PPT TRAINING
- 1. 6- MONTHS TRAINING AT TELCOCRATS PVT. LIMITED NAME-AAKASH SHARMA ROLL NO-CUN120102001 ECE-X1
- 2. INDEX • TOPICS • PREFACE • INTRODUCTION TO GSM • EVOLUTION OF G • GSM ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW • CELL NETWORK AREAS • FREQUENCY SPECTRUM • PROJECTS /SOFTWARES DONE AT TRAINING • DRIVE TEST • RF PLANNING(3G PLANNING) • PLANNING AND OPTIMISATION • ATOLL SOFTWARE(RESULTS) • CONCLUSION
- 3. PREFACE 1. This training is based on the telecommunication. The network planning is not only to define the initial network roll-out targets, but also to provide moving targets to the continuous process that takes the whole life time of the network. Before the2G and 3G network is launched, all the work is focused on estimating how the network should look like. After the network launch customer intake and behavior will decide the network development direction. 2. The most demanding tasks are to gather all the required information for the planning work and making the network roll-out decisions based on all these estimations, operator demands and assumptions of future costs. Cost estimations are usually very sensitive to the changes in basic assumptions and it is crucial that all assumptions are recorded to the network roll-out plan.
- 4. 1. Introduction to GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) • The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a set of recommendations and specifications for a digital cellular telephone network (known as a Public Land Mobile Network, or PLMN). • These recommendations ensure the compatibility of equipment from different GSM manufacturers, and interconnectivity between different administrations, including operation across international boundaries. • GSM networks are digital and can cater for high system capacities.
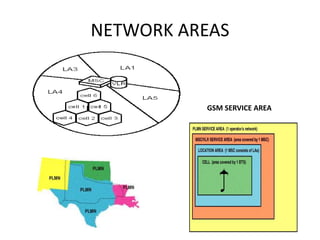
- 7. CELL • A cell is the basic unit of a cellular system and is defined as the area where radio coverage is given by one base station. Different cells are identified by a unique number called Cell Global Identity (CGI). In a complete network the number of cells is large. • There are a limited number of frequencies available within the frequency band specified for cellular systems. Each operator licensed to run a cellular network, has been provided with a number of frequencies. A cell has one or several frequencies, depending on traffic load. To cover a country, for example, the available frequencies must be reused. The same frequency cannot be used in neighboring cells due to interference
- 8. NETWORK AREAS GSM SERVICE AREA
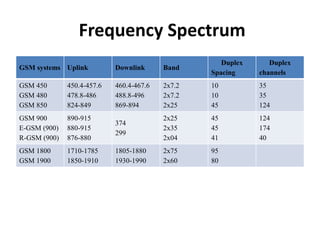
- 9. Frequency Spectrum GSM systems Uplink Downlink Band Duplex Spacing Duplex channels GSM 450 GSM 480 GSM 850 450.4-457.6 478.8-486 824-849 460.4-467.6 488.8-496 869-894 2x7.2 2x7.2 2x25 10 10 45 35 35 124 GSM 900 E-GSM (900) R-GSM (900) 890-915 880-915 876-880 374 299 2x25 2x35 2x04 45 45 41 124 174 40 GSM 1800 GSM 1900 1710-1785 1850-1910 1805-1880 1930-1990 2x75 2x60 95 80
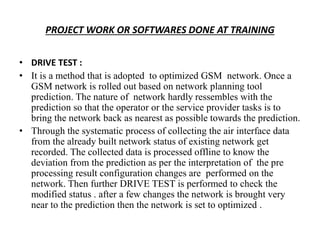
- 10. PROJECT WORK OR SOFTWARES DONE AT TRAINING • DRIVE TEST : • It is a method that is adopted to optimized GSM network. Once a GSM network is rolled out based on network planning tool prediction. The nature of network hardly ressembles with the prediction so that the operator or the service provider tasks is to bring the network back as nearest as possible towards the prediction. • Through the systematic process of collecting the air interface data from the already built network status of existing network get recorded. The collected data is processed offline to know the deviation from the prediction as per the interpretation of the pre processing result configuration changes are performed on the network. Then further DRIVE TEST is performed to check the modified status . after a few changes the network is brought very near to the prediction then the network is set to optimized .
