Plant & animal cell
- 1. Plant & Animal Cells
- 3. • Robert Hooke- in 1665 he discovered the cell composition of cork and introduced the word “cell” to science • Anton von Leeuwenhoek was first to observe one celled living things. Examples of these were bacteria and
- 4. • Robert Brown- in 1830, he identified a dark-stained structure at the center of every cell he observed. He referred to such structure as the nucleus.
- 5. The Cell Theory • All living things are made up of cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things • Living cells come only from other living cells • Rudolph Virchow Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann
- 6. • 1838- a German botanist discovered that all plants were composed of cells • 1839- a German zoologist discovered that all animals were composed of cells • 1856- a German physician was doing an experiment when he found that all cells come from other existing cells Schwann Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolph Virchow
- 7. Two Fundamentally Different Types of Cells A prokaryotic cell A eukaryotic cell
- 9. Animal and Plant Cells Have More Similarities Than Differences
- 10. Organelles maintain the life processes of the cell, including: Intake of nutrients Movement Growth Response to stimuli Exchange of gases Waste removal Reproduction The Purpose of Organelles
- 11. •Cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like material with organelles in it. If the organelles were removed, the soluble part that would be left is called the cytosol. It consists mainly of water with dissolved substances such as amino acids in it.
- 12. Cell Wall • Is a stiff non-living wall that surrounds the cell membrane made of cellulose • Protects the cell from injury • Gives the plant cell a fixed shape • Cell wall is fully permeable
- 13. • Cytoskeleton Is a network of thin fibrous filaments that serve as the “bones and muscles” of cells. Microfilaments are cytoskeletons that are also attached to the cell membrane. They are responsible for giving the cell its shape. Microtubules are cytoskeletons that are not connected to the cell membrane. They serve as the anchorage of the organelles in the cell
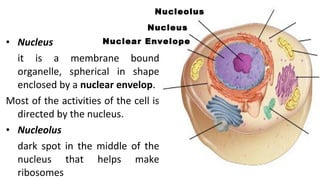
- 14. • Nucleus it is a membrane bound organelle, spherical in shape enclosed by a nuclear envelop. Most of the activities of the cell is directed by the nucleus. • Nucleolus dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope
- 15. • Ribosomes are found on the endoplasmic reticulum. Together they help in manufacturing proteins for the cell following instructions of the nucleus Ribosomes
- 16. • Endoplasmic Reticulum is a membranous structure forming a network of canals through which proteins and other molecules are transported Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumRough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- 17. • Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is an organelle where most of the ribosomes are attached. Proteins produced in the ribosomes needs to be transported through the Rough endoplasmic Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumRough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- 18. • Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum is a branching canal (without ribosomes) that transports large molecules inside the cell. Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumRough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- 19. • Golgi Complex they are flattened stacks of membrane bound sacs. They function as the packaging unit, the protein formed by the endoplasmic reticulum are packed into small membrane sacs called vesicles. Golgi Complex
- 20. • Lysosomes organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes (lysozymes) that digest bacteria, viruses, complex food particles, and damaged cell components that could be harmful to the cell, and may interfere with
- 21. Cell suicide (suicide is bad for cells, but good for us!) (The lysosome is not found in plant cells)
- 22. • Mitochondria are small, double- membraned, spherical or sausage-shaped organelles involved in the production of energy. The mitochondria is popularly known as the powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria
- 23. Plant Cell
- 24. • Vacuole a small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water, food, or metabolic waste Vacuol e
- 25. • Plastids are double-membraned organelles found in plant cells, some protozoans, and bacteria. Chloroplastids or chloroplasts are the most common plastids in green plants. It contains green pigments called chlorophyll. Chloroplast are the energy- capturing centers in plant cells, which are involved in the manufacture of the cell’s food, a
- 26. • Chloroplasts chlorophyll containing organelles found in cells of green plants and some protist; capture light energy and converted it to chemical energy Chloroplasts
- 27. Chloroplasts Think of the chloroplast as the solar panel of the plant cell.
- 28. • Cell wall is an additional boundary surrounding the cells of plants, fungi, bacteria, and some protozoans. The cell wall of plant cells is a very tough substance made up of cellulose, which support the cells and protects it from injury. The wood of fully-grown plants is basically made up of cell wall. Cell Wall
- 29. •Vesicles are organelles that carry materials in and out of the cell. These materials include food particles needed by the cell and waste products secreted by the cell.
- 30. Plant Cell Cell Membrane Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Wall Nucleolus Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi Bodies Mitochondria Ribosomes Cytoplasm
Editor's Notes
- It’s a jelly like substance surrounding the organelles This is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell. All other organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm. It contains the nutrients required by the cell.
- Permeable--- natatagusan
- Anchorage--- meaning ka-pitan ng mga organelle
- Nucleus Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA directing their growth, metabolism and reproduction and functioning in the transmission of genic characters The nucleus is surrounded by its own membrane called the nuclear envelope. Nuclear Envelope it’s a Double membrane that separates nucleus from rest of cell Parts: Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes
- Ribosomes Function: makes proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Ribosomes are the protein builders or the protein synthesizers of the cell. They are like construction guys who connect one amino acid at a time and build long chains. ribosomes make proteins that will be used inside of the cell.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) it is a large network of interconnecting membrane tunnels. Nickname: “Roads” Function: The internal delivery system of the cell The “highway” of the cell. It is made of a series of tubes that carry materials through the cell.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Rough appearance because it has ribosomes Function: They follow instructions from the nucleus and make protein the cells needs. Helps make proteins, that’s why it has ribosomes
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Function: NO ribosomes makes fats or lipids
- Golgi Complex Nickname: The shippers Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes
- Small organelles filled with enzymes. They break down invading bacteria and damaged parts of the cell. They are the “cleaners” of the cell
- Mitochondria Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Function: The “Powerplant” of the cell. The energy produced by the mitochondria is important for the vital activities of the cell such as growth and reproduction. Chemical energy in sugar is converted to useable energy in the mitochondria by a chemical reaction called cellular respiration.
- Vacuole (central) Function: stores water This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts
- Chloroplasts Function: traps energy from the sun to produce food for the plant cell Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment