Patients satisfaction on clinical laboratory services at nekemte
- 1. Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557 (Online) Vol.30, 2014 Patients Satisfaction on Clinical Laboratory Services at Nekemte Referral Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia Geletta Tadele1*, Eyasu Ejeta, 1Mikias Desalegn1, Shibabew Abere1, Keneni Elias1 1Department of Medical Laboratory Science, College of Medical and Health Sciences, Wollega University, Post Box No: 395, Nekemte, Ethiopia * Corresponding author: Email:geletta98@yahoo.com Abstract Background: Satisfaction is the extent to which the clients feel their needs are fulfilled and their expectations are being met by the service provider. Furthermore, understanding the level of client satisfaction and identifying the factors hindering client satisfaction are the most important base lines to improve the quality of service being delivered. Objective: to assess the extent to which patients were satisfied on clinical laboratory services provided at Nekemte Referral Hospital (NRH) . Method: A Hospital based cross sectional study was conducted on randomly selected 422 Patients requested for clinical laboratory service at NRH from March to April 2014. Data were collected using structured, pretested, interviewer-administered questionnaire. Data analysis was performed using SPSS for windows version 20. Result: Among the 422 patients, 255 (60.4%) were satisfied, 75 (17.8%) were neutral and 92(21.8%) were dissatisfied with the laboratory services given in Nekemte Referral Hospital. There was no significant association between socio-demographic characteristics and level of satisfaction of patients (P- value > 0.05).In Likert Scale, the overall mean rate of satisfaction of patients with laboratory services in Nekemte referral hospital was 3.65 out of the 5 points. The lowest mean rating of satisfaction were given for Cleanness of latrine and location of the laboratory in the hospital with mean rating of 2.15 and 2.17 respectively. Conclusion: The overall degree of patient customers’ satisfaction with the laboratory services at Nekemte Referral Hospital was 60.4% .patients were dissatisfied in cleanness and location of latrines in the hospital. Therefore; hospital administration and the laboratory department of Nekemte referral Hospital should strive more to enhance patients’ satisfaction, particularly in sanitation and location of the latrine in the hospital. Key Words: patients’ Satisfaction, Clinical Laboratory Services, Nekemte Referral Hospital Background Client satisfaction reflects provider's ability to successfully deliver care that meets clients' expectations and needs (1, 2). A number of factors have been shown to influence clients' satisfaction with health care services including clients' socio-demographic characters, physical health status, clients' personal understanding and expectations from various health care services (3, 4). The general physical appearance of the hospital as well as the general environment of the premises also influences the overall Satisfaction of the client (5). In every service providing organization what matters is whether the customer is satisfied or not. Now a day, the most important issue in health care service and other service providing organization is the level of satisfaction of the customers with available service(6). Patients’ satisfaction on service given in hospitals was assed in Nigeria and Tanzania (5, 7). In Ethiopia, some studies have done on clients’ satisfaction in different hospitals (8, 9, 10, 11) Customer service is an integral part of a quality management system. Most clinical laboratories in the United States are required to assess their customers’ Satisfaction in order to maintain their accreditations (12). Some studies conducted on patients and clinical services providers at selected government hospitals in eastern Ethiopia were revealed that most of patients (87.6%) and clinical services providers (80%) were satisfied with the laboratory services (13). The overall satisfaction rate for ART monitoring laboratory services in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia was (85.5%)(14). Patient satisfaction with laboratory services in selected government Hospitals, Eastern