Poms2017_Hemila
- 1. VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Best practices from lean startup innovation processes to traditional manufacturing industries innovations POMS2017, 6th May, Seattle, USA Senior Scientist Jukka Hemilä (jukka.hemila@vtt.fi)
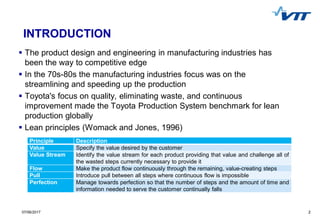
- 2. 207/06/2017 2 INTRODUCTION The product design and engineering in manufacturing industries has been the way to competitive edge In the 70s-80s the manufacturing industries focus was on the streamlining and speeding up the production Toyota's focus on quality, eliminating waste, and continuous improvement made the Toyota Production System benchmark for lean production globally Lean principles (Womack and Jones, 1996) Principle Description Value Specify the value desired by the customer Value Stream Identify the value stream for each product providing that value and challenge all of the wasted steps currently necessary to provide it Flow Make the product flow continuously through the remaining, value-creating steps Pull Introduce pull between all steps where continuous flow is impossible Perfection Manage towards perfection so that the number of steps and the amount of time and information needed to serve the customer continually falls
- 3. 307/06/2017 3 RESEARCH DESIGN European companies are over designing and engineering products before commercialization. Together lean thinking and agile methods have been successfully applied to product development at startup companies, which is called the lean startup methodology However, many lean startup principles may also be of benefit to established firms. The research question: how to improve mature (age 5+ years) companies’ product innovation lifecycle and time-to-market in traditional product-based businesses? The study is based on the state-of-the-art of innovation processes in startups from the literature review and on the empirical case data evidence from the multiple case studies. The outcome is a four-stage innovation lifecycle model.
- 4. 407/06/2017 4 INNOVATIONS AND TIME TO MARKET IN STARTUPS Innovation is the core for the startup: should provide something new for the market, or otherwise their existence is questioned Time to market innovation process is really fast, or otherwise the entire business opportunity might be lost. In product development, the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a product with just enough features to gather validated learning about the product and its continued development. The concept of MVP is hardly heard by mature companies’ employees. Startups are focusing to solve some customer problems and create business model to solve that customer problem. Only then startups are developing real product, and firstly MVP. Mature companies have a business plan how to operate, and product innovations are done in linear or step-by-step methods.
- 5. 507/06/2017 5 NEW METHOD FOR ACCELERATION IDEA TO MARKET IN MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIES Acceleration: the study understands acceleration as accelerating innovation go-to-market and commercialization. Acceleration is a combination of means: processes, tools and methods, which help companies go faster to the right markets It is time for mature companies to change their innovation culture towards their origins, the way successful startups are innovating. Companies should focus on searching for a product-market fit and a sustainable, scalable, profitable business model Mature companies, the business model is not typically changed. focus on the development of new product, which does not actually bring competitive advantage today. Product innovation should be continuous and lean process: Idea stage, Problem/Solution Fit, Product/Market Fit, Scaling
- 6. 607/06/2017 6 DIFFERENT STAGES OF ACCELERATION Self-test available: http://selftest.accelerateproject.eu/
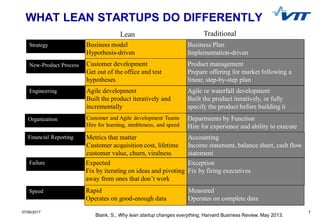
- 7. 707/06/2017 7 WHAT LEAN STARTUPS DO DIFFERENTLY Strategy Business model Hypothesis-driven Business Plan Implementation-driven New-Product Process Customer development Get out of the office and test hypotheses Product management Prepare offering for market following a linear, step-by-step plan Engineering Agile development Built the product iteratively and incrementally Agile or waterfall development Built the product iteratively, or fully specify the product before building it Organization Customer and Agile development Teams Hire for learning, nimbleness, and speed Departments by Function Hire for experience and ability to execute Financial Reporting Metrics that matter Customer acquisition cost, lifetime customer value, churn, viralness Accounting Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement Failure Expected Fix by iterating on ideas and pivoting away from ones that don’t work Exception Fix by firing executives Speed Rapid Operates on good-enough data Measured Operates on complete data Lean Traditional Blank, S., Why lean startup changes everything, Harvard Business Review, May 2013.
- 8. 807/06/2017 8 CONCLUSIONS A lean product development helps companies to launch products that customers actually want, and more quickly and cheaply than traditional methods. To ensure survival and growth, mature and even large companies need to keep inventing new business models Traditional manufacturers have usually long technology development cycles, which actually has been one of the main reasons for startups to failure Our model suggest improving design, engineering and product launch time in traditional companies. Self-test available: http://selftest.accelerateproject.eu/