Phytopharmacueticals.pdf for pharmacy students
- 2. PHYTO PHARMACUETICALS Scope and Objectives : •This subject gives the student the knowledge regarding Herbal drug industry Quality of raw material Guidelines for quality of herbal drugs, herbal cosmetics, Guidelines for quality of herbal drugs, herbal cosmetics, nutraceutical etc. •The subject also emphasizes on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Patenting and regulatory issues of herbal drugs.
- 3. •The term phyto-pharmacon / phyto-pharmaceutical is derived from the Greek designations phytón for plant and phármakon for medicine. •Basically, these are herbal remedies which are prepared from herbal substances like dried plant parts such as leaves, blossom, herb, bark, or the roots traditionally already known to cure undesired conditions or illnesses. PHYTO PHARMACUETICALS illnesses. •Herbal medicinal products can be variable in their composition. Therefore, to obtain consistent efficacy and safety, standardized medicinal plant extracts are being used. •In general, herbal medicinal products are better tolerated and provide a superior benefit-risk ratio to synthetic drugs.
- 4. •Therefore, evidence-based phyto-pharmaceuticals increasingly mentioned in clinical practice guidelines are first-line therapy in various diseases and indications •Highest quality (GMP), clinically confirmed efficacy and best tolerability and safety of standardized or quantified medicinal plant extracts are key measures for a successful phytotherapy approach. PHYTO PHARMACUETICALS measures for a successful phytotherapy approach. •Other than food supplements or botanicals phyto-pharmaceuticals have to follow comparable regulatory guidelines as conventional drugs. Therefore, a high level of scientific evidence supports their efficacy and safety. .
- 5. HERBS AS RAW MATERIALS
- 6. Objectives: upon compiletion of this ppt the student should be able to: 1. Understand raw material as source of herbal drugs from cultivation to herbal drug product 2. Understand about the methods for selection, identification and authentication of herbal drugs 3. Know about the processing of herbal and medicinal plants. Learning outcomes: the student will be able to: HERBS AS RAW MATERIALS Learning outcomes: the student will be able to: 1. Learn the definition of herbs as raw material, herbs, herbal medicinal products and sources of herbs. 2. Learn about the methods for selection, identification and authentication methods for herbal materials. 3. Learn about the processing methods of herbal drugs. 4. Learn about the safety parameters for herbal drugs
- 7. Medicinal and aromatic plans constitute a major part of the flora, which provides raw materials for use in the pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and drug industries. In one of the studies by WHO, it is estimated 80 percent of the population of developing countries relies on traditional plant based medicines for their health requirements. India and China are the two major producing countries having 40 percent of the global biodiversity and availability of rare species. Introduction These are well known as the home of medicinal and aromatic crops that constitute a segment of the flora and provide raw materials to the pharmaceutical, cosmetics, fragrance, flavor etc. industries. From the trade data available, it is clear that the global market for medicinal plants has always been large and has been on increase in the recent past.
- 8. Introduction Herbs have used in the traditional system of medicine since time immemorial to alleviate human illness and for the maintenance of general health. The interest of people in herbal medicines has increased significantly in both developed and developing countries. The WHO Traditional medicine (TM) strategy 2014-2023 focuses on promoting the safety, efficacy, and quality of TM by expanding the knowledge base and providing guidance on regulatory and quality assurance standards In 2012 , 119 WHO members states were regulating herbal medicines.
- 9. Herbs: It is defined as any plant with leaves, seeds or flowers used for flavoring, food, medicine or perfume. Herbal medicine: Practice of using herbs and herbal preparations to maintain health and to prevent, alleviate or cure disease or a plant or plant part or an extract or mixture of these used in herbal medicine. Herbal medicinal products: these are medicinal products where the active ingredient consists mainly of herbal substances. Definition Herbal drug preparations: They are prepared from herbal materials by different process, which is extraction with various solvents, purification, concentration and other processes. It includes such as powders, extracts and juices. Finished herbal products: Finished herbal products consist of one or more herbal preparations made from one or more herbs (i.e. from different herbal preparations made of the same plant as well as herbal preparations from different plants. Products containing different plant materials are called “mixture herbal products”.
