess workplace layout and symbolism, and determine their correlations with measured job performance.
Emkt final



Emkt finalJessica Allison The document discusses Amazon's e-marketing strategic planning. It covers market segmentation, positioning, and targeting of Amazon's market. It notes that Amazon segments its market through different brands that appeal to distinct demographics. It then discusses Amazon's objectives, which include providing excellent customer service to build loyalty. The document outlines Amazon's 4P marketing strategies of product, price, place, and promotion. It proposes enhancements Amazon could make, such as adding debit card payments and improving the search engine. Finally, it discusses implementing and evaluating the analysis, including potential metrics like sales conversion rates and website traffic.
ASGE



ASGEJessica Allison This document discusses the implications of globalization and free trade on East Asian economies. It provides background on East Asian countries and economic contexts. Some key points made include:
- East Asia has experienced rapid economic growth in recent decades, though growth has varied between countries.
- Globalization and free trade agreements have increased connectivity and lowered barriers between East Asian economies, facilitating trade and foreign investment.
- This has generally had positive impacts like boosting capital, production, and employment, but it has also increased competition and some economies faced difficulties during economic crises.
- The proliferation of free trade agreements in East Asia benefits economic growth, but questions remain around their complexity and potential to create new trade barriers.
Emkt chan



Emkt chanJessica Allison Amazon began in 1995 as an online bookseller operating out of Jeff Bezos' garage. It has since expanded significantly, selling a wide range of products and employing sophisticated personalization techniques and partnerships to optimize the customer experience. Amazon leverages customer data and third-party sellers to offer competitive pricing and a vast selection on its platform. It has also developed tools like Mechanical Turk to branch into new areas while maintaining a focus on customers.
Claude Resources Corporate Presentation: March 2012



Claude Resources Corporate Presentation: March 2012Claude Resources Inc. This document provides an overview of Claude Resources Inc., a Canadian gold mining company with projects in Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It summarizes Claude's three gold projects - Seabee, Amisk and Madsen - which are expected to host multi-million ounce ore bodies. Exploration programs are outlined for 2012 that aim to increase resources. Production at Seabee has increased from 2007 to 2016 and is expected to continue growing. The presentation highlights Claude's experienced management team, strong balance sheet, and potential for increased production and resource growth through exploration as catalysts for investment.
Claude Resources August 2012 Corporate Presentation



Claude Resources August 2012 Corporate PresentationClaude Resources Inc. - Claude Resources has three Canadian gold projects: Seabee, Amisk, and Madsen, which are expected to host multi-million ounce ore bodies and collectively produce over 100 thousand ounces per year.
- At its Seabee operation, Claude has produced over 1 million ounces of gold since 1991 and has a reserve and resource of 1.3 million ounces. Production is projected to increase from 50 thousand ounces currently to over 80 thousand ounces by 2016.
- Exploration is ongoing across the properties to expand resources and make new discoveries, with over 50 thousand meters of drilling planned for 2012.
Pl ple excel_lindo



Pl ple excel_lindoAndres Antonio Casquete Gomez This document contains the outputs of several linear programming problems solved using the simplex method. Each problem provides the objective function to maximize or minimize, subject to various constraints, and outputs the optimal solution including variable values and dual prices.
Claude Resources June 2012 Corporate Presentation



Claude Resources June 2012 Corporate PresentationClaude Resources Inc. Neil McMillan, President and CEO of Claude Resources Inc., presented at a meeting in June 2012. Claude Resources has three Canadian gold projects: Seabee, Amisk, and Madsen, which are expected to host multi-million ounce ore bodies with the potential to produce over 100 thousand ounces per year. The presentation provided an overview of Claude Resources' corporate information, operations at each project site, exploration plans and targets for 2012, and compared the company's valuation to peers.
Rows



RowsCia. Minera Kolpa S.A. (Ex-Caudalosa) The document summarizes the results of solving a linear programming problem with 2 variables and 6 constraints. The optimal solution was found at the first step with an objective value of 660. The values of the variables X1 and X2 at the optimal solution are 70 and 90, respectively. Ranges for the objective coefficients and right-hand side values are provided where the basis remains unchanged.
Rows



RowsCia. Minera Kolpa S.A. (Ex-Caudalosa) The document summarizes the results of solving a linear programming problem with 2 variables and 6 constraints. The optimal solution was found at the first step with an objective value of 660. The values of the variables X1 and X2 at the optimal solution are 70 and 90, respectively. Ranges for the objective coefficients and right-hand side values are provided where the basis remains unchanged.
Do not submit acc 422 week 3 wiley plus assignment exercises



Do not submit acc 422 week 3 wiley plus assignment exercisesjefferysbush1 The document contains information about various asset acquisitions and constructions by Impala Company. It provides details of the company receiving land valued at $81,000 as a donation, issuing stock to acquire land and buildings valued at $810,000, and constructing machinery internally. The appropriate accounting entries to record these transactions debit various asset accounts and credit equity/expense accounts.
All



Allguest7cfe7712 The document describes the results of several linear programming optimization problems involving the allocation of resources with constraints. The problems include selecting radio station licenses, installing traffic monitoring devices, and determining locations for distribution centers and transporting natural gas. For each problem, the optimal solution and objective value are provided.
Mafia Wars Expense Guide



Mafia Wars Expense Guideguest26cede The document provides information on the income, costs, and payouts of different jobs and properties in Mafia Wars. It includes a table listing various jobs/roles (e.g. Street Thug, Associate, Soldier), the experience points and energy costs for each job, and the range of possible income payouts. Another section shows properties that can be purchased, their costs and income amounts. The document aims to help players understand the most profitable activities.
Navneet accounts



Navneet accountsNavneet Rasha The document appears to be a student project on sole proprietorship. It includes sections on:
- The student's interest in becoming a sole trader and managing their own business.
- Steps for purchasing products in bulk or individually.
- Trial balance sheets, profit/loss statements, and sales/profit figures for years 2007-2010 of a sample sole proprietorship furniture business.
- Anticipated balance sheets and profit/loss statements for 2009-2010.
- Questions about increasing sales, problems setting up the business, and making the project.
Claude Resources Inc. Corporate Presentation



Claude Resources Inc. Corporate PresentationClaude Resources Inc. A bright future lies ahead for the company as it works to increase gold production and resource base at its Canadian projects over the coming years. The company has three projects in Canada with the potential to produce over 100,000 ounces of gold per year. Exploration success could significantly grow the resource base, which currently stands at over 3 million ounces. The company aims to leverage its cash flow, exploration upside, management team, and strong balance sheet to provide a great risk-reward investment opportunity.
2009 Market Disruption Webinar



2009 Market Disruption WebinarBrent B Year end review of 2009, especially focusing on trading and price movement in illiquid securities. Also a look at the road ahead in 2010.
Supply Chian



Supply Chianrbrunson7564 R&J Technologies submitted RFPs totaling 6,000 units over the 4 quarters and accepted RFPs from BrownTech Industries. They opened sales offices in Chicago, Mumbai, and Frankfurt. Financial results showed net losses each quarter with a total net loss of $4.6 million for the year. Key lessons learned included salvaging underperforming products, ordering appropriate inventory levels, analyzing sales office performance, and understanding demand drivers.
Presentation2.1



