Platform Economy Impact
- 1. Jan Roschek Thomas Mierschke Platform Economy Impact How multi-sided Platform Business Models disrupt existing Markets and impact Producer, Consumer & Startups Does a Digital Ego exist in the Platform Economies?
- 2. About Us Digital Business Development Execute Growth & Innovation Strategies Industry, IT, OT & Entrepreneurship Expertise Expert Ecosystem Orchestration
- 3. What makes a Platform?
- 4. Digital Biz Architecture Layers Community Networked Marketplace IT & OT Infrastructure Data Engagement & Interaction Digital Business Model Holistic Cyber & Physical Security Digital Biz Enablement Digital Biz Capabilities
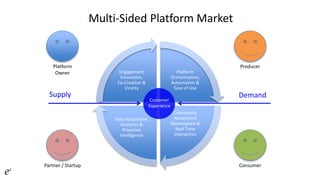
- 6. Platform Orchestration, Automation & Ease of Use Community Networked Marketplace & Real Time Interaction Data Acquisition, Analytics & Proactive Intelligence Engagement Innovation, Co-Creation & Virality Customer Experience Supply Demand Multi-Sided Platform Market Platform Owner ConsumerPartner / Startup Producer
- 7. Platform Attributes P U R P O S E Dashboards Algorithms Engagement Experimentation Interfaces Leveraged Assets Staff of Demand Community & Virality Collaboration Autonomy internal external
- 8. Platform Attributes P U R P O S E Dashboards Algorithms Engagement Experimentation Interfaces Leveraged Assets Staff of Demand Community & Virality Collaboration Autonomy internal external Order Control Stability Creativity Growth Agility
- 9. Platforms shine like Lighthouses They give Direction but no Position
- 10. Platform Play Your Position in the Platform Economy Producer Platform Owner Consumer Startup Supply Demand Innovation Who is in the Lead?
- 11. Workshop Thesis: The platform owner controls demand and supply The producer gets dependent on platform market places and is losing his customer relation The consumer loses his freedom of choice, he seems to be in control, but is prisoned in the closed looped platform economy The Startup is traped in the Innovation Game
- 12. Platform Impact on Producer Liberate Supply - Gatekeepers Dead New Deployment- & Consumption Models The Knowing Customer XaaS Networks & Communities, Virality Open Source Speed Perfection of Matching Demand & Supply
- 13. Does Customer Engagement Produce Faster Horses? The Innovation Trap in Co-Creation
- 14. Platform Impact on Customer Multi Layer Monopoly Robotic Curation Creates a False Reality Searched Knowing creates “Deformed” Customer Shared XaaS Consumption Liberty Perfection of Matching leaves No Choice Community Networked Marketplaces
- 15. Is a Startup an external Innovation Function or can it survive in the Digital Age on it‘s own? Platform Impact on Startups
- 16. Platform Impact on Startups Innovation Games Liberate Supply – No-Go To Market Freedom New Deployment- & Consumption Models XaaS The Knowing Customer Networks & Communities, Virality Open Source Speed Perfection of Matching Demand & Supply
- 17. Platform Business Control The Platform Provider exercises significant control over the platform & the value exchange: He owns: the identity of its participants the transportation logistics the payment mechanisms the pricing the rules that govern the marketplace The Hidden Risk of Platforms is Manipulation