Performance Management and Performance Appraisals
- 1. 1 Performance Management and Performance Appraisals Dr. Thin Nwe Oo Associate Professor Dept. of Management Studies Yangon University of Economics
- 2. 2 What is Performance? Doing something successfully by using skills, knowledge and motivation “Outcomes, results or accomplishments”
- 3. 3 Performance Management a process to establish a shared understanding about what is to be achieved, and an approach to managing and developing people in order to achieve it Getting better results for the organization via the measurement of individual performance
- 4. 4 Nature of Performance Management • Performance Management Processes used to identify, encourage, measure, evaluate, improve, and reward employee performance Provide information to employees about their performance. Clarify organizational performance expectations. Identify the development steps that are needed to enhance employee performance. Document performance for personnel actions. Informing and getting agreement on individual performance Facilitate them to achieve better results Provide rewards for achieving performance objectives.
- 5. 5 Performance Management is A Part of HRM Cycle Recruitment & Selection Performance Appraisal Reward Training and Development Performance depends upon each of the four components and how they are coordinated
- 7. 7 Types of Performance InformationTypes of Performance Information
- 8. 8 Performance Standards • Performance Standards ▫ Expected levels of performance Benchmarks, goals, and targets ▫ Characteristics of well-defined standards Realistic Measurable Clearly understood Challenging E.g. - Finish 20 bags per hour - Making 20 presentation with at least grade B in first semester - Innovate 3 new products in the first three months
- 9. 9 Performance Appraisal • “The systematic description of an employee’s strengths and weaknesses” • The process of evaluating how well employees perform their jobs when compared to a set of standards, and then communicating the information to employees. 9
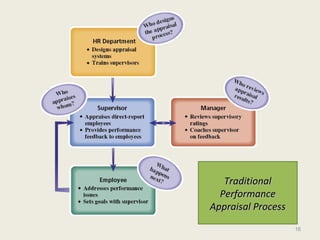
- 10. 10 Performance Appraisal ▫ Informal appraisals: ongoing basic within the organization ▫ Formal appraisals: occurrence at certain intervals throughout that person’s history of employment Performance Appraisal is a part of Performance Measurement Process
- 11. 11 Uses of Performance Appraisal Performance Appraisal Performance Appraisal To provide rewardsTo provide rewards To provide trainingTo provide training To review potentialTo review potential
- 12. 12 Benefits of Performance Appraisal Individual • Objectives can be established in relation the whole organization • Key results and timescale can be established • Can compare past performance and future activities against standards • Can be known pay on the basis of performance Organization • Suitable promotion candidates can be identified • Areas of improvement can be seen • Communication is improved • Basis for medium to long term HR planning
- 13. 13 The Process of Performance Appraisal • Step 1- Identification of criteria • Step 2- Appraise for a period of time • Step 3- Prepare an appraisal report by manager • Step 4- Appraisal interview • Step 5- Modify the report if necessary as a result of interview • Step 6- Review of the assessment • Step 7- Prepare the action plan for improvement • Step 8- Implement the action plan • Step 9- Follow up the result
- 14. 14 Where to Appraise? Common Performance Measures Quantity of Output Quality of Output Timeliness of Output Presence at Work
- 15. 15 Appraisal Techniques • Graphic Rating Scales • Check List • Essay • Behavioral Rating Scales • Management by Objectives (MBO)
- 17. 17 Types of Appraisals • Downward Appraisal • Upward Appraisal • Peer Appraisal • Self Appraisal • Customer Appraisal • Multi-source or 360 degree Appraisal
- 18. 18 Who Conducts Appraisals? Supervisors rating their employees Employees rating their superiors Multi-source Outside sources rating employees Team members rating each other Employees rating themselves Sources of Performance Appraisals
- 20. 20 Appraisal Interview • Interview between Manger (may be one of the appraiser) and subordinate (appraisee) • The purpose is to encourage collaborative problem solving and improvement planning • Three styles of manager that can be adopted – Tell and sell – Tell and listen – Problem solving
- 21. 21 Appraisal Errors • Halo error: A situation in which a supervisor generalizes from one dimension of a person’s job performance to all dimensions of performance. • Error of central tendency: An error that occurs when a manager rates all employees average, even when their performances vary. • Leniency error: A situation occurs when manager rates all employees in a group higher than they deserve.
- 22. 22 Why PA May Fail Unclear Language Mgr not taking PA seriously Mgr not prepared No on-going feedback Mgr not honest or sincere Ineffective discussion Lack appraisal skills Mgr Lacks Information Insuff. Rewards
- 23. 23 Sources of Ineffective Performance Organization Policies and Practices • Ineffective job placement • Insufficient job training • Lack of attention to employee needs or concerns • Inadequate communication within organization • Unclear reporting relationship Job Concerns • Boredom job • Lack of growth or advancement opportunities • Unsafe working conditions • Excessive workload • Lack of job skills Personal Problems • Marital problems • Financial worries • Emotional disorders • Conflict between work demand and family demand • Other family problems • Lack of effort External Factors • Industry decline or extreme competition • Conflict between ethical standards and job demands
- 24. 24 Contemporary PA Concepts Management by objectives (MBO) 360-degree feedback Self-managed teams
- 25. 25 Self-Managed Teams Characteristics • Focusing group result • Larger Span of control • More part- time/contract workers • More cross-functional workers Challenges • Measuring individual result Unfair & Hard • Quality and commitment std. Diverse • Measure cross- functional performance Tough
- 26. 26