PPT (1).pptx
- 1. SDLC Models 1. Water Fall Model 2. V Model 3. Spiral Model 4. Agile Model Water Fall Model: The waterfall model is a classical model used in system development life cycle to create a system with a linear and sequential approach. It is termed as waterfall because the model develops systematically from one phase to another in a downward fashion. This model is divided into different phases and the output of one phase is used as the input of the next phase. Every phase has to be completed before the next phase starts and there is no overlapping of the phases. The sequential phases described in the Waterfall model are: 1. Requirement Gathering- All possible requirements are captured in product requirement documents. 2. Analysis Read - the requirement and based on analysis define the schemas, models and business rules. 3. System Design -- Based on analysis design the software architecture. 4. Implementation Development of the software in the small units with functional testing. 5. Integration and Testing Integrating of each unit developed in previous phase and post integration test the entire system for any faults. 6. Deployment of system - Make the product live on production environment after all functional and nonfunctional testing completed. 7. Maintenance Fixing issues and release new version with the issue patches as required.
- 3. Advantages of waterfall model • This model is simple and easy to understand and use. • It is easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model – each phase has specific deliverables and a review process. • In this model phases are processed and completed one at a time. Phases do not overlap. • Waterfall model works well for smaller projects where requirements are clearly defined and very well understood. Disadvantages of waterfall model • Once an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go back and change something that was not well-thought out in the concept stage. • No working software is produced until late during the life cycle. • High amounts of risk and uncertainty. • Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects. • Poor model for long and ongoing projects. • Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate to high risk of changing.
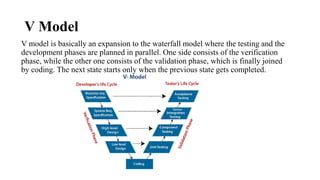
- 4. V Model V model is basically an expansion to the waterfall model where the testing and the development phases are planned in parallel. One side consists of the verification phase, while the other one consists of the validation phase, which is finally joined by coding. The next state starts only when the previous state gets completed.
- 5. When To Use The V Model? • When the requirements are pre-defined. • The project’s acceptance criteria are well defined. • The project is neither too small nor too complex. • Resources are stable. • Tools and technology implied are not dynamic. • There are no prototypes produced; therefore, only choose this model when you are highly confident of your user requirement.
- 6. Spiral Model This model is a combination of a Waterfall and Spiral model, and it works in an iterative manner. Based on the risk involved in the project, this model guides the team to adopt elements of one or more SDLC models such as a waterfall or Iterative model. Here the lifecycle of Software is divided into smaller parts, and new functionality can be added to the software even at the late stages of SDLC.
- 7. The spiral model has some advantages compared to other SDLC models: • Suitable for large projects: Spiral models are recommended when the project is large, bulky or complex to develop. • Risk Handling: There are a lot of projects that have un-estimated risks involved with them. For such projects, the spiral model is the best SDLC model to pursue because it can analyze risk as well as handling risks at each phase of development. • Customer Satisfaction: Customers can witness the development of product at every stage and thus, they can let themselves habituated with the system and throw feedbacks accordingly before the final product is made. • Requirements flexibility: All the specific requirements needed at later stages can be included precisely if the development is done using this model.
- 8. Agile Model Agile SDLC model is a combination of iterative and incremental process models with focus on process adaptability and customer satisfaction by rapid delivery of working software product. Agile Methods break the product into small incremental builds. These builds are provided in iterations.
- 9. • What is Quality? Quality refers to the conformance to implicit or explicit requirements, expectations, and standards. In order to fulfil these requirements, a quality control mechanism is set up. • What is Software Testing? Software Testing is a method to check whether the actual software product matches expected requirements and to ensure that software product is Defect free. • Why testing is necessary? The testing is important since it discovers defects/bugs before the delivery to the client, which guarantees the quality of the software. It makes the software more reliable and easy to use. • Who does the testing? Testing Team • What has to be tested? When is testing done? How often to test? What is cost of Quality? What are Testing Standards?