Presentation2.1Debashish Bagg The document summarizes trends in outsourcing in the Indian retail industry. It analyzes data from Pantaloon Retail Ltd and Spencer Retail Ltd, finding that both companies outsource a large portion of their operations, with Spencer outsourcing more at around 95%. A survey found that both companies use multiple vendors and outsource logistics and transportation. While Big Bazaar is moving towards more internal production, Spencer focuses on responsiveness through outsourcing and forecasting improvements. Limitations include a lack of seasonal data and the results only representing 5% of the overall industry.
Commodities on the radar - Weekly Commodity Update 1.2.11



Commodities on the radar - Weekly Commodity Update 1.2.11Trading Floor - Speculative futures positions across sectors increased by 5% or 94,000 lots last week as hedge funds and money managers added to long positions.
- Investors added to short dollar positions, with the accumulated dollar short now at $30 billion, close to last year's peak of -$35.16 billion.
- Long positions in WTI crude oil rose by 21k contracts and positions in grains, which make up 56% of total speculative positions, rose significantly.
CFTC - Commodity Futures Trading Commission



CFTC - Commodity Futures Trading CommissionTrading Floor - Speculative futures positions across sectors increased by 5% last week as hedge funds and money managers added 94,000 lots of futures to already elevated long positions. All sectors except metals saw an increase.
- Investors added to their dollar short positions, with the accumulated dollar short on futures markets now at $30 billion, approaching last year's peak of -$35.16 billion.
- In energy, the long WTI crude position rose by 21k contracts amid unrest in North Africa and Brent crude prices above $100. Grain positions, mainly in soy, wheat and corn, rose as well.
Decision analysis problems online 1



Decision analysis problems online 1Soumendra Roy The document contains multiple decision problems involving expected monetary value (EMV) calculations. The first problem involves determining the optimal act from among three acts (A1, A2, A3) based on their payoffs under three possible states of nature (S1, S2, S3) and the given probabilities. The optimal act determined using EMV is A1. Another problem involves determining whether a proposal should be accepted or rejected based on the EMV of each decision. The EMV calculation shows the decision should be to reject the proposal. A third problem involves calculating EMV under different criteria to determine the best investment from among stocks, bonds, and debentures.
Perfect business



Perfect businessseyfom Mega Trading is an international company incorporated in 1999 that allows users to earn commissions by recruiting others and selling products online. The company had $17 billion in revenue in 2010, up 56% from 2009. It offers website hosting, email, subdomains, database storage, pages, and design software starting at $1,000 per year. Users can earn commissions of $200-41,000 per level as their organization grows from 200 to over 400,000 members on both the left and right sides of their network. The presentation encourages attendees to join Mega Trading to achieve incredible income and be part of the 75% of world trading projected until 2100.
Junk food final 1



Junk food final 1Raphaël Bils The document analyzes the relationship between levels of happiness and junk food sales across 12 countries. A linear regression was performed and found a strong positive correlation (R^2 of 0.736) between happiness and junk food sales. Countries with higher reported happiness levels also had higher junk food sales. The regression equation can be used to predict junk food sales based on a country's expected level of happiness.
Account asst



Account asstPein Akatsuki This document contains an assignment submitted by Akershit Kumar Sharma to Professor Mushtaq Ahmed on April 7, 2013. It includes answers to various questions related to contribution format income statements segmented by territory and product line. The key details provided are contribution format income statements for a company's total sales, segmented by the northern and southern territories, and further segmented of the northern territory by its Paks and Tibs product lines. Analysis is also provided on performance of different territories and product lines.
Ecom presentation(1)



Ecom presentation(1)Jessica Allison The document outlines recommendations for an e-commerce website and payment options for KFC. It discusses including an e-commerce function, product overview, and latest information on the home page. The shopping list would allow for price checking, viewing outlets, and promotions. Advantages of e-commerce are enabling a global market, saving time and money, and 24/7 availability. Payment options suggested are payment cards like credit, debit, and charge cards as well as electronic cash via PayPal.
Youth jam 2012 ultimate youth survival



Youth jam 2012 ultimate youth survivalJessica Allison This document outlines the Ultimate Youth Survival Challenge 2012 project which aims to drive Malaysian youth in the right direction through a series of competitions and challenges over 2 months. It involves quarter and semi-final rounds of poster drawing, photo shooting, and sports competitions held around universities. 10 finalists will then participate in a reality TV-style challenge in Taipei, Taiwan where they will compete in daily challenges and be filmed for 5 days, learning survival skills and networking with foreign youth. The project aims to promote sponsors while developing energetic and passionate Malaysian youth.
More Related Content
Similar to Part b (20)
Claude Resources Corporate Presentation: March 2012



Claude Resources Corporate Presentation: March 2012Claude Resources Inc. This document provides an overview of Claude Resources Inc., a Canadian gold mining company with projects in Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It summarizes Claude's three gold projects - Seabee, Amisk and Madsen - which are expected to host multi-million ounce ore bodies. Exploration programs are outlined for 2012 that aim to increase resources. Production at Seabee has increased from 2007 to 2016 and is expected to continue growing. The presentation highlights Claude's experienced management team, strong balance sheet, and potential for increased production and resource growth through exploration as catalysts for investment.
Claude Resources August 2012 Corporate Presentation



Claude Resources August 2012 Corporate PresentationClaude Resources Inc. - Claude Resources has three Canadian gold projects: Seabee, Amisk, and Madsen, which are expected to host multi-million ounce ore bodies and collectively produce over 100 thousand ounces per year.
- At its Seabee operation, Claude has produced over 1 million ounces of gold since 1991 and has a reserve and resource of 1.3 million ounces. Production is projected to increase from 50 thousand ounces currently to over 80 thousand ounces by 2016.
- Exploration is ongoing across the properties to expand resources and make new discoveries, with over 50 thousand meters of drilling planned for 2012.
Pl ple excel_lindo



Pl ple excel_lindoAndres Antonio Casquete Gomez This document contains the outputs of several linear programming problems solved using the simplex method. Each problem provides the objective function to maximize or minimize, subject to various constraints, and outputs the optimal solution including variable values and dual prices.
Claude Resources June 2012 Corporate Presentation



Claude Resources June 2012 Corporate PresentationClaude Resources Inc. Neil McMillan, President and CEO of Claude Resources Inc., presented at a meeting in June 2012. Claude Resources has three Canadian gold projects: Seabee, Amisk, and Madsen, which are expected to host multi-million ounce ore bodies with the potential to produce over 100 thousand ounces per year. The presentation provided an overview of Claude Resources' corporate information, operations at each project site, exploration plans and targets for 2012, and compared the company's valuation to peers.
Rows



RowsCia. Minera Kolpa S.A. (Ex-Caudalosa) The document summarizes the results of solving a linear programming problem with 2 variables and 6 constraints. The optimal solution was found at the first step with an objective value of 660. The values of the variables X1 and X2 at the optimal solution are 70 and 90, respectively. Ranges for the objective coefficients and right-hand side values are provided where the basis remains unchanged.
Rows



