PMS.pptx
- 2. Concept PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Is the process of determining how well employees do their jobs relative to a standard and communicating that information to them. PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT Is a series of activities designed to ensure that the organization gets the performance it needs from its employees. PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Performance management system refers to set of organizational, managerial, team and individual metrics used to attain the aims and objectives of performance management. Performance management system design is one of the key methods HR management uses to contribute to organizational performance
- 3. PM –Categorized Into 2 Separate Types Of Management First: deals with the organization as a whole and evaluates the effectiveness of its managers Second: deals with the system of evaluating the employees in order to enable them to achieve reasonable goals and thus ensure that the organization performs better.
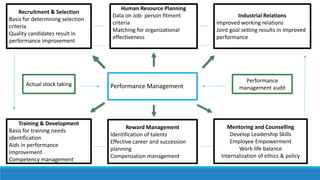
- 4. Recruitment & Selection Basis for determining selection criteria Quality candidates result in performance improvement Human Resource Planning Data on Job- person fitment criteria Matching for organizational effectiveness Industrial Relations Improved working relations Joint goal setting results in improved performance Training & Development Basis for training needs identification Aids in performance improvement Competency management Reward Management Identification of talents Effective career and succession planning Compensation management Mentoring and Counselling Develop Leadership Skills Employee Empowerment Work-life balance Internalization of ethics & policy Performance Management Actual stock taking Performance management audit
- 6. Performance- Focused Organizational Cultures ENTITLEMENT APPROACH Adequate performance and stability dominate the organization. Employee rewards vary little from person to person and are not based on individual performance differences. Performance appraisal activities are seen as having little tie to performance and as being primarily a “bureaucratic exercise” PERFORMANCE DRIVEN APPROACH Focused on results Performance appraisals link results to employee compensation and development
- 7. Detailed Appraisal Of Employee Performance Clear Expectations, Goals, and Deadlines Clear Feedback On Performance Manager And Employee Training As Needed Consequences For Performance Components of a Performance-Focused Culture
- 8. An effective performance management system should do the following Make clear what the organization expects Provide performance information to employees. Identify areas of success and needed development Document performance for personnel records
- 10. What Are the Different Approaches to Performance Management? Key Performance Indicators Roadmap Rewards And Recognition Programs Continuous Feedback Mentorship Program
- 11. Roadmap . The goals you want the employee to achieve within a defined period Milestones that will lead to said goals The action plan that will help achieve the goals and milestones Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that will help measure the performance of the employee
- 12. Key Performance Indicator (KPIs) KPI’s, help you decide what metrics you need to judge an employee What the baseline for these metrics should be How managers and stakeholders can measure and analyze progress. KPIs work when you set tangible and achievable goals for the employee Drawn after goals are finalized
- 13. • The basic responsibility of the employee which they are supposed to perform • Alludes to the sector of outcome within the business organization, for which the department or unit is responsible. KRA • Is the financial and non-financial metric used by the firms to gauge and fortify the success, towards the goals of the organization. • Evaluation technique to see how well the KRA’s are being performed. KPI
- 14. KRA •Recruitment & Selection KPI • Reduce Average time taken to fill vacancies • Reduce Average cost per recruitment • Finalize selection in 5 week for individual position
- 15. 1. Absenteeism 2. Turnover Rate 3. Active employee social ambassadors 4. Active intranet users 5. Employee satisfaction index (ESI) 6. Hires post-trial period 7. Employee Suggestion Box Outcomes 9. Internal Promotion Rate 10. Online company ratings Employee Engagement The following KPIs measure the employee engagement
- 16. Theories of Goal Setting GOAL- SETTING THEORY:(LOCKE-1968) MANAGERS MUST ENSURE THE FOLLOWING – EMPLOYEE TO BE WILLING TO PERFORM Goals must be specific Goals must be robust yet attainable Goals must be desirable Goals must be tied to feedback mechanism.
- 18. Self –Efficacy At Work(Albert Bandura-1977) Self-Efficacy is a person’s particular set of beliefs that determine how well one can execute a plan of action in prospective situations (Bandura, 1977). To put it in more simple terms, self-efficacy is a person’s belief in their ability to succeed in a particular situation.