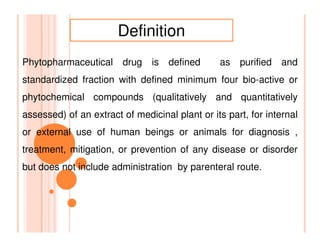
- 10. Definition Phytopharmaceutical drug is defined as purified and standardized fraction with defined minimum four bio-active or phytochemical compounds (qualitatively and quantitatively assessed) of an extract of medicinal plant or its part, for internal or external use of human beings or animals for diagnosis , treatment, mitigation, or prevention of any disease or disorder but does not include administration by parenteral route.
- 19. SELECTION • Selection of medicinal plant is very important parameter which influence the result of final product. • Albuquerque and Hanazaki in 2006 provide the method for selecting medicinal plants SELECTION, IDENTIFICATION AND AUTHENTICATION OF HERBAL DRUGS selecting medicinal plants The methods are : • Randomization • Ecological • Chemotaxonomic (Phytogenetic) • Etheno directed
- 20. Steps involved in processing of Herbal Drugs Selection of Herbs ↓ Identification & Authentication ↓ Cultivation of Herbs ↓ Collection of Herbs ↓ Processing of Herbal Raw Material
- 21. 1.Selection of herbs •The species or botanical variety selected for cultivation should be the same as specified in the official Pharmacopoeia or national documents. •In case of newly introduced medicinal plants, the •In case of newly introduced medicinal plants, the variety selected for cultivation should be identified and documented.
- 23. IDENTIFICATION Identification tests should be specific for the herbal material and are usually a combination of three or more of the following: • Macroscopic characters • Microscopic characters • Chromatographic procedures • Chemical reactions AUTHENTICATION AUTHENTICATION •Especially useful in cases of drugs that are frequently substituted or adulterated with other varieties which are morphologically and chemically indistinguishable. •Several herbal drugs in the market still cannot be identified or authenticated based on their morphological or histological characteristics. Use of wrong drugs may be ineffective or it may worsen the condition if two drugs are very similar we do this
- 24. good aculartar practices to grow your plants well like well soil and not too much or too little water and to get good species plant full of active consitutents in them then our formulation is good
- 25. Cultivation of medicinal plants Cultivation of medicinal plants requires intensive care and management as various factors such as environment, soil, irrigation pests, etc, play a vital role. These factors vary from one plant to another. Scientific documented methods should be followed, if no data available traditional methods should be adopted and a systematic method should be developed through research Good agricultural practices in cultivation (GACP) and conservation agriculture (CA) which aims to improve, conserve and make more efficient use of natural resources Collection of herbs For the collection of medicinal plants, a proper time should be selected. Herbs are selected for collection at a stage when they yield the maximum amount of chemical constituents. Skilled labour should be employed as they are trained to identify and select the herbs at a proper stage. The age of the plant also plays a vital factor for their selection. Diseased plants should be rejected. Season of collection should also be given due consideration while selecting the plants for collection.
- 26. in a plants theres so many biological reaction happens and you have to pick it at a paticular time and if before it nothing happens and after it it will reaction to others so by that we know if its a perfect time ot not
- 27. rhizomes will have not have root hairs
- 33. Simple herbal dosage forms may be prepared either from herbal materials (such as unprocssed seeds or plant exudates) or herbal preparations (such as jground powders and dried extracts) ready for administration to patients. These herbal dosage forms, produced under GMP conditions, include decoctions, tea bags, granules, syrups, ointments or creams, inhalations, Processing of Herbal raw materials Processing of Herbal raw materials patches, capsules, tablets and pills, among others. Primary processing: It includes simple procedures by which the herbs are prepared like sorting of different parts, garbling, cleaning, drying, etc. •Garbling: This process is desired when sand, dirt and foreign part of the same plant, not constituting drug are required to be removed. this all done for some plants some and not the other ones
- 34. The process may involve procedures such as removing dirt and foreign Substances, peeling of barks, sieving, trimming, removal of hairs from roots, remove of seeds from fruits, stripping of leaves from s t e m s . Excessive stems in case of lobelia and stramonium need to be removed Stalks in case of cloves are to be deleted Drugs constituting rhizomes need to be carefully removed from roots and rootlets. Pieces of iron must be removed with the help of magnet in case of castor seeds Pieces of bark should be removed by peeling as in gum acacia •Washing: After garbling the herbal raw material should be cleaned well to remove the traces of remaining soil, dirt and other impurities from the surface. The roots, rhizomes and tubers are washed with clean water. During process, scrapping and brushing may be necessary. •Parboiling: After washing, certain herbal raw materials need to undergo parboiling process in which they are put in boiling water for a short period.