RowsCia. Minera Kolpa S.A. (Ex-Caudalosa) The document summarizes the results of solving a linear programming problem with 2 variables and 6 constraints. The optimal solution was found at the first step with an objective value of 660. The values of the variables X1 and X2 at the optimal solution are 70 and 90, respectively. Ranges for the objective coefficients and right-hand side values are provided where the basis remains unchanged.
Do not submit acc 422 week 3 wiley plus assignment exercises



Do not submit acc 422 week 3 wiley plus assignment exercisesjefferysbush1 The document contains information about various asset acquisitions and constructions by Impala Company. It provides details of the company receiving land valued at $81,000 as a donation, issuing stock to acquire land and buildings valued at $810,000, and constructing machinery internally. The appropriate accounting entries to record these transactions debit various asset accounts and credit equity/expense accounts.
All



Allguest7cfe7712 The document describes the results of several linear programming optimization problems involving the allocation of resources with constraints. The problems include selecting radio station licenses, installing traffic monitoring devices, and determining locations for distribution centers and transporting natural gas. For each problem, the optimal solution and objective value are provided.
Mafia Wars Expense Guide



Mafia Wars Expense Guideguest26cede The document provides information on the income, costs, and payouts of different jobs and properties in Mafia Wars. It includes a table listing various jobs/roles (e.g. Street Thug, Associate, Soldier), the experience points and energy costs for each job, and the range of possible income payouts. Another section shows properties that can be purchased, their costs and income amounts. The document aims to help players understand the most profitable activities.
Navneet accounts



Navneet accountsNavneet Rasha The document appears to be a student project on sole proprietorship. It includes sections on:
- The student's interest in becoming a sole trader and managing their own business.
- Steps for purchasing products in bulk or individually.
- Trial balance sheets, profit/loss statements, and sales/profit figures for years 2007-2010 of a sample sole proprietorship furniture business.
- Anticipated balance sheets and profit/loss statements for 2009-2010.
- Questions about increasing sales, problems setting up the business, and making the project.
Claude Resources Inc. Corporate Presentation



Claude Resources Inc. Corporate PresentationClaude Resources Inc. A bright future lies ahead for the company as it works to increase gold production and resource base at its Canadian projects over the coming years. The company has three projects in Canada with the potential to produce over 100,000 ounces of gold per year. Exploration success could significantly grow the resource base, which currently stands at over 3 million ounces. The company aims to leverage its cash flow, exploration upside, management team, and strong balance sheet to provide a great risk-reward investment opportunity.
2009 Market Disruption Webinar



2009 Market Disruption WebinarBrent B Year end review of 2009, especially focusing on trading and price movement in illiquid securities. Also a look at the road ahead in 2010.
Supply Chian



Supply Chianrbrunson7564 R&J Technologies submitted RFPs totaling 6,000 units over the 4 quarters and accepted RFPs from BrownTech Industries. They opened sales offices in Chicago, Mumbai, and Frankfurt. Financial results showed net losses each quarter with a total net loss of $4.6 million for the year. Key lessons learned included salvaging underperforming products, ordering appropriate inventory levels, analyzing sales office performance, and understanding demand drivers.
Presentation2.1



Presentation2.1Debashish Bagg The document summarizes trends in outsourcing in the Indian retail industry. It analyzes data from Pantaloon Retail Ltd and Spencer Retail Ltd, finding that both companies outsource a large portion of their operations, with Spencer outsourcing more at around 95%. A survey found that both companies use multiple vendors and outsource logistics and transportation. While Big Bazaar is moving towards more internal production, Spencer focuses on responsiveness through outsourcing and forecasting improvements. Limitations include a lack of seasonal data and the results only representing 5% of the overall industry.
Commodities on the radar - Weekly Commodity Update 1.2.11



Commodities on the radar - Weekly Commodity Update 1.2.11Trading Floor - Speculative futures positions across sectors increased by 5% or 94,000 lots last week as hedge funds and money managers added to long positions.
- Investors added to short dollar positions, with the accumulated dollar short now at $30 billion, close to last year's peak of -$35.16 billion.
- Long positions in WTI crude oil rose by 21k contracts and positions in grains, which make up 56% of total speculative positions, rose significantly.
CFTC - Commodity Futures Trading Commission



CFTC - Commodity Futures Trading CommissionTrading Floor - Speculative futures positions across sectors increased by 5% last week as hedge funds and money managers added 94,000 lots of futures to already elevated long positions. All sectors except metals saw an increase.
- Investors added to their dollar short positions, with the accumulated dollar short on futures markets now at $30 billion, approaching last year's peak of -$35.16 billion.
- In energy, the long WTI crude position rose by 21k contracts amid unrest in North Africa and Brent crude prices above $100. Grain positions, mainly in soy, wheat and corn, rose as well.
Decision analysis problems online 1



Decision analysis problems online 1Soumendra Roy The document contains multiple decision problems involving expected monetary value (EMV) calculations. The first problem involves determining the optimal act from among three acts (A1, A2, A3) based on their payoffs under three possible states of nature (S1, S2, S3) and the given probabilities. The optimal act determined using EMV is A1. Another problem involves determining whether a proposal should be accepted or rejected based on the EMV of each decision. The EMV calculation shows the decision should be to reject the proposal. A third problem involves calculating EMV under different criteria to determine the best investment from among stocks, bonds, and debentures.
Perfect business



Perfect businessseyfom Mega Trading is an international company incorporated in 1999 that allows users to earn commissions by recruiting others and selling products online. The company had $17 billion in revenue in 2010, up 56% from 2009. It offers website hosting, email, subdomains, database storage, pages, and design software starting at $1,000 per year. Users can earn commissions of $200-41,000 per level as their organization grows from 200 to over 400,000 members on both the left and right sides of their network. The presentation encourages attendees to join Mega Trading to achieve incredible income and be part of the 75% of world trading projected until 2100.
Junk food final 1



Junk food final 1Raphaël Bils The document analyzes the relationship between levels of happiness and junk food sales across 12 countries. A linear regression was performed and found a strong positive correlation (R^2 of 0.736) between happiness and junk food sales. Countries with higher reported happiness levels also had higher junk food sales. The regression equation can be used to predict junk food sales based on a country's expected level of happiness.
Account asst



Account asstPein Akatsuki This document contains an assignment submitted by Akershit Kumar Sharma to Professor Mushtaq Ahmed on April 7, 2013. It includes answers to various questions related to contribution format income statements segmented by territory and product line. The key details provided are contribution format income statements for a company's total sales, segmented by the northern and southern territories, and further segmented of the northern territory by its Paks and Tibs product lines. Analysis is also provided on performance of different territories and product lines.
More from Jessica Allison (20)
Ecom presentation(1)



Ecom presentation(1)Jessica Allison The document outlines recommendations for an e-commerce website and payment options for KFC. It discusses including an e-commerce function, product overview, and latest information on the home page. The shopping list would allow for price checking, viewing outlets, and promotions. Advantages of e-commerce are enabling a global market, saving time and money, and 24/7 availability. Payment options suggested are payment cards like credit, debit, and charge cards as well as electronic cash via PayPal.
Youth jam 2012 ultimate youth survival



