POL 140, "The Bureaucracy"
- 1. POL 140 Fall 2014
- 7. Charged with carrying out responsibilities of federal government Includes executive branch departments, agencies, boards, and commissions
- 9. Cabinet-Level Departments Independent Agencies Regulatory Boards and Commissions Government Corporations
- 11. Fifteen Departments Secretary appointed by president What issues fall under the cabinet? Foreign Relations Agriculture Education
- 13. Enforce regulations and create policy Single head appointed by president Narrow areas of jurisdiction Size varies
- 14. Agency run by a small number of officials Appointed by the president, serve a fixed term Sector of economy or political arena Federal Communications Commission Food and Drug Administration
- 15. Service NOT provided by private business
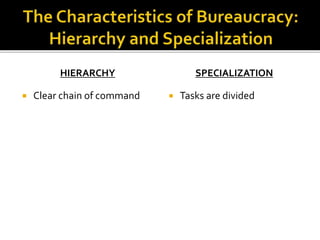
- 17. Hierarchy Specialization Explicit Rules Merit Max Weber
- 18. HIERARCHY Clear chain of command SPECIALIZATION Tasks are divided
- 19. EXPLICIT RULES Limited in personal discretion Standardization and predictability MERIT Hiring and promotions based on objective criteria Subjective measures (e.g. family connections) should NOT play role
- 21. Administrator Rule Maker Judge
- 22. Implements and administers laws Serves in professional and non-partisan way Examples: Park Rangers Police Officers
- 23. Writes details of legislation Bureaucracy is delegated legislative authority, known as bureaucratic discretion Importance of judgment Decisions not without safeguards Federal Register and Public
- 24. Interpreting the law in certain cases “Rules of the Game” Responsible for ensuring compliance Rulings can be overturned by Congress
- 26. Appointment Power The Budget Process Government Reorganization “The Power of Persuasion”
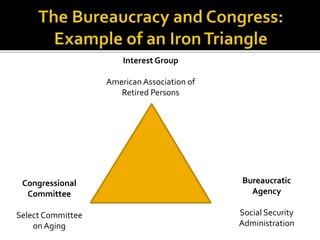
- 27. Relationship between government actors: Congressional Committee Interest Group Bureaucratic Agency
- 28. Congressional Committee Select Committee on Aging Interest Group American Association of Retired Persons Bureaucratic Agency Social Security Administration
- 29. Powerful check Members’ views on implementation Committees with jurisdiction over an issue can request agency testify before them Congress sets funding levels for agencies
- 30. Agencies sued by individuals and businesses Courts play minor role in process Bureaucratic deference Agencies being out of Court’s reach Time constraints