- 36. This may help in improving the storage life of the raw material and prevent insect/ mould contamination. Leaching: Some impurities can be removed by subjecting the plant material under running water known as leaching. However the duration of leaching should be controlled to prevent the loss of chemical constituents present in the drug. Drying: In some cases, the plant material should be thoroughly dried after In some cases, the plant material should be thoroughly dried after washing in order to prevent thedeterioration and degradation of active constituents. They must be dried as soon as possible to remove moisture and reduce the damage due to microbial or mould infestation. Drying also prevents the activation of certain enzymes which may otherwise degrade the active ingredients and also facilitate grinding and milling of the raw material. Depending on the drug & nature of ingredients, different drying methods can be used which are as follows:
- 37. I) Natural drying a) Sun drying • Most herbal raw material can be dried in open air under direct sunshine provided the climate is suitable. b)Shade drying • Some medicinal plants cannot be directly exposed to sunlight, hence need to be dried under shade. • This drying process is slow but helps in minimizing loss of colour, volatile oils and aromatic components from being evaporated 2) Artificial drying ► Drying by artificial heat is more rapid than open air drying and is necessary in rainy season and regions where there is high humidity. ► The temperature and equipment's used for drying depends on the physical and chemical nature of the drug and its constituents.
- 38. □ Secondary processing • The secondary processing differs from one herb to another depending on the nature of active ingredients as well as therapeutic properties. • Secondary processing includes techniques such as removal of foreign substances, prevention of microbial / infestation, enhancing the efficacy of drugs, reducing the toxicity, extraction using suitable solvents, cone. & drying of extracts. Cutting, Sectioning and Communition : • After thoroughly drying, the herbal materials are processed by cutting and sectioning into smaller sizes which are convenient for storage as well as extraction. • It may be small particles, coarse powder or fine powder
- 39. Aging /Sweating: • Aging refers to storing the raw material for a specified time after harvesting. • It is generally done under sun or in shade for up to a year. • During the process of aging excessive water is evaporated & enzymatic reactions may occur to alter the chemical composition of herbal material. Example: Cascara bark should be aged for at least one year prior to use in medicinal Example: Cascara bark should be aged for at least one year prior to use in medicinal preparations to reduce its irritant effects. Sweating is done by subjecting the herbal materials at a temperature between 45 to 65°C with high humidity for a period ranging from one week to few months. • The herbal materials are stacked between woolen blankets or other kind of cloth. • The sweating process is considered a hydrolytic and oxidative process in which some of the chemical ingredients of the herbs are hydrolysed or oxidized.
- 41. Infusion: • It is a liquid preparation obtained by extracting herbal materials with either cold or hot water without boiling. Other solvents may also be used. Decoction: • It is a liquid preparation obtained by boiling the herbal materials with water Fluid extract •It is a liquid preparation obtained by maceration or percolation of herbal materials in alcohol. The ratio will be one part of liquid containing one part of herbs (1:1). in alcohol. The ratio will be one part of liquid containing one part of herbs (1:1). Tinctures • It is a dilute alcoholic extract of herbal materials typically made up of 1 part of herbal material with 5 to 10 parts of the solvent Powdered extract •It is a form of herbal preparation which is processed into dried, granulated or powdered materials
- 46. THANKS THANKS