- 20. Edward W Deming (TQM):These systems encourage to meet the personal goals at the expense of organization Past accomplishments I know I can do the job and have outstanding quality Performance of others Emotional state I don’t think I can do the job on time and have quality outstanding Self efficacy High: Set goals/Targets Preserve/targets Creatively solve problems Visualize success Learn from failure Low: Avoid Difficult tasks Think of excuses for failing Develop low aspirations Quit Blame setbacks on lack of ability of luck
- 21. Expectancy Theory – Vroom 1964
- 22. Identifying And Measuring Employee Performance Quantity of output Quality of output Timeliness of output Presence at work 40% 20% 20% 20% percentage Classes Research MDP & Consultation Mentoring Weighting of Management Duties Weight Improve Customer Feedback 50% Control operational Cost 30% Encourage Quality Improvements 20% Total Management Performance 100%
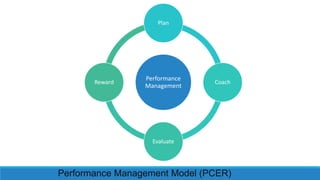
- 23. Performance Management Model (PCER) Performance Management Plan Coach Evaluate Reward
- 26. Performance Appraisal Performance appraisal always involves: Setting work standards Assessing the employee’s actual performance relative to those standards Providing feedback to the employee with the aim of motivating him or her to eliminate performance deficiencies or to continue to perform above par
- 27. Objectives of Performance Appraisal DEVELOPMENT DECISIONS Personal Development Development of skills and competencies Self analysis Self development planning ADMINISTRATIVE DECISIONS Personnel decisions Removal of deficiencies in performance Job re-design
- 28. PerformanceAppraisalProcess •What should be assessed? •Who should make the appraisal •Which procedure(s) should be utilized? •How will the results be communicated? Defining objectives of performance appraisal Defining performance expectations Designing performance appraisal system Implementing performance appraisal system Performance appraisal interview Post performance appraisal actions
- 29. WHO CONDUCTS APPRAISAL Supervisor rating employee Employees rating their superiors Team members rating each other Employee rating themselves Multisource or 360 degree
- 30. Tools of Performance Appraisal Scaling Methods • Graphic Rating Scales • Behavioural Rating Scale Comparative Methods • Ranking • Forced Distribution Narrative Method • Essay • Critical Incident Other Tools • MBO • 360 Degree /Multisource Appraisal
- 31. Three aspects of performance are appraised using graphic rating scales: Descriptive categories: Quality of work, Attendance, Dependability Job Duties: Roles and Responsibilities as per job description Behavioural Dimensions: decision making, employee development, communication etc.
- 32. Collect Critical Incidents Identify Performance Dimensions Reclassify the incidents Assign scale values to the incidents Develop a final Instrument Steps To Develop BARS Behaviourally – Anchored Rating Scale
- 33. Behaviorally-Anchored Rating Scale for Customer Service Skills
- 37. Assessment Centre Appraisal Method The Assessment Centre method of performance appraisal combines role plays, situational judgment tests, presentations, group activities, interviews, simulations, psychometric tests and other techniques to make critical talent decisions. An assessment center performance appraisal helps predict future behavior, make better talent decisions, diagnose development needs and groom employees to expand their KRAs Instrumental in identifying high-potential employees and professional training needs to bridge the skills gaps, leadership development and succession planning.
- 38. Why use the assessment center method of performance appraisal Best of many worlds They offer one platform to carry out many performance appraisal activities: behavioral profiling, psychometric tests, potential evaluation and more! Higher accuracy Assessors get to observe and evaluate employees in real-time, thereby eliminating biases concerning past performances. Adaptability Assessment centers can be designed and customized to match specific appraisal requirements and job profiles. Engagement The interactive quality of virtual assessment centers is a welcome alternative to monotonous performance appraisal methods.
- 39. Psychometric assessment as a performance appraisal method These assessments are also known as psychological appraisals and help analyze six major components of an employee’s performance: Psychometric assessments offer predictive insights about employees, allowing decision-makers to chart a more streamlined career trajectory for individuals within the company.
- 40. HUMAN-RESOURCE (COST) ACCOUNTING METHOD Analyses an employee’s performance through the monetary benefits he/she yields to the company. It is obtained by comparing the cost of retaining an employee (cost to company) and the monetary benefits (contributions) an organization has ascertained from that specific employee.
- 41. Performance Check-ins Performance check-ins, used as an appraisal method in HRM, refer to a frequent review and feedback process between managers and their direct reports. The process builds rapport and helps managers understand what their team members are working on throughout a timeline, between annual appraisal cycles.
- 43. Appraisal Interview Hints For Appraisers Prepare before interview Focus on objective performance Be specific about rating and feedback Develop a future improvement plan Reinforce employee successes Talk too much Lecture the employee Focus entirely on negative job performance Compare the employee with others Think that the employee has to agree
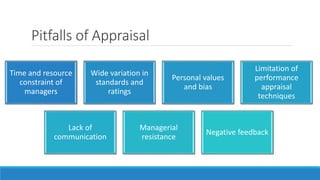
- 44. Pitfalls of Appraisal Time and resource constraint of managers Wide variation in standards and ratings Personal values and bias Limitation of performance appraisal techniques Lack of communication Managerial resistance Negative feedback
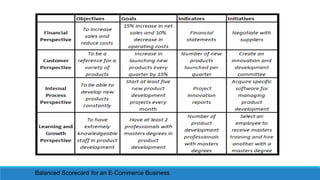
- 45. The term balanced scorecard (BSC) refers to a strategic management performance metric used to identify and improve various internal business functions and their resulting external outcomes. Used to measure and provide feedback to organizations Balanced scorecards are common among companies in the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan, and Europe. Balanced Scorecard David Norton and Robert Kaplan -1992
- 46. BSC can be Immensely Powerful In Helping Organization To Createa tangibleroad –map from the “ current state” to a more successful future state. Identify major roadblocks and areas where you lack the critical competencies to proceed to the next stage Articulate how your goals will directly helpthe organization to move upwards through the stages Prioritize business activities in the order they need to be tackled to allow the most rapid progression through the stages.
