Philippine diversity of Family Lamiaceae
- 1. Philippine Diversity of the Family Lamiaceae The Mint Family
- 2. Overview Overview of the Taxa
- 3. Lamiaceae, also called Labiatae, is the mint family of flowering plants. The enlarged Lamiaceae family contains about 239 genera and 6,900 to 7,200 species, the largest family of the order Lamiales.
- 4. The family was established by De Jussieu in 1789 as the order Labiatae. The name Labiatae alludes to the flowers typically having petals fused into an upper and lower lip, the flower thus having an open mouth! Although Labiatae is an acceptable, alternate name, botanists more often use Lamiaceae after the genus Lamium.
- 5. The majority of the Family Lamiaceae are annual or perennial herbs. The plants are frequently aromatic in all parts and contain volatile oils. The family includes many widely used culinary herbs, such as basil, mint, rosemary, sage, savory, marjoram, oregano, thyme, lavender, and perilla. Some are shrubs, trees, such as teak, or rarely, vines.
- 6. Philippine Diversity of the Family Lamiaceae Morphology and Anatomy Taxonomy Diversity Importance and Conservation
- 7. Morphology and Anatomy Internal and External Features of the Taxa
- 8. Members of the family Lamiaceae are mostly annual or perennial herbs or shrubs with opposite leaves, when crushed the foliage usually emitting various, mostly pleasant odors. The stems are usually square, especially when young, erect or procumbent (lying on the ground). Life cycles of the herbaceous members may be annular or perennial. Stem of a member of Lamiaceae
- 9. The leaves are opposite or whorled, decussate and gland-dotted. The leaves are often strongly aromatic due to ethereal oils located in the glandular hairs. The leaf blades are simple, rarely pinnately lobed (Teucrium) or digitately compound (Cedronella, Vitex), with entire or toothed margins.
- 10. Flowers usually abundant and quite attractive, with the sepals and corollas variously united. Arranged in compact axillary cymes (verticillasters) or are sometimes single in the axils of the leaves. Sometimes the inflorescences are congested as in Pycnostachys. Usually zygomorphic, rarely actinomorphic.
- 11. Calyx 2-lipped or not and are usually persistent with 5 teeth or lobes. Corollas strongly 2-lipped (labiate, hence the family name), rarely 1-lipped. Stamens 2 or4(didynamous), epipetalous Ovaries superior, deeply 4-lobed, rarely not, with the style mostly arising from the middle of the 4 lobes.
- 12. Fruit comprised of 4 nutlets, although some of these are not maturing, each containing a single seed. It may also be a drupe with 1-4 pyrenes, subtended by or enclosed within a persistent calyx. The outer surface of the nutlets may be smooth or rugose (wrinkled). Occasionally the nutlets are winged (Tinnea). http://www.plantzafrica.com/plantklm/lamiaceae.htm
- 13. Taxonomy Organization of the Taxa
- 14. Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Asterids Order: Lamiales Family: Lamiaceae Lindley
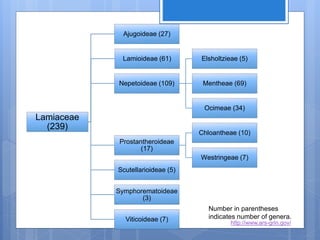
- 15. Lamiaceae (239) Ajugoideae (27) Lamioideae (61) Nepetoideae (109) Elsholtzieae (5) Mentheae (69) Ocimeae (34) Prostantheroideae (17) Chloantheae (10) Westringeae (7) Scutellarioideae (5) Symphorematoideae (3) Viticoideae (7) Number in parentheses indicates number of genera. http://www.ars-grin.gov/
- 16. The family is divided into several subfamilies and tribes of which subfamily Nepetoideae has the most genera. The largest genera are Salvia (900), Scutellaria (360), Stachys (300), Plectranthus (300), Hyptis (280), Teucrium (250), Vitex, (250) Thymus (220), and Nepeta (200). The Lamiaceae is closely related to the family Verbenaceae. Several recent, phylogenetic studies have shown that some genera classified in Verbenaceae belong, however, in Lamiaceae, for example, Vitex and Clerodendrum.
