PETROLOGY
- 1. PETROLOGYPETROLOGY Dr. P. Sarathbabu M.Sc. B.Ed. Ph.D. Department of Geology Acharya Nagarjuna University
- 2. Introduction: Petrology deals with the study of rocks Petro = rock , ( litho=rock ) Logos = study Petrology comprises the Origin, Association Occurrence Mineral composition Texture Structure Physical properties etc.. of rocks
- 3. Rock: Aggregated solids of minerals is called rock. (Or) A rock may be defined as “an unit of the earth’s crust All rocks are made of two or more minerals, but minerals are not made of rocks.
- 4. Geological Classification of Rocks • There are three main types of rocks: 1.1. IgneousIgneous - formed when molten rock cools. 2.2. MetamorphicMetamorphic – rocks changed by the effect of heat and pressure. 3.3. SedimentarySedimentary – formed by the consolidation of sediments in the layered or bedded rocks deposited in the ocean bottom or huge lakes, etc.
- 5. What type of rock is formed when magma cools and hardens? Characteristics A tough, frozen melt with little texture or layering; mostly black, white and/or gray minerals; may look like granite or like lava
- 6. What type of rock is formed when change occurs from heat and pressure in the Earth? Characteristics Hardened sediment with layers (strata) of sandy or clayey stone; mostly brown to gray; may have fossils and water or wind marks
- 7. What type of rock is formed when weathering and erosion cause sediments to press together in layers? Characteristics Tough rock with layers (foliation) of light and dark minerals, often curved; various colors; often glittery from mica
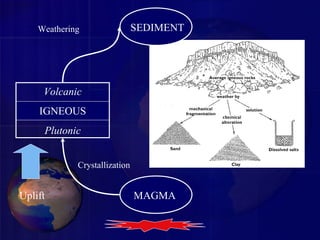
- 9. Rock Cycle • The three different types of rocks--- igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic---are constantly being changed from one type to another type through various geological processes.
- 10. Early stage of Earth = Molten stage
- 22. MAGMA Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENT SEDIMENTARY METAMORPHIC Uplift Burial Increased P&T Melting Crystallization Weathering Erosion Transport Deposition Can you see any shortcuts?
- 24. • The rock cycle demonstrates the relationships among the three major rock groups • It is powered by the interior heat of the Earth • As well as earth’s momentum and… • The energy from the sun • It involves processes on the Earth’s surface as well as the Earth’s interior • It connects the “hydrologic cycle” with the “tectonic cycle”. In Conclusion…
- 29. Granite
- 30. Marble
- 31. Sandstone
- 32. Civil Engineering importance of Petrology • Petrology provides a proper concept and logical basis for interpreting physical properties of rocks. • The study of texture, structure, mineral composition, chemical composition etc., gives all necessary details regarding the strength,durabiliy,colour,appeareance, workability, etc., These inherent characters of rocks are of chief concern for a civil engineer to judiciously assess the suitability occurring at project site for required purpose