- 47. 2017 survey - (2CG - strategic execution consultancy firm) •77% report that their Balanced Scorecard is extremely or very useful. •75% use the Balanced Scorecard to influence business actions. •Of the 64% of organizations that have refreshed their Balanced Scorecard, the majority—71%—did so during the previous 12 months. •The Balanced Scorecard is used by both small and large organizations: 61% of respondents had less than 500 employees, and 9% had over 10,000 employees.
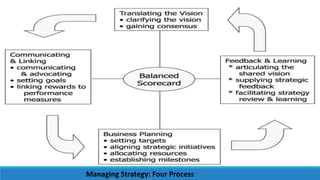
- 48. Managing Strategy: Four Process
- 49. Finance Customer Internal Business Process Learning and Growth The balanced scorecard involves measuring four main aspects of a business
- 50. Learning and Growth This perspective is also called “organizational capacity.” It looks at organizational performance through the lens of human capital, culture, technology, and infrastructure. The learning and growth perspective considers how well information and knowledge are captured and implemented by employees to create a competitive advantage. For instance, are your employees using your technology stack to execute tasks and manage processes? Does your organization provide adequate training and resources? What steps are you taking to remain competitive?
- 51. INTERNAL BUSINESS PROCESSES The next perspective focuses on how well your internal processes are operating. Are there gaps, delays, or bottlenecks in the pipeline that need to be addressed? How can you streamline your processes for greater efficiency and effectiveness? How quickly can your organization adapt to changing business needs or conditions?
- 52. Customer The customer perspective asks, “What is important to our customers and stakeholders?” This perspective focuses on finding new customers, building brand recognition and trust, and increasing customer satisfaction. In other words, how well are you serving your customers and the stakeholders your organization was designed to serve?
- 53. Financial The final piece of the puzzle is the organization’s financial state. Finances are lagging indicators of past decisions; they are still an important part of any organization’s health and key to understanding overall performance and creating strategies for the future. Clear long-range targets for profit seeking organizations, operating in a purely commercial environment
- 57. Objective Measurement Target Grow Revenues Sales growth 10% Increase Firm value Market Value 10% Grow profit Net Income 15% Make customer happy Satisfaction Survey 10 rating Keeping customers coming back % customers who return 85% Targeting new customers % of new customers 10% Provide fast customer service second or a minute to serve customers 30secs -1 min Offer many new interesting products number of stock keeping units 100 Build employees skill Hours of training 10 hrs/m Stay informed of customer's taste survey- Face book/link 1/m Cu st om er Internal Process Le a r ni ng a nd Gr owt h Finance Ba l a nce d Scor e ca r d wit h St r a t e g y Ma pping Delicious Biryani Theme/ Vis ion: Opertional excellence and Innovation Strategy Sales Revenue Firm Valve Profit Customer Satisfaction Customer retention New Customer Prompt Service Product Variety Train employees Stay with current trends
- 58. Balanced Scorecard for an E-Commerce Business
- 59. Rationale for the Balanced Scorecard
- 60. Elements of Good Performance Appraisal System Aligning individual performance expectations with the organizations Vision and values Measuring key results and competencies Appraising against clearly defined performance expectations Working together to develop performance expectations Providing frequent and timely feedback Conducting performance appraisals as scheduled Encouraging employees to conduct self appraisal Evaluating employee performance against established performance standards Scheduling training on the appraisal process Demonstrating organizational commitment
- 61. Process of Performance Monitoring Performance appraisal Performance monitoring Identify gaps in planned performance and actual performance Discuss, provide feedback and develop improvement plan Seek employee commitment and verify
- 62. Reward Management Organizational values and want to pay for For the value they create or the organization Right behavior and actions Foster and maintain high performance work culture Motivate employee –to obtain commitment and engagement Attract and retail talents Emphasize the right mix of financial and non-financial rewards Operate in ways that are fair,equitable,consistent and transparent
- 63. Nutshell – Trident Group Performance Planning Organizational goal setting and finalization of balance score Individual goals/KPI Evaluation Framework Goal Key initiatives Competencies and values Roles and traits Evaluation framework Mid year review Self Appraisal Rating and appraisal by the appraiser Feedback discussion with appraiser Approval thought by review committee Appeals procedure if any Coaching and feedback session Output of Performance review Input for training and development Input for promotions/increment / transfer decisions