PPT The Sun.ppt
- 1. THE SUN
- 2. Is the Sun a star? • The Sun is the closest star to Earth. • It makes its own heat and light. • The earth orbits around the sun. • It gives the earth heat and light.
- 4. Sun’s Energy • 37)Suns’ Energy is generated by Nuclear Fusion. • Hydrogen to Helium
- 5. LARGEST… • The Sun is the largest object in the solar system! • Example: Mass 333,000 x Earth or 1000 x Jupiter • 32)Approximately 99% of the solar system is located in this celestial object.
- 6. The Sun and planets, shown to scale. Earth is the small blue dot in the middle of the box.
- 7. LAYERS OF THE SUN • Major Regions: Interior (“Inner-sphere”) • Core • Radiative Zone • Convective Zone Atmosphere (“Outer-sphere”) • Photosphere • Chromosphere • Corona No real “surface” - it is gaseous all the way to the center!
- 8. What is the hottest portion/part of the sun? • 35)The CORE! • Location of Sun’s energy generation by nuclear fusion.
- 9. Radiative zone • The radiative zone of the solar interior is characterized by the process of radiation.
- 10. Convection Zone • The convection zone is a region of the Sun where hot and cooler gases circulate in convection currents.
- 11. Now lets look at the… OUTER-SPHERE OR ATMOSHPHERE OF THE SUN
- 12. ATMOSPHERE… • The atmosphere of the sun is composed of several layers, mainly the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona.
- 13. PHOTOSPHERE • The lowest layer of the sun's atmosphere is the photosphere. • Coolest layer of the sun
- 14. CHROMOPSHERE • The next layer is the chromosphere. The chromosphere emits a reddish glow as super-heated hydrogen burns off.
- 15. CORONA • The third layer of the sun's atmosphere is the corona. • It can only be seen during a total solar eclipse as well. It appears as white streamers or plumes of ionized gas that flow outward into space. • As the gases cool, they become the solar wind.
- 16. Solar Eclipse
- 18. • 39) A solar flare is a violent explosion above the suns surface. • A large amount of energy is released.
- 20. • Solar flares may last for 10 minutes and will produce more energy than a MILLION hydrogen bombs. • This results in the production of a magnetic field that interacts with the earth’s magnetic field.
- 21. • When this occurs on the Sun, the Earth can experience problems with satellite communications.
- 23. • Sunspots appear as dark spots on the surface of the Sun. • They typically last for several days, although very large ones may live for several weeks.
- 24. • 38)Sunspots are the coolest locations on the surface of the Sun! • Appears dark only because its gases are a few thousand degrees cooler than surround gas….so it radiates less energy.
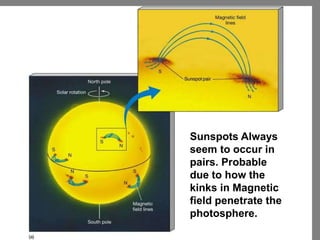
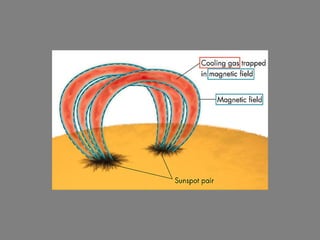
- 25. Sunspots Always seem to occur in pairs. Probable due to how the kinks in Magnetic field penetrate the photosphere.
- 27. • The solar wind is a stream of energized, charged particles, primarily electrons and protons, flowing outward from the Sun.
- 28. • They cause magnetic storms! • Auroras, called the northern lights, occur when layers of our atmosphere are energized by solar winds.
- 29. • The solar wind is what blows the tails of comets back away from the bodies of comets as they go through the solar system.