Ethiopia, revealed that the mean rating values ranged from 2.93 (±1.67) to 4.78 (±0.6) out of a possible 5 Likert scale( 15). The Likert scale results of patient satisfaction of the laboratory Services in selected governmental hospitals, Sidamma zone, southern Ethiopia indicated that the mean rating values ranged from 3.07 (±0.96) to 4.25 (±0.56) (16). The problems related to clinical laboratory are aggravated particularly at peripheral level due to lack of properly designed laboratory rooms, shortage of short term and long term training for laboratory staff, lack of water and electricity, shortage of equipment and supplies, absence of effective maintenance and spare parts and lack of follow-up and supervision of laboratory staff are said to be among major clinical laboratory problems (17, 18). 25
- 2. Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557 (Online) Vol.30, 2014 Patients’ were satisfied with waiting time to get blood drawing service, availability of ordered laboratory tests and waiting time to get laboratory result ( 14).The lowest rate of patient satisfaction were reported on cleanness of latrine to collect specimens ( 13). A study done in Tanzania showed that the main compliant reported on the laboratory service were: long waiting time for result notification, privacy and timely instructions. In addition to this level of privacy in the consultation room was described as unsatisfactory by 24.1% of clients (19). Stepwise Laboratory (Quality) Improvement process is required in developing countries to strengthen for accreditation in laboratory service (20). Thus, this study assed level of patient satisfaction on clinical laboratory service to give quality service for clients and enable clinical laboratories of Nekemte referral hospital to fill the gap to maximize service given to patient customers and the strive toward accreditation. 26 OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY General Objective To assess patients satisfaction on clinical laboratory service provided by Nekemte Referral Hospital. Specific Objectives To assess patient customers satisfaction level on clinical laboratory service provided by Nekemte Referral Hospital. To assess association between patients satisfaction with clinical laboratory service at Nekemte Referral Hospital and sociodemographic characteristics of patients. MATERIALS AND METHODES Study area and period The study was conducted in Nekemte Referral Hospital from April-May 2014. Nekemte Referral Hospital is the major health service providing governmental institute in the Nekemte town which is found at a distance of 331 kilometers from Addis Ababa. Nekemte Referral Hospital is the only referral hospital in East wollega zone and gives different health service for more than 1,756,952 populations. Sample size determination and sampling Institution based cross sectional study was conducted on patients whose age was 18 years and requested for diagnosis of parasites at clinical laboratory of Nekemte Referral Hospital. Sample size was calculated using a formula for estimating single population proportion for cross-sectional studies that is corrected for finite population. Taking the assumptions, proportion of customers’ satisfaction 51.5% (11) at 95% confidence level and with margin of error of 5 %, and 10% non-respondent rate, sample size of 422 patients were included in the study. The study participants were distributed to the units of the laboratories based on the average patient flow per month. The study participants selected from source population using systemic random sampling. Data collection methods Data were collected by using structured, pre-tested and interviewer-administered questionnaire initially prepared in English and then translated to local language Amharic and Affan Oromo. The Amharic and Affan Oromo versions of the questionnaire were used for data collection. Data were collected by 3 medical laboratory technologists. Besides their socio-demographic characteristics study participants were asked to rate each aspect of their laboratory service on a five-point scales (very dissatisfied, dissatisfied, Neutral, Satisfied, and very Satisfied). 