Prepositions
- 1. PREPOSITIONS, CONJUNCTIONS, AND INTERJECTIONS 6th Grade Language Arts and Reading AMS
- 2. PREPOSITIONS Introduction Activity Write a few sentences that explain how to find the closest public library. Put your sentences aside for now. Let’s watch the video link on the next slide and then we will share our sentences underlining the prepositions we used to give the directions.
- 3. PREPOSITIONS Watch the video linked below to find out what a preposition is and listen for some examples of words that are prepositions as well! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =j-C7Rffelb8&feature=bf_prev&list =PL4E423BB171CD8715&lf=results_main Go back to your sentences and share them with your partner and underline any prepositions like down, to, under, near, on, around, and so on….
- 4. PREPOSITIONS Answer these questions after the video! What is a preposition? A preposition is a word that relates a noun or a pronoun to some other word in a sentence. Examples: The dictionary on the desk was open. An almanac was under the dictionary. Meet me at three o’clock tomorrow.
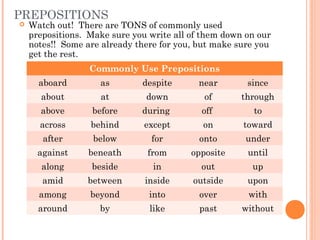
- 5. PREPOSITIONS Watch out! There are TONS of commonly used prepositions. Make sure you write all of them down on our notes!! Some are already there for you, but make sure you get the rest. Commonly Use Prepositions aboard as despite near since about at down of through above before during off to across behind except on toward after below for onto under against beneath from opposite until along beside in out up amid between inside outside upon among beyond into over with around by like past without
- 6. PREPOSITIONS A preposition can consist of more than one word. Example: I borrowed the dictionary along with some other reference books. Prepositions of MORE than one word according to along with because of in spite of on top of across from aside from in front of instead of out of
- 7. PREPOSITIONS Read the sentences below. Fill in the blank using a preposition. Use the dictionary that is __________ the table. I took the atlas ________ your room. Notice several prepositions fit each sentence. The preposition you use changes where the item is that you are connecting in the sentence.
- 8. PREPOSITIONS Day 1 Activity and Homework
- 9. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Introduction Activity: Write a sentence or two that tells where and when you might read a book. Share your sentences with your table. Underline the prepositions in the sentence based off of yesterday’s lesson.
- 10. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Now let’s talk about prepositional phrases! A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun, which is called the object of the preposition. Examples: Mr. Fromwiller has an almanac from the nineteenth century. Preposition Object of preposition (noun) The almanac has a special meaning for him. Preposition Object of preposition (pronoun)
- 11. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Now go back to your introduction activity sentences and underline the prepositional phrase. Draw an arrow from the preposition to the noun/pronoun that is the object of the preposition. Example: We met in front of the library at noon. In front- tells where Of the library- tells where At noon- tells when
- 12. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Prepositional Phrases: can have a compound (more than one) object. Examples: Almanacs contain lists of facts and figures. Grace shows one to her sisters and her classmates. Prepositional Phrases: can have more than one prepositional phrase Example: We left our notes under the almanac on the shelf.
- 13. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Prepositional Phrases: Can appear anywhere in the sentence- at the beginning, in the middle, or at the end. Examples: At the library students examind the almanac. Students at the library examined the almanac. Students examined the almanac at the library.
- 14. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Day 2 Activity and Homework
- 15. PRONOUNS AFTER PREPOSITIONS Introduction Activity Read the sentence below. Tell what is wrong with it and then write it correctly. Lisa’s dog ran to Lisa, jumped on Lisa, and stole a cookie with Lisa. Remember back to our pronoun unit? We use pronouns to replace nouns to avoid using nouns over and over. Now that you have corrected the sentence find the prepositions and circle them. Then, Underline the prepositional phrases, and draw an arrow from the preposition to the pronoun in the prepositional phrase.
- 16. PRONOUNS AFTER PREPOSITIONS When a pronoun is the object of a preposition, remember to use an object pronoun and not a subject pronoun. Example: Michael handed the dictionary to Sarah. Replace Sarah with object pronoun- HER Michael handed the dictionary to her.
- 17. PRONOUNS AFTER PREPOSITIONS Sometimes a preposition will have a compound object consisting of a noun and pronoun. Remember to use an object pronoun in a compound object. Example: I borrowed the dictionary from Sam and Jacob. Replace Jacob with object pronoun HIM I borrowed the dictionary from Sam and him. How do you know to use HIM rather than HE? Test it out- try saying the sentence aloud with only the pronoun following the preposition. I borrowed the dictonary from him (NOT he).
- 18. PRONOUNS AFTER PREPOSITIONS Confusing WHO and WHOM The pronouns who and whom are often confused. Who is a subject pronoun, and whom is an object pronoun. Note how the pronouns are used in the following sentences: Who told you about it? (Who is the subject) To whom did you lend the almanac? ( whom is the object) YOU is the subject of the sentence
- 19. PRONOUNS AFTER PREPOSITIONS Day 3 Activity and Homework
- 20. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES AS ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS Introduction activity Before starting today’s lesson, let’s learn a song to help us remember some of those commonly used prepositions!! Follow along singing to the tune of Twinkle, Twinkle little star!
