Physics ms
- 1. 1 Marking Scheme PHYSICS SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-2018 Section- A 1. As VA – VB = VB – VC magnitude of work done is same. (1) 2. I = (1) 3. Factors are : (i) magnetic permeability of the medium (1/2) (ii) electric permittivity of the medium (1/2) 4. Diagram (1) 5. In photon picture, intensity is determined by the number of photons crossing per unit time. (1) Section – B 6. As the current leads the voltage by , the element used in black box is a ‘capacitor’.( ½ ) (ii) Phasor diagram ( ½ )
- 2. 2 tan = Vc / VR Vc = VR Xc = R Impedance Z = ( ½ ) Z = R ( ½ ) 7. (i) Energy density u = ( ½ ) u= 11.5 X 10-9 J/m3 . ( ½ ) (ii) Speed = ( ½ ) speed= 3 X 108 m/s ( ½ ) 8. 2/v - 1/u = (2 - 1 )/ R ( ½ ) correct sign convention ( ½ ) 1.0/v – 1.5/-30 = (1.0 – 1.5) / 20 ( ½ ) v = - 13.3 cm ( ½ ) 9. Photodiode ( ½ ) Reverse biasing ( ½ ) I-V characteristics NCERT page no. 487 (1) 10.a) need for long antenna diminishes, with explanation (1) power is inversely proportional to (wavelength)2 ( ½ ), signals from different transmitters can be distinguished( ½ ) OR Range: 76-88 MHz and 420-890 MHz (1) Factors: by increasing height of transmitting antenna and using repeater stations. (1) Section- C 11.(a) C = 5 X 10 -9 F, U = 25 J U = Q2 / 2C ( ½ ) Q2 = 2 U C = 2 X 25 X 5 X 10-9 Q = 5 X 10-4 C ( ½ ) Q = n e ( ½ )
- 3. 3 n = = 3.125 X 1015 electrons ( ½ ) (b) Without changing charge on the plates, we can make C half. C = , i.e. double the plate separation or inserting dielectric of dielectric of a value such that C becomes (1). 12.(a) As the electrostatic field inside a conductor is zero, using Gauss’s law, charge on the inner surface of the shell = -Q ( ½ ) Charge on the outer surface of the shell = +Q ( ½ ) (b) To show using Gauss’s law expression Expression for electric field for radius, r= : E = (1) Expression for electric field for radius, r = 2b : E = (1) 13. (i) E1 = , E2 = , E3 = ( ½ ) E2 < E3 < E1 ( ½ ) (ii) Vd α E ( ½ ) Vd2< Vd3< Vd1 ( ½ ) (iii) I = nAe Vd / J= σE ( ½ ) J = n e Vd J2 < J3<J1 ( ½ ) 14.NCERT Exemplar Q4.21 R1, R2, R3 (each 1 mark) 15.NCERT pg no. 301 Q6.14 (1 mark each part) 16.Device : Transformer ( ½ ) Diagram on page number 260 NCERT part I (1) Principle: statement of mutual induction (1) Efficiency: Assuming no energy losses, the transformer is 100% efficient i.e. IpVp= IsVs. ( ½ ) 17. = D / d ( ½ ) 5th bright = 51 = 51D/d = 5 x 480 x 10-9 x 2 / 3 x 10-3 = 16 x 10-4 m (1) 5th bright = 52 = 52D/d = 5 x 600 x 10-9 x 2 / 3 x 10-3 = 20 x 10-4 m (1) distance between two 5th bright fringes = (20 – 16) x 10-4 = 4 x 10-4 m ( ½ ) 18. ‘Light from the sun is unpolarised’ means the electric field vector vibrates in all possible directions in the transverse plane rapidly and randomly. (1)
- 4. 4 Polarisation of sunlight by the method of scattering: page number 379 of NCERT part II : Diagram + explanation. (1+1) 19. i) Page no. 391 figure 11.4 +explanation ( ½ +1) ii) Page no. 392 + explanation ( ½ + 1) OR (i) Davisson- Germer experiment ( ½ ) An electron of charge e, mass m accelerated through a potential difference of v volts, Kinetic energy equals the work done (eV) on it by the electric field: K = eV ( ½ ) K = , p = ( ½ ) p= the de- Broglie wavelength λ of the electron is : λ = ( ½ ) λ= ( ½ ) (ii) For same KE, λ α As mass of proton is greater than that of electron, λp< λe. ( ½ ) 20. E = hc / = 6.6. x 10-34 x 3 x 108 / 620 x 10-9 (1) = 3.2 x 10-19 J ( ½ ) = 3.2 x 10-19 / 1.6 x 10-19 = 2 eV ( ½ ) This corresponds to the transition “D” (1) 21. NCERT figure 13.1 on page no. 444 (1) Fission (1) , Fusion (1) 22.