4.10. Data Analysis Data were checked daily for completeness, entered in to computer and analyzed using SPSS for window version 20. A 5 point Likert scale rating of very dissatisfied (1-point), dissatisfied (2-points), neutral (3-points), satisfied (4-points) and very satisfied (5point) were used. To calculate level of patients satisfaction on different laboratory services; Very dissatisfied and dissatisfied were considered as dissatisfied, satisfied and very satisfied were considered as satisfied. Patients with neutral rating responses were excluded. The percentage satisfaction or dissatisfaction was calculated by dividing the number of satisfied or dissatisfied responses by the total number of respondents excluding neutral response ratings, respectively. The overall rate of satisfaction by Likert scale was calculated as (No. of very satisfied rating x5) + (No. of satisfied rating x4) + (No. of Neutral rating x3) + (No. of Dissatisfied rating x2) + ( No. of very dissatisfied rating x1) divided by the total number of ratings (1–5) for the specific laboratory service. Association between sociodemographic characteristics of patients and level of satisfaction on laboratory services was determined by using Chi-square test. P-value 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
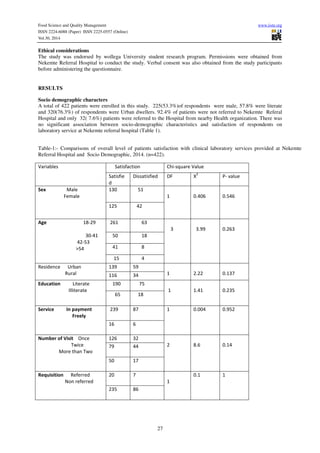
- 3. Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557 (Online) Vol.30, 2014 Ethical considerations The study was endorsed by wollega University student research program. Permissions were obtained from Nekemte Referral Hospital to conduct the study. Verbal consent was also obtained from the study participants before administering the questionnaire. 116 34 0.137 79 44 0.14 27 RESULTS Socio demographic characters A total of 422 patients were enrolled in this study. 225(53.3%)of respondents were male, 57.8% were literate and 320(76.3%) of respondents were Urban dwellers. 92.4% of patients were not referred to Nekemte Referal Hospital and only 32( 7.6%) patients were referred to the Hospital from nearby Health organization. There was no significant association between socio-demographic characteristics and satisfaction of respondents on laboratory service at Nekemte referral hospital (Table 1). Table-1:- Comparisons of overall level of patients satisfaction with clinical laboratory services provided at Nekemte Referral Hospital and Socio Demographic, 2014. (n=422). Variables Satisfaction Chi-square Value Satisfie d Dissatisfied DF X2 P- value Sex Male Female 130 51 1 0.406 0.546 125 42 Age 18-29 30-41 42-53 54 261 63 3 3.99 0.263 50 18 41 8 15 4 Residence Urban Rural 139 59 1 2.22 Education Literate Illiterate 190 75 1 1.41 0.235 65 18 Service In payment Freely 239 87 1 0.004 0.952 16 6 Number of Visit Once Twice More than Two 126 32 2 8.6 50 17 Requisition Referred Non referred 20 7 1 0.1 1 235 86
- 4. Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557 (Online) Vol.30, 2014 Satisfaction level of patient on clinical Laboratory Services Of 422 respondents, 255(60.4%) were satisfied, 75(17.8%) were neutral and 92(21.8%) were dissatisfied with general Laboratory service provided at Nekemte Referral Hospital ( Figure 1). Figure 1: Level of patients satisfaction on laboratory services at Nekemte Referal Hospital, 2014(n=422). In Likert Scale, the overall mean rate of satisfaction of patients by laboratory services in Nekemte referral hospital was 3.65. The mean rate of satisfaction for different aspects of laboratory services ranged from 2.15 to 3.82. The lowest mean rating of satisfaction were given for cleanness of latrine and location of the laboratory in the hospital with mean rating of 2.15 and 2.17 respectively. Higher mean rating of satisfaction was obtained for the language the clinical laboratory workers use (3.82) and the presence of waiting place nearby laboratory building in the Hospital (3.72) as indicated in Table 2. Table -2:-Patients’ ratings of satisfaction with different aspects of clinical laboratory services given at Nekemte Referral Hospital, April –MAY 2014, (n=422). 28 Variables Very Dissatisfied Neutral Satisfied Very mean Dissatisfied Satisfied Rating Satisfied Percentage General satisfaction by the hospital laboratory 39(9.2) 53( 12.6) 75(17.8) 104 (24.6) 151 (35.8) 3.6 5 73.5 Waiting Place 30(7.1) 55(13) 78(18.5) 98(23.5) 161( 38.2) 3.7 2 7 5 . 3 Cleanness of room 38(9.0) 51(12.1) 97(23) 115( 27.3) 121(28.7) 3.55 72.6 Privacy of room 40(9.5) 5 3(12.6) 96(22.7) 120(28.4 ) 113(26.8) 3.5 71.5 Communication 37(8.8) 41(9.7) 101 101(23.9) 109(25.8 ) 134(31.8) 3 . 6 275.7 Patience 39(9.2) 57(13.5) 83(19.7) 100(23.7) 143(33.9) 3.6 71.7 Respect 74(17.5) 52(12.3) 62(14.7) 93(22) 141(33.4) 3 . 4 166.9 Language 32(7.6) 38(9) 75(17.8) 101(23.9) 175(41.5) 3 . 8 2 7 9 . 5 Location of Latrine 207(49.1) 5 6(13.3) 73(17.3) 53(12.6) 33(7.8) 2 . 1 7 24.6 Cleanness of Latrine 206(48.8) 5 4(12.8) 83(19.7) 49(11.6) 30(7.1) 2 . 1 5 23.3
