Personal hygiene
- 1. Personal Hygiene Mrs.Puvaneswari Ramesh Assoc. Professor NHCON
- 2. Contents Hygiene and Elements Personal hygiene – Definition Care of Hair Skin and Face Teeth Ears Hands Nails and cuticles Feet
- 3. Hygiene From the Greek word “hygies”(Hygiea- Goddess of Health) Meaning “healthy, sound”
- 4. Hygiene – Common elements Personal hygiene Environmental hygiene Environmental Personal hygiene hygiene
- 5. Personal hygiene - Definition Personal hygiene may be described as the principle of maintaining cleanliness and grooming of the external body. Failure to keep up a standard of hygiene can have many implications. Not only is there an increased risk of getting an infection or illness, but there are many social and psychological aspects that can be affected.
- 6. What is Personal Hygiene? Regular Routine of Personal Care Washing and Grooming of Hair Face and Skin Teeth Ears Hands Nails Feet
- 7. Hair Hair is made of dead cells. Hair is important because it brings oil to the surface of the skin. Hair helps warm the body by trapping a layer of air next to the scalp.
- 8. Hair Care Tips • Wash regularly with shampoo. Rinse hair thoroughly with clear water after shampooing to remove all the soap • Don't scrub or rub too hard . It may irritate your scalp or damage your hair.
- 9. Massage your scalp well. It will remove dead skin cells, excess oil and dirt Brush hair daily Wash combs and brushes frequently Don’t share combs, brushes etc.
- 10. Why Brush Your Hair? Brushing helps keep the scalp clean by loosening and removing dust and dead cells. It also adds shine
- 11. Hair & Scalp problems Dandruff Head lice Splitting and breaking
- 12. Dandruff A flaking of the outer layer of dead skin cells on the scalp. This condition is usually caused by dry skin. There is no cure for dandruff, but it can be controlled with special shampoos.
- 13. Head Lice Parasiticinsects that live on the hair shaft and cause itching. Lice can’t fly or jump from person to person, but they are easy to catch from other people.
- 14. Avoiding and Treating Head Lice Don’t share: Combs, brushes, hats ,barrettes or other hair things, headphones Use special shampoo and wash your hair immediately. Any linens and clothes you have used should be washed in hot water or dry-cleaned.
- 15. Splitting & Breaking Too much heat can cause the layered cells of your hair to split apart and even break off. Wind, chlorine, chemical treatments, and permanent hair dye can weaken hair in the same way. If you put your hair in a ponytail , use a coated rubber band or soft cloth hair band. Noncushioned or uncovered elastic bands can cause severe breakage.
- 16. Skin The human skin is the outer covering of the body. Functions of Skin Protection. Vitamin D formation Temperature control Sensation Water resistance Control of evaporation Excretion Absorption
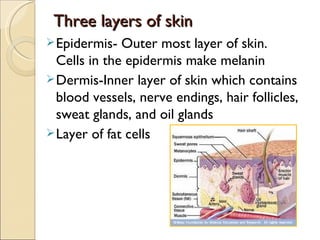
- 17. Three layers of skin Epidermis- Outer most layer of skin. Cells in the epidermis make melanin Dermis-Inner layer of skin which contains blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, sweat glands, and oil glands Layer of fat cells
- 18. Common Skin problems Bad odor Acne
- 19. Body odor Perspiration itself doesn’t smell. However, during sweating, another liquid called apocrine is also secreted. When apocrine combines with the bacteria naturally present on the skin, odor results Bad odor is Caused by Poor hygiene Foods such as onions and garlic
- 20. Acne Acne is created when oil from the oil glands mix with the dead cells and plug up the hair follicles in the skin it creates a “whitehead.” A “blackhead” is when the air touches the plug, the plug turns black
- 21. What makes acne worse? Oil-based makeup, suntan oil, hair jells and spray. For girls, menstruation For Boys it may get worse because they have more skin oil. Squeezing or picking at blemishes Hard scrubbing of the skin
- 22. Daily baths or showers using soap and scrubbing the entire body with a washcloth Do not need to scrub violently. The use antiperspirants decreases perspiration and cover odor with a manly smell Wash the face two times a day with a mild soap or gentle cleanser. It is best to Use lotions only if needed, and use ones that are oil-free and water-based. Try to stay out of the sun, and use a sunscreen every day during summer and winter.