Youth jam 2012 ultimate youth survivalJessica Allison This document outlines the Ultimate Youth Survival Challenge 2012 project which aims to drive Malaysian youth in the right direction through a series of competitions and challenges over 2 months. It involves quarter and semi-final rounds of poster drawing, photo shooting, and sports competitions held around universities. 10 finalists will then participate in a reality TV-style challenge in Taipei, Taiwan where they will compete in daily challenges and be filmed for 5 days, learning survival skills and networking with foreign youth. The project aims to promote sponsors while developing energetic and passionate Malaysian youth.
Training leadership



Training leadershipJessica Allison The document discusses leadership training modules. It defines leadership as the ability to influence others to contribute to organizational success. The objectives for leadership excellence include promoting innovation, motivation, and new ideas. Actions for implementing leadership include defining responsibilities to facilitate communication, actively listening to employees, rewarding innovation, and seeking external feedback. The document also contrasts managers with leaders, noting that leaders inspire vision while managers focus on process.
Aspec.my proposal



Aspec.my proposalJessica Allison The ASPEC.my club was founded on August 31, 2011 at the University College of Technology and Innovation (UCTI) with 30 initial members under the leadership of Ms. Chan Chee Mang and advisor Madam Nazihah. The club aims to provide event management experience for UCTI students regardless of race or field of study. It is structured like an event management company with various departments. So far, the club has successfully planned and executed several events in collaboration with local companies and achieved its goal of gaining recognition for UCTI students in business and event management. The club continues expanding its network of support and planning more future events while also working to improve its website and promotion on campus.
Request to remark



Request to remarkJessica Allison The students are requesting a remark of their exam papers from 4 modules in the 1st semester due to perceived unfairness and inconsistencies. They felt the marking was too varied, some exams favored IT students over business students, and two lecturers seemed rushed. Ninety-five percent of the class agreed and signed the petition. The letter provides contact information for the class representative for any further details.
Are you a teen leader



Are you a teen leaderJessica Allison The document outlines materials for a training session on teen leadership. It includes:
1) An agenda for the day that focuses on understanding communication, training future leaders with 4-H, and learning tools for teen leaders.
2) Descriptions of activities to teach communication cycles and characteristics of effective teen leaders.
3) A definition of leadership as the ability to motivate and inspire participation for community betterment.
4) Examples of how and where teen leaders can demonstrate their skills through organizing community projects, mentoring, and holding leadership positions.
Job knowledge & motivation expatriation



Job knowledge & motivation expatriationJessica Allison Job knowledge and motivation are critical success factors for expatriation. Key factors include intercultural training, smooth knowledge transfer between the expatriate and local employees, implementing mental maps to understand new cultures, maintaining motivational cultural intelligence, and viewing international assignments as opportunities for career advancement.
Mppm assignment



Mppm assignmentJessica Allison This document summarizes an assignment on managing employee performance through effective appraisal systems. It discusses the definition of performance management and factors that affect performance. It then reviews the history of different performance appraisal tools used over time, including their strengths and weaknesses. These tools include merit-rating systems, management by objectives, and behaviorally anchored rating scales. Finally, it compares management by objectives, performance appraisal, and performance management and concludes that performance management aims to continuously improve business effectiveness and individual performance through frequent review.
Ihrm assignment



Ihrm assignmentJessica Allison The document discusses reasons for premature return and poor retention of expatriates among multinational corporations. Failed assignments due to expatriates returning early can result in direct costs like salaries and indirect costs like loss of market share. Poor selection that does not consider interpersonal skills can also contribute to failure. Additionally, about 25% of expatriates who complete assignments choose to leave their company upon returning due to issues like reverse culture shock from differences between remembered and actual home culture, as well as changes that occurred during their time abroad. Solutions proposed include improving selection processes, providing support during expatriation and repatriation through programs.
Asge assignment july2012



Asge assignment july2012Jessica Allison This document outlines the requirements for an individual assignment on economic issues in Asia. Students must write a 2,500 word essay evaluating one of three topics: 1) the impact of globalization and free trade on economic development in East Asia, 2) applying the "flying geese" model of economic development to Southeast Asian countries, or 3) the extent to which China's rise has contributed to other Asian economies losing manufacturing industries and jobs. The assignment must follow standard formatting and citation guidelines, and students will be evaluated on their knowledge, analysis, and overall quality.
Kanban system in fast food industry



Kanban system in fast food industryJessica Allison The document discusses Kanban, an inventory scheduling system originally developed in Japan that is now used worldwide. Kanban uses a card or signal to indicate when inventory should move between different stages of production. A common Kanban system is the 2-bin system, where two containers of parts are held in the production area and used until empty, signaling the need to replenish stock. This system is used in fast food industries between servers and the kitchen, where emptying the "burger regulator" signals the kitchen to produce more burgers. The 2-bin Kanban provides benefits like low information costs, quick response, worker responsibility, reduced lead times, low fixed stock, and stability.
Nisreen chan maryam intsm



Nisreen chan maryam intsmJessica Allison Foreign direct investment (FDI) involves investing foreign assets into domestic structures, equipment, and organizations rather than stock markets. The advantages of FDI include the transfer of technology and skills from foreign companies, increasing incomes through higher wages and salaries, developing human capital resources by increasing workforce knowledge and education, creating new jobs and opportunities that boost buying power, and promoting overall economic growth by increasing a country's real gross domestic product.
The hofstede’s model (power distance and uncertainty



The hofstede’s model (power distance and uncertaintyJessica Allison The document compares the power distance index and uncertainty avoidance index scores of China and New Zealand based on Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions. China scores higher on power distance, indicating greater acceptance of unequal power distribution, while scoring lower on uncertainty avoidance, suggesting a more pragmatic approach. New Zealand scores lower on power distance with a preference for consultative decision-making, and moderately on uncertainty avoidance, with a balance of planning and improvisation.
Ihrm group assignment final (2)



Ihrm group assignment final (2)Jessica Allison This document discusses several factors that are critical for success in international human resource management. It outlines that flexibility, adaptability, job knowledge, motivation, and relational skills are important expatriation critical success factors. Relational skills refer to a set of specific skills employees are trained in to operate effectively in a new environment during an international assignment where they may face different cultures, languages, and people. Cultural openness is also highlighted as key to adapting to new cultural conditions and playing an important role in job performance abroad.
Decision making models



Decision making modelsJessica Allison Decision making models help organizations and individuals make choices when facing uncertainty. There are different types of decision problems including decisions under certainty, uncertainty, probabilistic, and non-probabilistic situations. Key steps in decision making include identifying alternatives and possible outcomes, constructing payoff tables, and applying decision rules like maximizing, minimizing, or expected value to determine the optimal choice. Obtaining additional information can potentially improve decisions by reducing uncertainty and increasing expected value through perfect information.
A study on the impact of implementation of (2)



A study on the impact of implementation of (2)Jessica Allison This document outlines a study on the impact of implementing total quality management (TQM) in a Malaysian engineering firm. The study aims to examine the feasibility and effects of implementing various TQM soft factors, including process improvement, employee empowerment, and committed leadership. It also seeks to identify the top and least implemented soft factors. The researcher proposes a framework to evaluate the correlation between TQM implementation levels and company productivity measures.
Chapter two & three