- 17. Salvia is the largest genus of the family, representing ± 1,000 species, differing remarkably in their morphology. Flowers of Salvia officinalis
- 18. List of Genera Acanthomintha· Achyrospermum· Acinos · Acrocephalus· Acrotome· Acrymia· Adelosa· Aegiphila· Aeollanthus · Agastache· Ajuga· Ajugoides· Alajja· Alvesia· Amasonia· Amethystea· Anisochilus· Anisomeles· Archboldia · Asterohyptis· Ballota http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 19. Basilicum· Becium· Benguellia· Blephilia· Bostrychanthera· Bovonia· Brazoria· Bystropogon· Calamintha· Callicarpa· Capitanopsis· Capitanya· Caryopteris· Catoferia· Cedronella· Ceratanthus· Chaiturus· Chamaesphacos· Chaunostoma· Chelonopsis· Chloanthes· Cleonia· Clerodendrum· Clinopodium· Colebrookea· Collinsonia· Colquhounia· Comanthosphace· Congea· Conradina· Coridothymus· Cornutia· Craniotome· Cuminia· Cunila· Cyanostegia http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 20. Cyclotrichium· Cymaria· Dauphinea· Dicerandra· Dicrastylis· Dorystaechas· Dracocephalum· Drepanocaryum· Elsholtzia· Endostemon· Englerastrum· Eremostachys· Eriope· Eriophyton· Eriopidion· Eriothymus· Erythrochlamys· Euhesperida· Eurysolen· Faradaya· Fuerstia· Galeopsis· Gardoquia· Garrettia· Geniosporum· Glechoma· Glechon· Glossocarya· Gmelina· Gomphostemma· Gontscharovia· Hanceola· Haplostachys· Haumaniastrum http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 21. Hedeoma· Hemiandra· Hemigenia· Hemiphora· Hemizygia· Hesperozygis· Heterolamium· Hoehnea· Holmskioldia· Holocheila· Holostylon· Horminum· Hosea· Hoslundia· Huxleya· Hymenocrater· Hymenopyramis· Hypenia· Hypogomphia· Hyptidendron· Hyptis· Hyssopus· Isodictyophorus· Isodon· Isoleucas· Karomia· Keiskea· Kudrjaschevia· Kurzamra· Lachnostachys· Lagochilus· Lallemantia · Lamium· Lavandula · Leocus· Leonotis· Leonurus· Lepechinia http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 22. Leucas· Leucosceptrum· Limniboza· Lophanthus· Loxocalyx· Lycopus· Macbridea· Mallophora· Marmoritis· Marrubium· Marsypianthes· Meehania· Melissa· Melittis· Mentha· Meriandra· Mesona· Metastachydium· Microcorys· Micromeria· Microtoena· Minthostachys· Moluccella· Monarda· Monardella· Monochilus· Mosla· Neoeplingia· Neohyptis· Neorapinia· Nepeta· Newcastelia· Nosema· Notochaete· Ocimum· Octomeron· Ombrocharis http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 23. Oncinocalyx· Origanum· Orthosiphon· Otostegia· Oxera· Panzerina· Paralamium· Paraphlomis· Paravitex· Peltodon· Pentapleura· Perilla· Perillula· Peronema· Perovskia· Perrierastrum· Petitia· Petraeovitex· Phlomidoschema· Phlomis· Phyllostegia· Physopsis· Physostegia· Piloblephis· Pitardia· Pityrodia· Platostoma· Plectranthus· Pogogyne · Pogostemon · Poliomintha· Prasium· Premna· Prostanthera· Prunella· Pseuderemostachys http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 24. Pseudocarpidium · Pseudomarrubium· Puntia · Pycnanthemum · Pycnostachys · Rabdosiella · Renschia · Rhabdocaulon · Rhaphiodon · Rhododon · Rosmarinus · Rostrinucula · Roylea · Rubiteucris · Sabaudia · Saccocalyx · Salvia · Satureja · Schizonepeta · Schnabelia · Scutellaria · Sideritis · Solenostemon · Spartothamnella · Sphenodesme · Stachydeoma · Stachyopsis · Stachys · Stenogyne · Sulaimania · Suzukia · Symphorema · Symphostemon· Synandra · Syncolostemon · Tectona · Teijsmanniodendron · Tetraclea · etradenia · Teucridium · Teucrium · Thorncroftia · Thuspeinanta · Thymbra · Thymus http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 25. Tinnea · Trichostema · Tsoongia · Vitex · Viticipremna · Wenchengia · Westringia · Wiedemannia · Wrixonia · Zataria · Zhumeria· Ziziphora http://www.mobot.org/mobot/research/apweb/genera/lamiaceaegen.html
- 26. Diversity World and Philippine Diversity of the Taxa
- 27. Distribution The family has a cosmopolitan distribution.The main centre of diversity is the Mediterranean region to central Asia. Members are found in tropical and temperate regions.
- 28. About 60 genera with ± 980 species occur in the Sub-Saharan African region (Klopper et al. 2006). In South Africa, there are ± 255 species in 35 genera. The species occur predominantly in the summer rainfall areas, but are also found in the winter rainfall areas. The habitats vary to a great extent. The species inhabit not only dry, often rocky, woodland or grassland, but also occur along forest margins and in fynbos.
- 29. Specimen and observational data for Lamiaceae from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility Network
- 32. Critically Endangered Lamiaceae species Cuminia eriantha Status: Critically Endangered B1+2c Cuminia fernandezia Status: Critically Endangered B1+2c Hyptis argutifolia Status: Critically Endangered B1ab(iii) Hyptis diversifolia Status: Critically Endangered B1ab(iii) Phyllostegia kaalaensis Status: Critically Endangered D Phyllostegia mollis Status: Critically Endangered D Plectranthus dissitiflorus Status: Critically Endangered A1c Salvia veneris (Kythrean Sage) Status: Critically Endangered B1ab(i,iii)
- 33. Pogostemon cablin P. cablin syn. P. patchouli Native to Malaysia and the Philippines, Patchouli is now cultivated in tropical and sub-tropical regions around the world. Patchouli has been used extensively in Asian medicine, apperaring in the Chinese, Indian and Arabic traditions. The oil is widely employed as a fragrance and, in India, as an insect repellent. Patchouli is used in herbal medicine in Asia as an aphrodisiac, antidepressant and antiseptic. It is also employed for headaches and fever. Patchouli essential oil is used in aromatherapy to treat skin complaints. It is thought to have a regenerative effect on skin tone and to help clear conditions such as eczema and acne. The oil may also be used for varicose veins and hemorrhoids.
- 34. Pogostemon philippinensis Native to the Philippines Found in dipterocarp forests.
- 35. Plectranthus merrilli Native to the Philippines Found in mossy forests