Planning
- 2. ` Planning is the process of deciding in advance what is to be done, where, how and by whom it is to be done. it is basically a process of ‘thinking before doing Planning is the selection from among alternatives for future courses of action for the enterprise as a whole and each department within it.
- 3. NATURE OF PLANNING (a) Planning is a mental activity. (b)Planning is goal-oriented c) Planning is forward looking (d)Planning pervades all managerial activity (e) Planning is the primary function (f) Planning is based on facts. (g)Planning is flexible. (h) Planning is essentially decision making
- 4. SIGNIFICANCE OF PLANNING (a) Minimizes uncertainty. (b) Emphasis on objectives (c) Promotes coordination (d)Facilitates control (e) Improves competitive strength (f) Economical operation (g)Encourages innovation h)Tackling complexities of modern business
- 6. You all know Business organizations serve a purpose in the society. Simply you can understand this why to run a business? To earn profit( return on investment) To serves society/customer needs( to satisfy customer needs)
- 7. This purpose which is also called strategic intent is jointly stated by Vision, mission and goal of an organization. Before going into the details of planning, there is a need to understand these terms
- 8. Vision: Vision is a picture of what the firm wants to be and, in broad terms, what it wants to ultimately achieve Example: • Our vision is to be the world’s best quick service restaurant (McDonald’s) • To make the automobile accessible to every American (Ford Motor Company’s vision when established by Henry Ford)
- 9. Mission Mission : answers three questions Why a company is in existence? What it is offering? Whom it is serving to ? How it is serving ? Example: Be the best employer for our people in each community around the world and deliver operational excellence to our customers in each of our restaurants (McDonald’s)
- 10. Goals What an organization wants to accomplish in a future period of time. A desired future state an organization wants to realize. Goals are general statement about profitability , growth and survival of business for a longer period of time
- 11. objectives Objectives are desired targets in specific relevant areas that an organization wants to achieve during a fixed time period. Objectives are concrete , specific and quantitative. Objectives are statement of results, a firm seeks to achieve during a specified period of time
- 13. Examples of objectives Decrease overall customer complaints from 3% to less than 1% by 2012 Increase the cash flow of the business by 10% within 2 years.
- 14. Process of Planning in organizations . The Environmental Context The organization’s mission • Purpose • Premises • Values • Directions Strategic goals Strategic plans Tactical goals Tactical plans Operational goals Operational plans
- 15. Steps in Planning Being aware of opportunity Comparing alternatives in light of goals The market , competition , customer needs Which alternative will give us the best chance of meeting goals at , strengths and weaknesses lowest costs and highest proffit Setting objectives or goals Choosing an alternative Where we want to be and what we want to Selecting the cosur accomplish and when Considering planning premises Formulating supporting plans In what environment :internal and external our Buy equipments, materials, hire workers, develop a new product plans Identifying alternatives: ? Numberizing plans by making budgets What are the most appropriate alternatives Develop budgets such as volume and price of sales, operating expenses, necessary for plans , expenditure for capital equipment
- 16. Types of Plans
- 17. Types of Planning • Strategic Planning • A general plan outlining resource allocation, priorities, and action steps to achieve strategic goals. The plans are set by and for top management. • Tactical Planning • A plan aimed at achieving the tactical goals set by and for middle management. • Operational Planning • Plans that have a short-term focus. These plans are set by and for lower-level managers.