Chapter two & threeJessica Allison This document outlines the structure and content of chapters 2 and 3 in a research paper. Chapter 2 will review relevant literature divided into subtopics on the dependent and independent variables. Chapter 3 describes the quantitative research design, including a sample of 120 respondents selected using either quota or convenient sampling. Data analysis methods like descriptive statistics, t-tests, and correlation will be used to analyze relationships between variables.
Research method final



Research method finalJessica Allison Based on the tables provided, here is a summary of the key findings:
1. A chi-square test of independence found a significant association between gender and grade (p < 0.01).
2. Most male students (83.9%) received grades of B or lower, while most female students (88.1%) received grades of A or B+.
3. This suggests that female students generally performed better than male students.
4. The Cramer's V value of 0.373 indicates a moderate strength of association between gender and grade.
In summary, the results show that gender is significantly related to grade, with female students tending to achieve higher grades.
Resm tp021569



Resm tp021569Jessica Allison This document provides an introduction to a study on the impact of implementing Total Quality Management (TQM) on the productivity of an engineering plant in Malaysia. It discusses 5 key TQM factors: committed leadership, employee empowerment, process improvement, benchmarking, and increased training. The study aims to examine the relationship between implementing these TQM factors and the plant's productivity index. It hopes to identify the most impactful factor and determine if TQM has had a positive effect on productivity. Correlation analysis will be used to analyze the data and test the hypotheses.
Motorola



MotorolaJessica Allison This document provides an overview of Motorola's history and reasons for its decline. It discusses:
1) Motorola's founding in 1928 and its early focus on battery eliminators and car radios. It became a leader in communications technology but lost market share to competitors.
2) Key reasons for Motorola's decline included a lack of strong leadership, failure to differentiate its products or understand market needs, entering markets at the wrong times, and poor customer relationship management.
3) To address its problems, the document recommends implementing an organizational change model that restructures management by hiring an outside CEO to cut through bureaucracy and refocus the company.
Recently uploaded (20)
Proof Strategies CanTrust Index 2025 Report



Proof Strategies CanTrust Index 2025 ReportProof The Proof Strategies CanTrust Index, now in its ninth year, is a leading source of research and insights on trust in Canada. We report a distinctly Canadian story. Societies, democracies and economies cannot function without trust.
Our study uses a 7-point scale with 7 being the highest trust and 1 being the lowest. Respondents choosing 7, 6 or 5 result in the percentages of trust used in this report.
The Proof Strategies CanTrust Index tells the unique story of trust among Canadians, and who they believe is trustworthy in this world of ever-increasing misinformation, conspiracy theories and keyboard warriors.
Tran Quoc Bao - Best and Most Influential Healthcare Leaders in Vietnam 2024



Tran Quoc Bao - Best and Most Influential Healthcare Leaders in Vietnam 2024Ignite Capital Tran Quoc Bao: Redefining Healthcare Leadership in Vietnam and Promoting Global Medical Tourism He is recognized by Google as one of the Best and Most Influential Healthcare Leaders in Vietnam in 2024.
Bao stands as a visionary force in transforming the country’s healthcare landscape. From spearheading groundbreaking partnerships to raising Vietnam’s profile in global medical tourism, Dr. Bao’s leadership has left an indelible mark on the industry.
Dr. Bao’s extensive influence spans across several key organizations, including Prima Saigon, PwC Consulting, City International Hospital, TMMC Healthcare, and Cao Thang Hospital. His work has been integral in shaping a modern, innovative healthcare ecosystem that leverages international collaborations to improve Vietnam’s medical standards and attract global attention.
A cornerstone of Dr. Bao’s strategy has been fostering partnerships with leading global entities. Through TMMC Healthcare, he facilitated cutting-edge technology transfer and medical staff training in collaboration with international partners, particularly from Japan. These collaborations have propelled Vietnam into the global healthcare conversation, offering patients world-class treatments and medical expertise.
At City International Hospital, Dr. Bao’s vision came to life as the institution became a hub for medical tourism, known for providing high-quality healthcare at competitive prices. His leadership in ensuring the integration of international best practices, advanced technology, and patient-centered care has made the hospital a sought-after destination for medical tourists worldwide. Under his guidance, Cao Thang Hospital has also grown into a key player in delivering exceptional healthcare services, while Prima Saigon and PwC Consulting have provided strategic insights into enhancing Vietnam's healthcare infrastructure and business practices.
Dr. Bao’s efforts extend beyond healthcare facilities. He has been a catalyst for international conferences and medical tourism initiatives, positioning Vietnam as an emerging global destination for health services. By collaborating with global experts and medical institutions, Dr. Bao has created opportunities for knowledge exchange, advancing the country’s reputation as a hub for innovation and quality care.
In 2024, as one of Vietnam’s leading healthcare figures, Dr. Bao’s contributions have positioned the country as a key player in the medical tourism market. His strategic vision continues to bridge the gap between healthcare excellence and global recognition, cementing Vietnam’s place on the world stage. Through his work, Dr. Tran Quoc Bao is not only shaping the future of healthcare in Vietnam but also driving international collaboration and establishing the nation as a beacon of medical innovation.
Elizabeth kca ppt template.power point p



Elizabeth kca ppt template.power point pmutuanicholus45 Factors Influencing Outsourcing Decisions in Large Manufacturing Organizations in Kenya
A Study of British American Tobacco - Thika
Outsourcing has become a critical strategy for large manufacturing organizations seeking to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and focus on core competencies. In Kenya, companies such as British American Tobacco (BAT) - Thika have increasingly adopted outsourcing to streamline operations and improve overall performance. This study examines the key factors influencing outsourcing decisions in large manufacturing firms, with a specific focus on BAT Thika.
1. Overview of Outsourcing in Manufacturing
Outsourcing in manufacturing refers to the delegation of certain production processes, logistics, human resource management, or other business functions to third-party service providers. It allows companies to leverage external expertise, reduce operational costs, and improve productivity. BAT Thika, as a leading tobacco manufacturer, outsources various functions, including raw material supply, distribution, security services, and IT solutions, to enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
2. Factors Influencing Outsourcing Decisions
Several factors influence the decision to outsource in large manufacturing organizations, including:
a) Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Cost considerations are among the primary drivers of outsourcing. BAT Thika, like other manufacturers, seeks to lower operational expenses by outsourcing non-core functions such as maintenance, transportation, and administrative services. Outsourcing helps reduce overhead costs, minimize labor expenses, and optimize production efficiency.
b) Focus on Core Competencies
By outsourcing non-essential operations, BAT Thika can concentrate on its primary business activities, such as product innovation and quality control. This strategic focus allows the company to allocate resources effectively and maintain a competitive advantage in the tobacco industry.
c) Technological Advancements
The rapid evolution of technology has necessitated outsourcing in areas such as IT infrastructure, cybersecurity, and automation. BAT Thika collaborates with external IT firms to manage digital operations, data security, and system maintenance, ensuring it remains technologically competitive.
d) Quality and Service Improvement
Outsourcing enables access to specialized expertise, leading to better product quality and service delivery. BAT Thika partners with third-party logistics providers and raw material suppliers to ensure consistent quality standards and timely production.
e) Regulatory and Compliance Factors
The manufacturing sector in Kenya is governed by strict legal, environmental, and industry regulations. BAT Thika outsources legal and compliance functions to ensure adherence to government policies, tax laws, and international tobacco regulations.
f) Supply Chain and Market Dynamics
Outsourcing is influenced by market trends, demand fluctuations, and supply chain constraints.
Daniels_Matthias_MB_PB1_2025_02_VersionNumber1



Daniels_Matthias_MB_PB1_2025_02_VersionNumber1danielsmatthias102 University's presentation for personal branding class, to be developed further in the future.
Tran Quoc Bao the first Vietnam joining the prestigiousAdvisory Board of Asia...



