PERIFERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx
- 1. THE PERIFERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Presented by:- Kashish Wilson Assistant Professor, MMCP
- 2. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 🞇 The (PNS) is that portion of the nervous system outside the central nervous system 🞇 Sensory receptors within the sensory organs, neurons, nerve, ganglia, and plexuses are all part of the PNS 🞇 The nerves of the PNS are classified as; cranial nerves or spinal nerves,
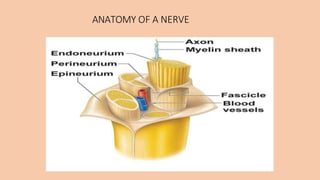
- 3. GENERAL ANATOMY OF NERVES AND GANGLIA 🞇 A nerve is a cordlike organ composed of numerous nerve fibers (axons) bound together by connective tissue. 🞇 Nerve fibers of the peripheral nervous system are ensheathed in Schwann cells, which form a neurilemma and often a myelin sheath around the axon. Nerves has: 🞇 endoneurium, perineurium and epineurium
- 4. ANATOMY OF A NERVE
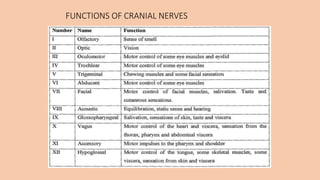
- 5. CRANIAL NERVES 🞇 Cranial nerves are nerves that emerge directly from the brain and the brainstem. 🞇 There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves, numbered I to XII 🞇 They relay information between the brain and parts of the body. 🞇 Considers to be parts of both CNS and PNS 🞇 They are traditionally classified as sensory, motor or mixed base on their functions.
- 7. FUNCTIONS OF CRANIAL NERVES
- 8. SPINAL NERVES 🞇 There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves: 8 cervical (C1–C8), 12 thoracic (T1–T12), 5 lumbar (L1–L5), 5 sacral (S1–S5), and 1 coccygeal (Co). 🞇 The first cervical nerve emerges between the skull and atlas 🞇 The others emerge through intervertebral foramina, including the anterior and posterior foramina of the sacrum and the sacral hiatus.
- 10. AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) 🞇 ANS is motor nervous system that controls glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle 🞇 The primary target organs of the ANS are the viscera of the thoracic and abdominal cavities 🞇 Its job is to regulate such fundamental states and life processes as heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, respiratory airflow, pupillary diameter, digestion, energy metabolism, defecation, and urination.
- 11. DIVISION OF THE ANS 🞇 The ANS has two subsystems 🞇 Sympathetic 🞇 parasympathetic divisions 🞇 Sympathetic (Thoracolumbar) Division The sympathetic division is also called the thoracolumbar division 🞇 It has relatively short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers
- 12. PARASYMPATHETIC DIVISION 🞇 The parasympathetic division is also called the craniosacral 🞇 Somas of the preganglionic neurons are located in the pons, medulla oblongata, and segments S2 to S4 of the spinal cord 🞇 The parasympathetic division has long preganglionic fibers reaching almost all the way to the target cells 🞇 short postganglionic fibers that cover the rest of the distance.