- 5. Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557 (Online) Vol.30, 2014 48(11.4) 54(12.8) 82(19.4) 110 (26.1) 128 (30.3) 3 . 5 17 0 29 54(12.8) Total waiting time to Get results 60(14.2) 47(11.1) 86(20.4) 103(24.4) 126(29.9) 3 . 4 568.2 Accessibility of sample Collector 41(9.7) 48(11.4) 67(15.9) 118(28) 148(35.1) 3 . 6 8 75 The whole availability of Requested tests 53(12.5) 4(191 .6) 77(18.2) 90(21.3) 153(36.2) 3 . 5 77 0 . 4 Information given before during specimen collection out side the laboratory room Measures taken during loss of laboratory results 59 ( 14) 44(13.1) 85(20.1) 87(20.6) 147 (34.8) 3 . 5 6 9 . 4 Improvement of laboratory service from time to time 44 (10.4) 54(12.8) 86(20.4) 103 (24.4) 135 (32) 3 . 5 5 70.8 The Cost of the laboratory service 45 (10.7) 38(9) 89(21.1) 113(26.8) 137 (32.5) 75.1 Discussion Satisfaction of clients is one of the outcome measures for health care services and it serves as a useful quality improvement tool, required by most clinical laboratories. Satisfaction rate of patients with clinical laboratory service in Nekemte referral hospital was 60.4%. This satisfaction rate was lower than a study conducted in some government hospitals in eastern part of Ethiopia (13). A lower in patients’ satisfaction might be due to excess patients to the laboratory as Nekemte referral hospital is the only referral hospital used in east wollega zone, west wollega zone and Kelem wollega. Level of patient satisfaction was not statistically different by sex, Age, educational status and residence of respondents. The mean rating of satisfactions for different aspects of clinical laboratory services in Nekemte referral hospital range from 2.15 to 3.82. This range was lower as compared with some studies done in Ethiopia (15, 16). From different laboratory service given in Nekemte referral hospital, patients’ higher rate of satisfaction was showed on language used in laboratory workers and presence of adequate waiting place nearby the clinical laboratory. The Likert scale results of the patient ratings for the level of satisfaction on laboratory services showed the lowest rate 2.15 for cleanliness of the latrines for specimen collection and the second lowest rate 2.17 was recorded for the location of latrine in the hospital to brought specimen. Dissatisfaction of patients with the sanitation of the latrines in this study was in line with study done in some hospitals in eastern and southern part of Ethiopia ( 15, 16). Conclusions The overall degree of Patients satisfaction with the laboratory services was high. Patient satisfaction was lowest with the sanitation and location of latrines in the laboratory .Therefore; hospital administration and the laboratory department of Nekemte referral Hospital should strive more to enhance patients’ satisfaction, particularly in sanitation and location of the latrine in the hospital. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are very much grateful to all study participants for their kind cooperation and participation in the study. We also acknowledge Nekemte Referral Hospital administrative and laboratory staffs for their support and encouragement during the study. References 1. Sitzia J and Wood N. Patient satisfaction: A review of Issues and concepts. Social Science and Medicine; 1997, 5(12):1829–1843. 2. Thiedke C. What do we really know about Patient Satisfation? Farm PractManag; 2007,14(1):33–36. 3. Muula A, Chipeta J, Siziya S, Rudatsikira E, Mataya R and ataika E. Human resource requirements for highly active antiretroviral therapy scale-up in Malawi. BMC Health Services Research; 2007, 7:208.