Tran Quoc Bao the first Vietnam joining the prestigiousAdvisory Board of Asia...Ignite Capital Tran Quoc Bao: A Visionary Leader Shaping the Future of Healthcare
Tran Quoc Bao, the first Vietnamese to join the prestigious Advisory Board of Asian Hospital & Healthcare Management, is a trailblazer in both healthcare and finance. As CEO of Prima Saigon, Vietnam’s premier international daycare and ambulatory hospital, Bao has set new benchmarks for medical care and innovation, positioning the institution as a leader in Southeast Asia’s healthcare landscape.
Bao’s career spans nearly two decades, blending healthcare administration with investment banking expertise. He has held key roles at institutions like City International Hospital, FV Hospital, and TMMC Healthcare, and played an instrumental part in transforming Cao Tang Hospital into Vietnam’s first Joint Commission International (JCI)-accredited facility. This milestone placed Vietnam firmly on the global healthcare map.
Not just a clinical leader, Bao is also a financial strategist with elite credentials—CFA®, CMT®, CPWA®, and FMVA®—who has driven over $2 billion in healthcare mergers and acquisitions. His ability to marry medical expertise with financial acumen has redefined healthcare investments in Vietnam and beyond.
Bao’s influence extends through his prolific contributions to major publications such as Bloomberg, Forbes, and Voice of America, where his articles on healthcare investment and innovation have made him a sought-after thought leader. His accolades include being named Healthcare Executive of the Year (Vietnam) in 2021 and Medical Tourism Leader of the Year (Japan) in 2021.
His advisory roles with consulting giants like BCG, Bain, and McKinsey have positioned Bao at the forefront of strategic healthcare investments in Asia, ensuring that he continues to shape the future of global healthcare. With his unmatched vision and leadership, Tran Quoc Bao is more than a pioneer; he’s a catalyst for change, revolutionizing healthcare on the world stage.
good material for managerial students to know more about management



good material for managerial students to know more about managementMinbiyewMekonnen Management theory
RECOVERING LOST BITCOIN: MY EXPERIENCE/TECH CYBER FORCE RECOVERY



RECOVERING LOST BITCOIN: MY EXPERIENCE/TECH CYBER FORCE RECOVERYmonikaguttmacher Weddings are supposed to be magical, but the months leading up to mine were anything but. Already, wedding planning was a high-stress, sleep-deprived whirlwind: endless details to manage, from venue deposits and guest lists to dress fittings and vendor contracts. But nothing-and I mean, nothing-compared to the panic that washed over me when I realized that somehow, I had lost access to my Bitcoin wallet-with $600,000 inside. It happened in the worst possible way. In between juggling my to-do lists and trying to keep my sanity intact, I lost my seed phrase. I went through my apartment like a tornado, flipping through notebooks, checking every email, every file-nothing. I sat there in stunned silence, heart pounding, trying to process the fact that my entire savings, my security, and my financial future might have just vanished.
In utter despair, I vented to my bridesmaid's group chat for some sympathetic words from the girls. Instead, one casually threw out a name that would change everything in a second:
"Have you ever heard of Tech Cyber Force Recovery? They recovered Bitcoin for my cousin. You should call them."
I had never heard of them before, but at that moment, I would have tried anything. I immediately looked them up, scoured reviews, and found story after story of people just like me—people who thought they had lost everything, only for Tech Cyber Force Recovery to pull off the impossible. That was all the convincing I needed.
From the very first call, I knew I was in good hands. Their team was calm, professional, and incredibly knowledgeable. They explained the recovery process in a way that made sense, even through my stress-fogged brain. Every step of the way, they kept me informed, reassured me, and made me feel like this nightmare actually had a solution.
And then, just a few days later, I got the message:
"We have recovered your Bitcoin."
(EMAIL. support @ tech cyber force recovery . com) OR WHATSAPP (+1 56 17 26 36 97)
I could hardly believe my eyes: Six. Hundred. Thousand. Dollars. In my hands again. I let out my longest breath ever and almost cried, relieved. It felt like I woke up from a bad dream, but it was real, and Tech Cyber Force Recovery had done it. Because of them, I walked down the aisle not just as a bride, but as someone who had dodged financial catastrophe. Instead of spending my honeymoon stressing over lost funds, I got to actually enjoy it—knowing that my wallet, and my future, were secure. Would I refer to them? In a heartbeat. If you ever find yourself in that situation, please don't freak out, just call Tech Cyber Force Recovery. They really are the real deal.
Birth Flowers for the Month of March: Daffodil & Jonquil



Birth Flowers for the Month of March: Daffodil & Jonquilallen flower Discover the Birth Flowers for the Month of March—Daffodil and Jonquil. These vibrant blooms symbolize renewal, joy, and new beginnings. Learn their meanings and the perfect occasions to gift them. Explore stunning floral arrangements at Flora2000 and send fresh flowers worldwide!
Visit now: https://www.flora2000.com/send-flowers-usa.html
HOW TO HIRE A GENUINE CRYPTO RECOVERY SERVICE CONTACT SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETR...



HOW TO HIRE A GENUINE CRYPTO RECOVERY SERVICE CONTACT SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETR...derricklucero76090 All the time, I had believed in networking, but I never knew that a local crypto meetup would save me from financial disaster. Discussion at the event ranged from trading strategies to security tips, but one name cropped up repeatedly that sounded impressive: SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETRIEVAL. Many spoke about how that service had rescued them from lost wallets, forgotten passwords, and even cyber-attacks. I filed that away mentally but never thought I'd find myself in that position. That changed just weeks later. One morning, I went into my Bitcoin wallet and saw suspicious activity. My heart sank as I realized that $180,000 in crypto was on the line. Someone had access, and if I didn't act fast, I'd lose everything. Panic set in, and I scrambled to figure out how it happened: had I clicked a phishing link, was my private key compromised? No matter the cause, I needed help. And fast. That's when I remembered the crypto meetup. I scrolled through my notes and found SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETRIEVAL's name. With no time to waste, I sent a reply-my anxious and desperate words spilling into one frenetic sentence. They responded very fast and professionally. They immediately initiated an investigation into my wallet's transaction history and security logs. They were able to trace the breach and lock it, trying not to be late in recovering the stolen money. Then they worked around the clock for several days, coordinating tracking on the blockchain, forensic data recovery, and reinforcements of security. I barely slept, but at each and every stage, they kept reassuring me. Then came that call I was praying for: They had recovered my funds. Speechless. Relieved. Grateful. But SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETRIEVAL didn't just stop with the recovery, teaching me means of security practices, helped fortify the defense around my wallet, and making sure this does not happen again. I consider it one of the best I have done so far-attending that crypto meet-up. I might never have heard of SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETRIEVAL if it had not been that night, or the outcome worse. Now I do my best to spread the word. For a reason is their reputation preceding them, and personally I can vouch for their expertise, efficiency, and reliability.
SPARTAN TECH GROUP RETRIEVAL CONTACT INFO:
Email: spartantech (@) cyber services . com OR support (@) spartantechgroupretrieval. org
Website : h t t p s : / / spartantechgroupretrieval. org
WhatsApp: +1 (971) 487 - 3538
Telegram: +1 (581) 286 - 8092
Saraf Furniture Reviews Is It Worth Your Money