- 21. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES AS ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS Preposition Song (To the tune of Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star) At, around, above, about Over, nearer, nearest, out For, becoming, after, through From, beneath, beyond, of, to Since, beside, between, by, at Off, on, up, along, into
- 22. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES AS ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS Now that we reviewed some of the many prepositions that are out there, write FIVE sentences that have at least one prepositional phrase in each. We will come back to those sentences at the end of our lesson.
- 23. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES AS ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS Prepositional phrases function as adjectives and adverbs in sentences. A preprepositional phrase functioning as an adjective describes a noun or pronoun. These phrases usually come directly after the noun or pronoun it describes. Example: (underline the prepositional phrase, and then draw an arrow to the noun/pronoun it is describing) Africa is continent with many natural resources. One of the articles describes Africa vividly. The wildlife of Africa is varied and abundant.
- 24. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES AS ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS A prepositional phrase functioning as an adverb describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Adverb Phrases Function Examples Describes a VERB Wildlife abounds in Africa. Dry savannas extend over many acres. Describes an ADJECTIVE Birds are exotic in color. Describes an ADVERB The Nile River flow west of Cairo.
- 25. PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES AS ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS Go back to the sentences you wrote at the beginning of the lesson. Now, exchange papers at your tables. Draw a line from each prepositional phrase in the sentence to the word being described. Day 4 Activity and Homework
- 26. TELLING PREPOSITIONS AND ADVERBS APART Introduction Activity: Let’s practice our song we learned from yesterday first! Now, I would like you to create FOUR sentences using the following words: ABOVE OVER INSIDE BEFORE For each sentence write the word or words that answer the question where? Or when? Example: The clock is above the door. Where is the clock? (above the door)
- 27. TELLING PREPOSITIONS AND ADVERBS APART Sometimes it is difficult to tell whether a word is a preposition or an adverb. Both types of words can answer the questions: Where? And When? as we just saw with our introduction activity. Several words are commonly used as prepositions and adverbs. These are the words you want to look at carefully when you see them! Words that can be used as Prepositions or Adverbs about below out above down outside around in over before inside through behind near up
- 28. TELLING PREPOSITIONS AND ADVERBS APART Having trouble decided whether a word is used as preposition or adverb? LOOK at the other words in the sentence Followed closely by a noun- it is most likely a preposition and it is the object of the preposition. A preposition will be followed by the prepositional phrase, whereas the adverb will not. Examples: We ate our lunch outside the library. Preposition or Adverb? Preposition OUTSIDE is followed by LIBRARY prepositional phrase: outside the library. We ate our lunch outside. Adverb OUTSIDE answeres the question where? But is not followed by a noun, which makes it an adverb in this sentence.
- 29. PREPOSITIONS Wrap up video: http:// www.brainpop.com/english/grammar/prepositionalphrases / Day 5 Activity and Homework
- 30. CONJUNCTIONS Introduction Activity On your notes, write four sentences using each of the following conjunctions: AND, BUT, OR, EITHER Volunteers to share sentences on board? What does each conjunction connect? Underline the words in your sentences that the conjunctions connect
- 31. CONJUNCTIONS Now that you can see conjunctions connect things, lets find out what types of things they connect Watch the video and listen for what types of things conjunctions connect AND other examples of conjunctions! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =eZqI5b5wGA4&feature=related
- 32. CONJUNCTIONS Fill in your notes as you follow along A conjunction is a word that joins words or groups of words in a sentence. The most common conjunctions are: And But Or They are called Cordinating conjunctions
- 33. CONJUNCTIONS What do and, but, and or combine? Using Conjunctions to Form Compounds Compound Mrs. O’Toole and Mr. Malloy are both science Subject teachers at Kenston. Compound Students can draw an elephant or a lion. Predicate Compound I would lend you my pencil, but Andrea already Sentence borrowed it.
- 34. CONJUNCTIONS A comma should be placed before the conjunction in a compound sentence. BE CAREFUL!! Conjunctions are all used to join words or groups of words together. However, they are not interchangeable. Each has a different meaning. Coordinating Conjunctions Conjunction Meaning Example AND Introduces an additional idea The pizza and pop were so tasty. BUT Introduces contrasting ideas Mrs. Cingcade likes chocolate cake, but she enjoys cheesecake even more. OR Introduces a choice or second Mrs. Miller could eat a chicken possibility or turkey sandwich for lunch.
- 35. CONJUNCATIONS Conjunctions ALSO come in PAIRS! These pairs are called correlative conjunctions. Examples: Either, or Neither, nore Both, and Either Jake or I will hit a home run tomorrow!
- 36. CONJUNCTIONS Day 6 Activity and Homework
- 37. INTERJECTIONS Watch the video and listen for what types of words interjections are! http://www.schooltube.com/video/5eb2d59975159f0343b7/Sc
- 38. INTEJECTIONS An interjection is word or group of words that expresses strong feeling. Common Interjections aha great oh phew awesome ha oh, no well come on hey oops wow gee hooray ouch yes
- 39. INTERJECTIONS Expressing a strong feeling: May stand alone Either before or after a sentence Followed by an exclamation mark Example: Oh no! I wrote there instead of their.
- 40. INTERJECTIONS Expressing a milder feeling: Appears as part of the sentence Separated from the rest of the sentence by a comma Example: Oh, I thought I knew the definition of that word. Use interjections sparingly. Overuse ruins the effect.
- 41. INTERJECTIONS Day 6 Activity and Homework