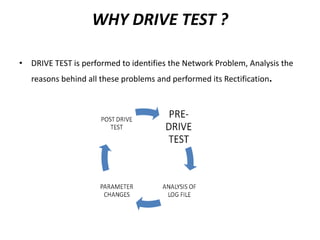
- 11. WHY DRIVE TEST ? • DRIVE TEST is performed to identifies the Network Problem, Analysis the reasons behind all these problems and performed its Rectification.
- 12. RF PLANNING(3G) • Project description: • Introduction • In the context of mobile and cellular communication systems, RF Planning is the process of assigning frequencies, transmitter locations and parameters of a wireless communications system to provide sufficient coverage and capacity for the services required (e.g. mobile telephony). The RF plan of a cellular communication system revolves around two principal objectives; Coverage and Capacity Coverage relates to the geographical footprint within the system that has sufficient RF signal strength to provide for a call/data session. Capacity relates to the capability of the system to sustain a given number of subscribers. In 3GPP GSM systems, both capacity and coverage are interrelated. To improve quality some coverage, capacity has to be sacrificed, while to improve capacity, coverage will have to be sacrificed.
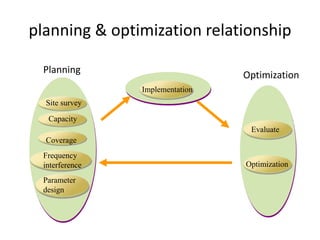
- 13. Site survey Capacity Coverage Frequency interference Parameter design Implementation Optimization Evaluate Planning Optimization planning & optimization relationship
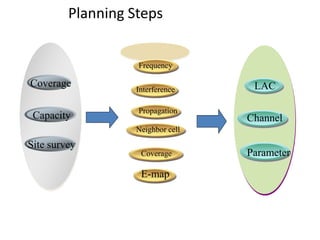
- 14. Planning Steps Coverage Capacity Site survey Frequency Interference Propagation Neighbor cell Coverage LAC Channel Parameter E-map
- 15. Data Collection • Data of network plan – Network basic information collection • The base of network plan and optimization – The engineering survey data of new sites – Confirm the network plan information. – The Engineering data of the current network – Understand the current network . – The configuration NMS data. • Understand the current network configuration. Collection of various performance reports of the currently deployed network. – Subscribers’ complain – The supplement information showing the network quality. Let’s begin!
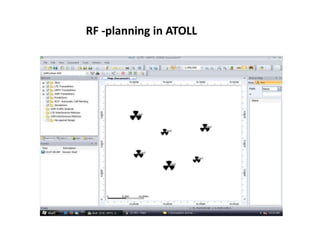
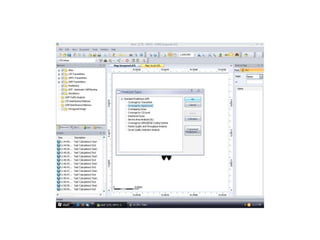
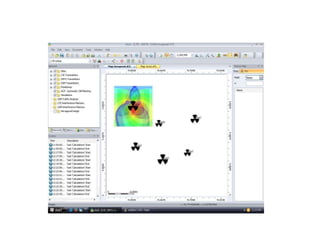
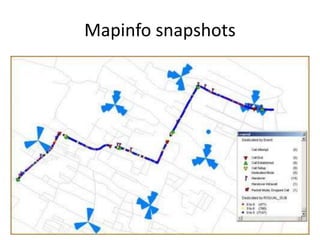
- 16. RF -planning in ATOLL
- 22. CONCLUSION • Working knowledge of GSM, WCDMA network technologies and architecture Working knowledge Cell planning and Optimization. • An introduction to LTE system architecture and air Interface Knowledge of Protocols and radio network functionality of LTE Systems • Learn how to plan an efficient LTE radio network Gain a clear understanding of the OFDMA principle and application within LTE • Understand the role of MIMO and Adaptive antennas to improve performance in LTE systems • Coverage and Capacity planning in LTE systems • Detailed planning and analysis using industry leading tool Forks • ATOLL Optimization and Site Selection through Automatic cell Planning tool. • Designing and optimizing an example network An overview of Initial tuning and Drive Test data analysis for optimization