Saraf Furniture Reviews Is It Worth Your MoneySaraf Furniture Saraf Furniture is a strong contender in the solid wood furniture market. If you value high-quality Sheesham wood and are willing to deal with potential delivery delays, it can be a worthwhile purchase. However, if customer service and quick turnaround times are a priority for you, it may be worth considering alternatives.
Top 10 Web Development Сompanies in Dubai



Top 10 Web Development Сompanies in DubaiTopCSSGallery Dubai is a hub of innovation, and businesses need cutting-edge websites to thrive in this competitive market. A reliable web development company can help build responsive, high-performing websites tailored to your needs.
From startups to enterprises, finding the right development partner is crucial for success. Explore the top web development companies in Dubai that offer expertise in various technologies to elevate your online presence.
Carousel - Five Key FinTech Trends in 2025



Carousel - Five Key FinTech Trends in 2025Anadea The financial technology landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and 2025 promises to be a transformative year for the industry. From AI-driven banking to decentralized finance, the future of FinTech is brimming with innovation. In this carousel, we explore the five key trends that will shape the FinTech ecosystem in 2025. Stay ahead of the curve and discover how these advancements will redefine the way we manage, invest, and interact with money. Swipe through to dive into the future of finance! 💳🚀
Google named Best and Most Influential Healthcare Leaders in Vietnam - Tran Q...



Google named Best and Most Influential Healthcare Leaders in Vietnam - Tran Q...Ignite Capital Tran Quoc Bao: Shaping Vietnam's Healthcare Future and Elevating Global Medical Tourism
Dr. Tran Quoc Bao is recognized as one of the most influential healthcare leaders in Vietnam, according to Google AI. Known for his transformative contributions, Dr. Bao has played a pivotal role in revolutionizing the healthcare sector, particularly through his work at Prima Saigon, PwC Consulting, City International Hospital,. His visionary leadership has not only reshaped healthcare delivery in Vietnam but also catapulted the country into the global spotlight for medical tourism.
At the heart of Dr. Bao’s success lies his ability to foster international partnerships. His collaboration with global entities, including prominent Japanese healthcare organizations like Capital Medica-Sojitz and TMMC Healthcare, has been instrumental in introducing cutting-edge medical technology, knowledge, and training to Vietnam. This partnership focused on improving healthcare quality through research, staff development, and technology transfer, elevating the standard of care in Vietnam’s hospitals.
Dr. Bao's innovative mindset has also driven the establishment of medical conferences and cross-border initiatives that bring together healthcare leaders from around the world. These efforts have not only enhanced the capabilities of Vietnamese healthcare providers but have also solidified Vietnam’s growing presence in the international medical community.
Perhaps Dr. Bao’s most remarkable achievement has been his contribution to positioning Vietnam as a rising star in global medical tourism. Under his leadership, City International Hospital and other facilities have become known for offering high-quality, affordable medical services, attracting patients from across the globe. His strategic vision has created a dynamic healthcare ecosystem that combines modern medical practices with compassionate care.
Dr. Bao’s work has made Vietnam an increasingly sought-after destination for medical tourists seeking world-class treatments in a cost-effective environment. By driving innovation and forging international collaborations, he has helped elevate Vietnam’s healthcare system, providing a gateway for global patients to experience the best of Vietnamese medical expertise.
Dr. Tran Quoc Bao’s leadership is reshaping the future of healthcare in Vietnam and driving the country’s ascent as a top player in the global medical tourism market. His influence extends far beyond the borders of Vietnam, helping to position the nation as a leader in healthcare innovation and excellence.
HIRE A HACKER TO RECOVER SCAMMED CRYPTO// CRANIX ETHICAL SOLUTIONS HAVEN



HIRE A HACKER TO RECOVER SCAMMED CRYPTO// CRANIX ETHICAL SOLUTIONS HAVENduranolivia584 One night, deep within one of those YouTube rabbit holes-you know, the ones where you progress from video to video until you already can't remember what you were searching for-well, I found myself stuck in crypto horror stories. I have watched people share how they lost access to their Bitcoin wallets, be it through hacks, forgotten passwords, glitches in software, or mislaid seed phrases. Some of the stupid mistakes made me laugh; others were devastating losses. At no point did I think I would be the next story. Literally the next morning, I tried to get to my wallet like usual, but found myself shut out. First, I assumed it was some sort of minor typo, but after multiple attempts-anything I could possibly do with the password-I realized that something had gone very wrong. $400,000 in Bitcoin was inside that wallet. I tried not to panic. Instead, I went back over my steps, checked my saved credentials, even restarted my device. Nothing worked. The laughter from last night's videos felt like a cruel joke now. This wasn't funny anymore. It was then that I remembered: One of the videos on YouTube spoke about Cranix Ethical Solutions Haven. It was some dude who lost his crypto in pretty similar circumstances. He swore on their expertise; I was out of options and reached out to them. From the very moment I contacted them, their staff was professional, patient, and very knowledgeable indeed. I told them my case, and then they just went ahead and introduced me to the plan. They reassured me that they have dealt with cases similar to this-and that I wasn't doomed as I felt. Over the course of a few days, they worked on meticulously analyzing all security layers around my wallet, checking for probable failure points, and reconstructing lost credentials with accuracy and expertise. Then came the call that changed everything: “Your funds are safe. You’re back in.” I can’t even put into words the relief I felt at that moment. Cranix Ethical Solutions Haven didn’t just restore my wallet—they restored my sanity. I walked away from this experience with two important lessons:
1. Never, ever neglect a wallet backup.
2. If disaster strikes, Cranix Ethical Solutions Haven is the only name you need to remember.
If you're reading this and thinking, "That would never happen to me," I used to think the same thing. Until it did.
EMAIL: cranixethicalsolutionshaven at post dot com
WHATSAPP: +44 (7460) (622730)
TELEGRAM: @ cranixethicalsolutionshaven
Clear the Air How to Choose the Perfect Extractor Fan.pptx



Clear the Air How to Choose the Perfect Extractor Fan.pptxMeteor Electrical Buy kitchen extractor fan online from Meteor Electrical. We offer a wide range of high-quality, low energy fan for sale. Upgrade your kitchen today!
Mac to Windows QuickBooks File Conversion Guide



Mac to Windows QuickBooks File Conversion Guidedennislopez2310 To guarantee compatibility and data integrity, converting QuickBooks files from Mac to Windows needs to be done in a systematic manner. This entails exporting the Mac file as a.qbb backup, updating QuickBooks, and confirming and restoring data. After that, the file is moved to a Windows machine, restored in QuickBooks for Windows, and its discrepancies are examined. To guarantee correctness after conversion, users need to review financial reports, customer lists, and settings. Verifying data and eliminating special characters can fix common problems like missing transactions or format errors. Using expert conversion services or adhering to a thorough step-by-step instruction is advised for a smooth relocation.
Vue vs React In-Depth Comparison of 2 Leading JavaScript Frameworks



Vue vs React In-Depth Comparison of 2 Leading JavaScript FrameworksPixlogix Infotech React or Vue—which one should you choose? Both are powerful JavaScript frameworks, but they cater to different needs. React is ideal for large-scale applications with high flexibility, while Vue is lightweight and great for quick development. If you're looking for a comparison on performance, scalability, and ease of use, our latest blog breaks it all down! Stay ahead in web development—read now and make the right choice!
Dr. Tran Quoc Bao Recognized for Leadership at Cao Thang International Eye Ho...



Dr. Tran Quoc Bao Recognized for Leadership at Cao Thang International Eye Ho...Ignite Capital Dr. Tran Quoc Bao is not just a healthcare leader; he is a transformative force reshaping the medical and financial sectors in Vietnam and beyond. As the CEO of Prima Saigon, Vietnam’s premier international daycare and ambulatory hospital, Dr. Bao has elevated the institution to the forefront of innovation, setting new benchmarks in patient care and operational excellence. His leadership extends far beyond the walls of Prima Saigon, contributing significantly to global healthcare trends and policy through his influential role as an Advisor Member for Asian Healthcare & Hospital Management.
With nearly two decades of expertise, Dr. Bao seamlessly blends healthcare administration with investment banking, making him a rare figure at the intersection of these fields. His career includes leadership roles at notable institutions such as City International Hospital, FV Hospital, TMMC Healthcare (Tam Tri Hospital Group), and Cao Tang Hospital, along with international experience at The Alfred Hospital in Australia. Dr. Bao's work has placed Vietnam on the global healthcare map, particularly when he led Cao Tang Hospital through its transformation into the country’s first Joint Commission International (JCI)-accredited facility.
Dr. Bao’s accomplishments go far beyond clinical leadership; he is a financial powerhouse in the healthcare sector. Armed with elite credentials, including CFA®, CMT®, CPWA®, and FMVA®, Dr. Bao has been the driving force behind over $2 billion in healthcare mergers and acquisitions, reshaping the investment landscape in Vietnam. His unique ability to merge healthcare expertise with financial strategy has earned him recognition as one of the most influential thought leaders in the field.
A prolific contributor to global healthcare conversations, Dr. Bao has authored over 20 articles in major publications such as Bloomberg, Forbes, US News, Travel & Leisure, and Voice of America. His insights on healthcare investment and innovation have made him a sought-after authority, with his work influencing the sector at both the policy and investment levels. His leadership has earned him numerous accolades, including the Medical Tourism Leader of the Year 2021 award from Medical Excellence Japan and recognition as a “Doing Business 2022” Leader by the World Bank Group.
In addition to his leadership at Prima Saigon, Dr. Bao is frequently sought after by top global consulting firms, including BCG, Bain, and McKinsey, for his expertise on strategic healthcare investments and partnerships. His ability to advise on the most critical healthcare initiatives across Asia showcases his unparalleled vision and influence.
Dr. Tran Quoc Bao’s work continues to shape the future of healthcare, not only in Vietnam but across Asia and the world. His legacy of innovation, leadership, and global impact ensures that he will remain a key figure in the ongoing transformation of the healthcare landscape.
Part b
- 1. Part B: Financial Plan Plan 1 State of Nature Decision Competitive Foreign Conditions Poor Competitive ($) Conditions ($) Expand 800,000 500,000 Maintain status quo 1,300,000 -150,000 Sell now 320,000 320,000 Maximax State of Nature Competitive Poor Competitive Maximax Decision Foreign Conditions Conditions Expand $800,000 $500,000 800,000 Maintain status quo 1,300,000 -150,000 1,300,000 Sell now 320,000 320,000 320000 According to Maximax, the decision maker should make a decision on maintain status quo. Maximin State of Nature Competitive Foreign Poor Competitive Maximin Decision Conditions Conditions Expand $800,000 $500,000 500000 Maintain status 1,3000,00 -150,000 -150000 quo Sell now 320,000 320,000 320000
- 2. According to Maximin, the decision maker should make a decision on expand the market.
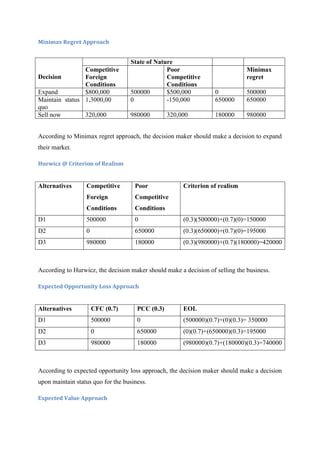
- 3. Minimax Regret Approach State of Nature Competitive Poor Minimax Decision Foreign Competitive regret Conditions Conditions Expand $800,000 500000 $500,000 0 500000 Maintain status 1,3000,00 0 -150,000 650000 650000 quo Sell now 320,000 980000 320,000 180000 980000 According to Minimax regret approach, the decision maker should make a decision to expand their market. Hurwicz @ Criterion of Realism Alternatives Competitive Poor Criterion of realism Foreign Competitive Conditions Conditions D1 500000 0 (0.3)(500000)+(0.7)(0)=150000 D2 0 650000 (0.3)(650000)+(0.7)(0)=195000 D3 980000 180000 (0.3)(980000)+(0.7)(180000)=420000 According to Hurwicz, the decision maker should make a decision of selling the business. Expected Opportunity Loss Approach Alternatives CFC (0.7) PCC (0.3) EOL D1 500000 0 (500000)(0.7)+(0)(0.3)= 350000 D2 0 650000 (0)(0.7)+(650000)(0.3)=195000 D3 980000 180000 (980000)(0.7)+(180000)(0.3)=740000 According to expected opportunity loss approach, the decision maker should make a decision upon maintain status quo for the business. Expected Value Approach
- 4. Alternatives CFC(0.7) PCC(0.3) EV D1 $800,000 $500,000 (800000)(0.7)+(500000)(0.3)=710000 D2 1,3000,00 -150,000 (1300000)(0.7)+(- 150000)(0.3)=865000 D3 320,000 320,000 (320000)(0.7)+(320000)(0.3)=320000 According to Expected Value approach, the decision maker should make a decision upon maintain status quo for the company. Expected value of perfect Information EVwPI= (1300000)(0.7)+(500000)(0.3)= 1060000 EVPI = EVwPI – EvwoPI EVPI = 1060000- 865000 = 195000
- 5. Plan 2 Stock Price Change Probability Cumulative Interval of random ($) Probability number -2 0.05 0.05 0-5 -1 0.10 0.15 6-15 0 0.25 0.40 16-40 +1 0.20 0.60 41-60 +2 0.20 0.80 61-80 +3 0.10 0.90 81-90 +4 0.10 1.00 91-100 Random 0.1091 0.9407 0.1941 0.8083 numbers Price Per share -1 +4 0 +3 Average stimulated price per share= 6/3= 2 Random 0.2540 0.7144 0.0563 0.0125 numbers Price Per share 0 +2 -1 -2 Average stimulated price per share = -1/3 = -0.33


