Plastic ppt
- 2. Presentation by SHABEEL KAHLID 21 ATEEQ AHMAD 31
- 3. CONTENTS Classification of material What is plastic? Or why plastic are called plastic? plastic made of?? Types of plastic Why Design with Plastics Origins Types processes
- 4. CLASSIFICATION OF MATERIALS Materials used in the design and manufacture of products • Plastics Wood Composites Ceramics Metals Fabrics • • • • • Layers of lens Balsa wood Acrylic polycarbonate, model aluminium & acrylic
- 5. What is plastic The word plastic itself comes from the Greek word plasticos, which means to be able to be shaped or molded by heat. As we will see, shaping plastics by using heat is a basic part of nearly all plastics manufacturing processes. plastic made of…? Plastic is made by combining long chains of small carbon molecules known as monomers to for a polymer. Monomers are atoms of general petroleum chemicals such as crude oil and natural gas. There are different types of monomers such as styrene and vinyl chloride which is used to make PVC.
- 6. TYPES Natural plastics - these are naturally occurring materials that can be said to be plastics because they can be shaped and moulded by heat. An example of this is amber, which is a form of fossilised pine tree resin and is often used in jewellery manufacture. Synthetic plastics - these are materials that are derived from breaking down, or ’cracking’ carbon based materials, usually crude oil, coal or gas, so that their molecular structure changes. This is generally done in petrochemical refineries under heat and pressure,. It is further divided into two catagiries. 1. Thermoseting 2. Thermoplastic
- 7. THERMOPLASTIC PLASTICS The majority of common plastics are thermoplastics. Thermoplastics can be heated and reshaped because of the ways in which the molecules are joined together. This can be repeated many times (as long as no damage is caused by overheating). Heat Harden Soften Cool
- 8. USES OF PLASTICS (THERMOPLASTICS) Here are some common products made from thermoplastics. Polystyrene Polypropylene High density polythene Acrylic Low density polythene
- 9. PLASTICS Thermosetting plastics: Initially set by heat Consist of polymer chains with strong bonds between each chain Strong and durable Cannot be reshaped once set Common in powder or resin forms
- 10. USES OF PLASTICS (THERMOSETS) Thermosets have different qualities to thermoplastics. Epoxy resin Phenol formaldehyde Urea formaldehyde
- 11. Plastics production. Most modern plastics are derived from natural materials such as oil, coal and natural gas with crude oil remaining the most important raw material for their production. The starting point for the production process is the distillation, in petrochemical refineries, of the raw material into fractions (different parts). The heavy fractions give us lubrication oils and the heavy oils used for heating fuels. The lighter fractions give us gas, petrol, paraffin and naphtha. The chemical building blocks for making plastics come mainly from naphtha.
- 12. DISTILLATION FROM CRUDE OIL. The start of making plastics is to subject naphtha to a cracking process in which complex organic chemical compounds are separated into smaller molecules, dependent on their molecular weight. These smaller molecules include ethylene, propylene, butene and other hydrocarbons. The compounds produced through the cracking process are then further refined to produce the base plastic materials.
- 13. WHY DESIGN WITH PLASTICS? Corrosion resistance Low electrical and thermal conductivity, insulator Easily formed into complex shapes, can be formed, casted and joined. Wide choice of appearance, colors and transparencies 13
- 14. Plastic Processing Extrusion Compression Moulding Injection Moulding Rotational Moulding Blow Moulding Vacuum Forming
- 15. Extrusion Continuous process used to produce both solid and hollow products that have a constant cross-section. E.g. window frames, hose pipe, Thermoplastic granules are fed from a hopper by a rotating screw through a heated cylinder. The tapered screw compacts the plastic as it becomes elasticised. The die which is fitted to the end of the extruder barrel determines the crosssection of the extrusion. Materials used in Extrusion This extrusion is part of a window seal made from thermoplastic elastomer (TPE).
- 16. Extrusion
- 18. Injection Moulding Powder or granules from a hopper into a steel barrel with a rotating screw. The barrel is surrounded by heaters The screw is forced back as plastic collects at the end of the barrel . Once a sufficient charge of melted plastic has accumulated a hydraulic ram forces the screw forward injecting the thermoplastic through a sprue into the mould cavity.
- 19. Injection Moulding Pressure is kept on the mould until the plastic has cooled sufficiently for the mould to be opened and the component ejected. Materials used Normally thermoplastics are used in this process although a few thermosetting plastics can also be injection moulded. Toy made from high impact polystyrene (HIPS).
- 21. Vacuum Forming 1. Mould is attached to a platen (support plate). The platen and mould are then lowered and a rigid thermoplastic sheet material is clamped onto an air tight gasket and usually heated from above. 2. Once the thermoplastic sheet is softened enough (reaches a plastic state) then air is blown in to raise the sheet in a slight bubble before the platen is raised bringing the mould into contact with the plastic.
- 22. Vacuum Forming 3. trapped air remaining between the platen and the heated plastic sheet is then evacuated by a vacuum pump. Atmospheric pressure acting over the top surface completes the forming process by pressing the plastic sheet onto the mould. 4. Once the plastic sheet has cooled down to below it's freeze point the air flow is reversed to lift the forming off the mould and the mould lowered
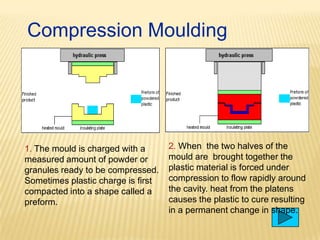
- 25. Compression Moulding 1. The mould is charged with a measured amount of powder or granules ready to be compressed. Sometimes plastic charge is first compacted into a shape called a preform. 2. When the two halves of the mould are brought together the plastic material is forced under compression to flow rapidly around the cavity. heat from the platens causes the plastic to cure resulting in a permanent change in shape.
- 26. Compression Moulding The component is ejected from the mould and any excess material formed at edges (flash) is removed. Materials used. Typical thermosetting plastics used in compression moulding are urea formaldehyde and phenol formaldehyde.
- 29. DISADVANTAGES OF USING PLASTICS Low strength o Low useful temperature range (up to 600 F) Less dimensional stability over period of time (creep effect) hardens and become brittle over time Sensitive to environment, moisture and chemicals Poor machinability 29
Editor's Notes
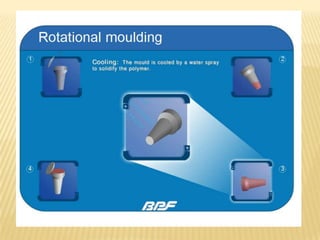
- 90% of rotational mouldings are made from polyethylene (PE), used mainly to manufacture hollow shaped products such as footballs, road cones and storage tanks up to 3m³ capacity.