- 6. Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557 (Online) Vol.30, 2014 4. Tsasis P, Tsoukas C, and Deutsch G. Evaluation of Patient Satisfaction in a Specialized HIV/AIDS Care Unit of a Major Hospital. AIDS Patient Care and STDs;2002, 14(7):347–349. 5. Muhondwa E, Leshabary M, Mwangu M, Mbembati N and Ezekiel M. Patient Satisfaction at the Muhimbili National Hospital in Dares Salaam Tanzania. East African Journal of Public health; 2008, 5(2):67–73. 6. Lionel A.Varnadoe. Madical Laboratory Management and supervision operations, review and study guide, 30 1986. 7. Patient’s satisfaction with service obtained from Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano, Northern Nigeria. http://www.njcponline. Com/ted.asp? 2010/13/4/371/74619. 8. Olijera L, Gebresilasses S. Satisfaction with outpatient health services at Jimma hospital, South West Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Dev; 2001, 15(3): 179 – 184 9. Dagnew M, Zakus D. Community perception on OPD performance of a teaching hospital in Gondar town Ethiopia. Ethiop.Med. J Dev; 1997, 35:153 – 160 10. Mitike G, Mekonnen A, Osman M. Satisfaction on outpatient services in hospitals of the Amhara Region. Ethiop. Med. J; 2002,40:387 – 395. 11. Zelalem A, Wubet B, Dejene D, Biruktawit S and Netsanet G. Physicians’ and Nurses’ Satisfaction with the Clinical Laboratory Service of Gondar University Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Am J ClinPathol 2013 140:289- 29 12. Oakbrook T. Joint Commission on accreditation of Health care organizations. Comprehensive Accreditation Manual for Pathology and clinical Laboratory services; 2005,3-12. 13. Zelalem T, Abiyu M, Haji K and Getachew K. Clients and clinician satisfaction with laboratory services at selected government hospitals in eastern Ethiopia. BMC Research Notes 2013, 6:15 14. Tedla M and Bineyam T. Patients satisfaction with laboratory services at antiretroviral therapy clinics in public hospitals, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Research Notes 2012, 5:184. 15. Abiyu M., Zelalem T., Haji K., Getachew K.Patient Satisfaction with Laboratory Services in Selected Government Hospitals, Eastern Ethiopia.Harar Bulletin of Health Sciencesyear 1 16. Million B, Seid A, Debela B, Derese D, Moges D, Misganaw B. HIV/AIDS patients’ satisfaction on ART laboratory service in selected governmental hospitals, Sidamma Zone, Southern Ethiopia. Science Journal of Public Health2013; 1(2): 85-90. 17. Carter JY. Role of laboratory services in health care: The present status in eastern Africa and recommendations for the future. East Africa Med J. 1999;73(7). 18. Belete T, Hailu A. Medical laboratory services in hospital laboratories in Ethiopia. Ethiop. J of Health Dev. 2004; 18(1):43-7. 19. Mfinanga S, Kahwa A, Kimaro G, Kilale A, Kivuyo S, Senkoro M, Ngowi B, Mtandu R, Mutayoba B, Ngadaya E and Mashoto K. Dissatisfaction with the laboratory services in conducting HIV related testing among public and private medical personnel in Tanzani. BMC Health Services Research 2008, 8:171. 20. World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa. Stepwise Laboratory (Quality) Improvement process towards accreditation: Checklist for Clinical and Public Health Laboratories, 2012.
- 7. The IISTE is a pioneer in the Open-Access hosting service and academic event management. The aim of the firm is Accelerating Global Knowledge Sharing. More information about the firm can be found on the homepage: http://www.iiste.org CALL FOR JOURNAL PAPERS There are more than 30 peer-reviewed academic journals hosted under the hosting platform. Prospective authors of journals can find the submission instruction on the following page: http://www.iiste.org/journals/ All the journals articles are available online to the readers all over the world without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself. Paper version of the journals is also available upon request of readers and authors. MORE RESOURCES Book publication information: http://www.iiste.org/book/ IISTE Knowledge Sharing Partners EBSCO, Index Copernicus, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, JournalTOCS, PKP Open Archives Harvester, Bielefeld Academic Search Engine, Elektronische Zeitschriftenbibliothek EZB, Open J-Gate, OCLC WorldCat, Universe Digtial Library , NewJour, Google Scholar