- 23. Skin Care Tips Bathe or shower regularly using soap Do not scrub violently If possible, bathe or shower after exercise – especially after sweating Use antiperspirants decreases perspiration and cover odor with a manly smell Wear clean clothes Reduce stress levels which irritates the skin Maintain a healthy diet
- 24. Skin Care Tips Wash your face 2 times a day. Avoid washing too often, as the skin will become irritated and dry out. Keep oily hair away from your skin Avoid touching acne except when washing Don’t squeeze or pick the pimples Try to avoid touching the face. Keep hands clean by washing them often.
- 25. Protect yourself from the sun Wear sunscreen and reapply it every hour. Wear a hat, T-shirt, and sunglasses. Drink plenty of fluids. Protect yourself from UV Rays
- 26. Teeth Healthy teeth and gums enable you to: Chew food thoroughly Speak clearly Give shape and structure to your mouth
- 27. Structure of teeth Enamel (top) The hard material on the outer surface of the tooth. Dentin (middle) Below the enamel – the bonelike material that surrounds the sensitive inner parts of the tooth. Pulp (inside) Tissue that contains nerve endings and blood vessels.
- 28. Dental problems Dental problems are caused by the activity of certain types of oral bacteria Other causes: Tongue not cleaned Food stuck in teeth Sinus problems Stomach problems
- 29. Dental Problems Halitosis Tooth decay Plaque Tartar Periodontal Disease
- 30. How to avoid Dental problems- Brushing & Flossing Daily dental hygiene routine that consist of brushing for 2-4 minutes and flossing I f possible, brush after every meal or rinse your mouth with warm water. Use a soft-bristled brush.
- 31. Brushing & Flossing Replace your toothbrush every 2-3 months or after an illness. Use toothpaste that contains fluoride. Flossing removes food trapped between your teeth and gum lines that rinsing and brushing miss. FLOSSING
- 32. Dental care Eat at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables each day. Include foods that contain calcium, such as milk and yogurt. Limit intake of sugar. See a dentist every 6 months
- 33. Ears Wash ears daily with a wash cloth don’t forget behind the ears Do not use Q tips in ears it will smash the ear wax deep into the ear canal Usually Ear wax is usually removed when you chew food or gum
- 34. Hands
- 35. HAND HYGIENE First, wet hands and apply liquid or clean bar of soap. Next, rub your hands together and scrub all surfaces (palms, fingers, and in between). Continue for 10-15 seconds. Soap combined with the scrubbing action that helps remove germs. Rinse well and dry your hands.
- 36. Nails and cuticles The part of the nail that can be seen and touched is composed of dead cells. Thin skin-like layer at the base of each nail is called cuticle .A non-living band of tissue. Nails protect the sensitive tip of our fingers and toes. Without proper care they can become weak, ingrown or infected.
- 37. Nail Care Keep nails trim but do not cut nails shorter than skin level. Keep nails clean. Round your fingernails slightly when trimming them. Cut toe nails straight across. Smooth rough nail edges with a file or emery board.
- 38. Cuticles Care Clean and soften your hands in warm water. To keep your cuticles neat, push them back after soaking your hands, while they are soft. You may also use cuticle remover , a chemical that dissolves the cuticle
- 39. Feet Care Large collection of sweat glands live in our feet Wash your feet well at least once a day. Dry them carefully, especially between the toes. Keep feet and skin clean and dry Change socks daily Avoid walking barefoot in public areas
- 40. Make Hygiene part of your daily routine