(i) Modulation Index = Am/ Ac = 20/40 = 0.5 ( ½ + ½ ) The side bands are (2000 + 20) KHz = 2020 KHz and (2000 - 20) KHz = 1980 KHz ( ½ + ½ ) Amplitude versus ω for amplitude modulated signal : page number 525 NCERT part (ii) Figure 15.9, Ac = 40 volts, μAc/2 = 10 volts. (1) Section -D 23. (a) critical thinking, hard working (1) (b) One should not touch electrical appliances with wet hands/ any one
- 5. 5 precaution. (1) (c) IA = ( ½ ) For an ideal ammeter RA = 0 I = ( ½ ) Percentage error: X 100 = X 100 (1) Section –E 24. (a) Condition qE = q vB ( ½ ) v= ( ½ ) Trajectory becomes helical about the direction of magnetic field (1) (b) To derive the expression of magnetic force acting per unit length of the wire: = , upwards on wire AB (2) At equilibrium Magnetic Force per unit length = mass per unit length X g = (1) OR (a) Using the condition mvr = (1/2) For H-atom n=1, v= Time period T = T= , I = = (1/2) M = I A (1/2) M = ( ) M = (1/2) (b) Diagram for magnetic field lines Cu- diamagnetic (1) Al- Paramagnetic (1) Fe- Ferromagnetic (1) 25. (a) Diagram (2) + labelling ( ½ ) (b) me = 1 + 25/5 = 6 ( ½ ) mo = 30 / me = 5 ( ½ ) mo = vo / -uovo = - 5 uo
- 6. 6 1/fo = 1/vo – 1/uofo = - (5/6) uo ( ½ ) uo = 1.5 cm , vo = 7.5 cm ue = - 4.17 cm ( ½ ) Length of the tube = ue + vo = 11.67 cm ( ½ ) OR (a) Diagram (2) + labelling ( ½ ) (b) m = - fo / fe ( ½ ) fo = 5 fe ( ½ ) L = fo + fe ( ½ ) fe = 36/6 = 6 cm ( ½ ) fo = 30 cm ( ½ ) 26. (a) circuit diagram (1) NCERT page no.492 ( explanation: 2) (b) NCERT page no. 511 Q. No.14.17 Logic operation (1) Truth table (1) OR Diagram (1 ½ ) Input Characteristics (1 ½ ) Output Characteristics (1 ½ ) Current amplification factor ( ½ )
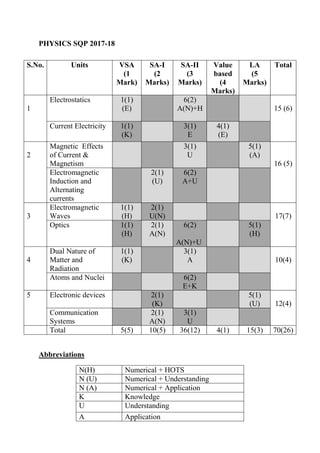
- 7. PHYSICS SQP 2017-18 Abbreviations N(H) Numerical + HOTS N (U) Numerical + Understanding N (A) Numerical + Application K Knowledge U Understanding A Application S.No. Units VSA (1 Mark) SA-I (2 Marks) SA-II (3 Marks) Value based (4 Marks) LA (5 Marks) Total 1 Electrostatics 1(1) (E) 6(2) A(N)+H 15 (6) Current Electricity 1(1) (K) 3(1) E 4(1) (E) 2 Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism 3(1) U 5(1) (A) 16 (5) Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating currents 2(1) (U) 6(2) A+U 3 Electromagnetic Waves 1(1) (H) 2(1) U(N) 17(7) Optics 1(1) (H) 2(1) A(N) 6(2) A(N)+U 5(1) (H) 4 Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation 1(1) (K) 3(1) A 10(4) Atoms and Nuclei 6(2) E+K 5 Electronic devices 2(1) (K) 5(1) (U) 12(4) Communication Systems 2(1) A(N) 3(1) U Total 5(5) 10(5) 36(12) 4(1) 15(3) 70(26)
- 8. H HOTS EMD Evaluation and Multi disciplinary Marks wise weightage to different typology of questions Typology (Marks) Number of Questions(Marks) Marks (questions) K (7 marks) 3(3) + 4(2) 7(5) U (21 Marks) 2(1) + 9 (3) +10(2) 21(6) A (21 Marks) 4(2) +12(4) + 5(1) 21(7) H (10 Marks) 1(1) + 9(3) 10(4) EMD (11 Marks) 1(1) + 6 (2) + 4 (1) 11(4) Total 70 (26)