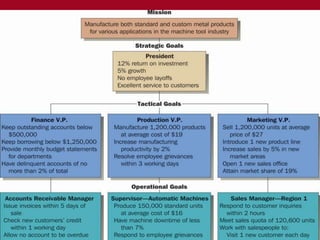
- 19. Strategic Goal (formed by top level management) 1.Provide 14 % return to investors for at least ten years 2.Start and purchase new restaurant chain within five years 3. Negotiate new labor contract this year TACTICAL GOALS (formed by Middle level Managers) V.P OPERATIONS •Open 150 new restaurant V.P MARKETING V.P FINANCE in next ten Keep corporate debt to no Increase per store sell 5% per more than 20 percent of years, Decreasing food container costs by 15% in 5 year for next 10 yrs., target liquid assets for next ten and attract two new market years, Revise computerized years, decrease average accounting customer wait by 30 sec. segments during next 5 years, system within five years OPERATIONAL LEVEL GOAL : LOWER LEVEL MANAGEMENTACCOUNTING MANAGER ADVERTISING MANAGER Split accounts RESTAURANT MANAGER Develop regional marketing receivable/payable Implement employee incentive campaign this year, Negotiate 5% functions from other areas system within one cheaper advertising next within year, Decrease waste by 5 year, implement this year two years, Computerize percent this year, Hire and train promotional strategy payroll system for each new assistant manager restaurant this year, Pay all
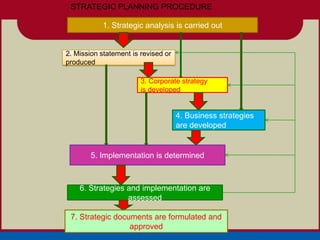
- 20. STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCEDURE 1. Strategic analysis is carried out 2. Mission statement is revised or produced 3. Corporate strategy is developed 4. Business strategies are developed 5. Implementation is determined 6. Strategies and implementation are assessed 7. Strategic documents are formulated and approved
- 21. STRATEGIC PLAN INCLUDE DOCUMENT STANDARD COMPONENT Mission statement Description of product, customer group, technology and values Corporate strategy • Definition of businesses (combinations of products and/or services offered and served markets or niches) • Market position aspirations (usually in terms of market share objectives for the Businesses • Investment objectives (priorities given to the investments in the different businesses)
- 22. DOCUMENT STANDARD COMPONENT Business Level • Generic competitive strategy Strategy (separate (cost leadership or differentiation) for each business) • Competitive advantages on the level of offers • Competitive advantages on the level of resources Strategic program • Program objectives (for each group of • Program organization implementation (organizational structure, persons involved) measures) • Process and milestones (program steps, timetable) • Budget (internal and external program cost)
- 23. Tactical goals • Tactical goals and objectives are directly related to the strategic goals of the organization. They indicate the levels of achievement necessary in the departments and divisions of the organization. Tactical goals and objectives must support the strategic goals of the organization. For example, if a strategic goal states that the organization is going to reduce total costs by 15 percent next year, then the different departments of the company would set tactical objectives to decrease their costs by a certain percentage so that the average of all departments equals 15 percent.
- 24. Tactical Planning Tactical plan A plan aimed at achieving tactical goals and developed to implement specific parts of a strategic plan
- 25. Developing and executing Tactical plans Developing tactical plans Executing tactical plans • Recognize and understand • Evaluate each course of action overarching strategic plans in light of its goal and tactical goals • Obtain and distribute • Specify relevant resource and information and resources time issues • Monitor horizontal and vertical • Recognize and identify human communication and integration resource commitments of activities • Monitor ongoing activities for goal achievement
- 26. Example of Tactical Planning Coca cola developed strategic plan to cement its dominance in soft drink industry • they identified a threat :- independent bottling plants. • Coca-Cola bought several large independent bottlers and combined them into one new organization called “Coca-Cola Enterprises • Establishing new business was a tactical plan to realise strategic plan.
- 27. Operational Goals & Operational Planning Operational Goals. Operational goals and objectives are determined at the lowest level of the organization and apply to specific employees or subdivisions in the organization. They focus on the individual responsibilities of employees. For example, if the department’s tactical goal is related to an increase in return on assets by 5 percent, then the sales manager may have an operational objective of increasing sales by 10 percent.
- 28. Operational planning generally assumes the existence of objectives and specifies ways to achieve them. Operational planning is short- range planning that is designed to develop specific action steps that support the strategic and tactical plans. Operational planning usually has a very short time horizon, from one week to one year.
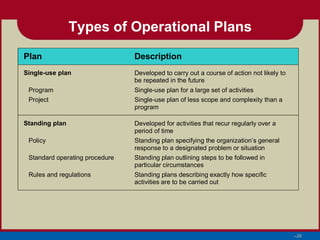
- 29. Types of Operational Plans Plan Description Single-use plan Developed to carry out a course of action not likely to be repeated in the future Program Single-use plan for a large set of activities Project Single-use plan of less scope and complexity than a program Standing plan Developed for activities that recur regularly over a period of time Policy Standing plan specifying the organization’s general response to a designated problem or situation Standard operating procedure Standing plan outlining steps to be followed in particular circumstances Rules and regulations Standing plans describing exactly how specific activities are to be carried out –29