Presentation earth and space
- 1. Earth and Space (1)
- 2. What is so fascinating about space and life beyond earth?
- 4. Is the earth round or flat?
- 6. Which is the largest?
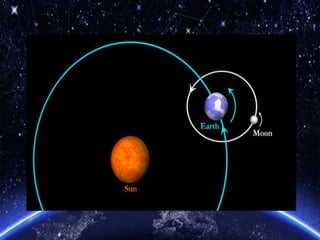
- 9. Are the Earth, Moon and Sun static? Or do they move about in some ways?
- 11. Orbits • The earth and other planets rotate around the sun. • The path they take is called an orbit. • The moon orbits earth NOT the sun. • The Earth ROTATES on its own axis. • The moon orbits the earth but also rotates on its own axis.
- 13. Day & Night
- 14. • The part of the earth that is facing the sun experiences day-time. • The part of the earth facing opposite the sun experiences night-time. • During night time in Malta, it means that Malta is facing away from the sun.
- 15. NO The sun is always “on” During night – time does that mean that the sun switches off?
- 16. What do we mean when we say the sun is “rising” or the sun is “setting? •The sun does not actually rise or set because it does not move. •It is the earth that moves about the sun. •On earth we see the sun rising from the East, this is due to rotation of the earth. •The sun sets in the west.
- 18. How long does it take for the earth to rotate about its own axis? •24hours •One whole DAY
- 20. How long does it take the earth to orbit the sun? • It takes a YEAR •365 days
- 21. What is a leap year? •To be very precise every year is 365 days and ¼ of a day. •¼ + ¼ + ¼ + ¼ = 1 •So that ¼ adds up to a whole day in one year. •Thus once every 4 years we have an extra day in February.
- 22. Do all the planets orbit the Sun in 365 days? • NO •The length of the cycle depends on the distance of the planet from the sun.
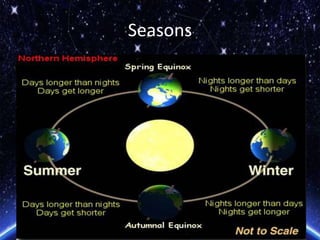
- 23. The seasons
- 24. • Winter days are cold and wet and humid. • Summer days are hot and dry. • Also winter days are shorter than summer days. • This is a cause of the different seasons on earth.
- 25. During our summer people in Australia have winter. We celebrate our Christmas in the cold and snow, whereas people in Australia celebrate it on the beach.
- 26. Why do we have seasons? How do seasons occur?
- 27. Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceMechanism of The Seasons.flv
- 28. The seasons are caused by 3 factors: • The revolution of the Earth around the Sun. • The tilt of the earth’s axis of rotation with respect to the sun, which is 23.5 degrees. • The tilt of the earth’s axis remains constant throughout its orbit around the sun.
- 29. Seasons
- 30. Why are winter days shorter than summer days? • During winter the angle of the sun is lower than it is in summer. • This gives it less time to heat the earth. • In summer the angle of the Sun is higher. • This gives us long hot summer days.
- 31. The Sun’s Changing Position •In summer since it is higher it takes longer to go from one horizon to the other. •This gives rise to shorter shadows. •In winter since the sun is lower there is longer shadows.
- 32. Do other planets with different TILTS have the same seasons as Earth? •NO •Planets with different tilts have different seasons •Earth Mars and Saturn have the closest tilts. •Planets with no tilts have no seasons. •Planets with 90o tilt have extreme seasons
- 33. THE MOON
- 35. Interesting facts •The moon is not a planet, but a satellite of the Earth. •The surface area of the moon is 9.4 billion acres (3.8x1013 square meters). • Only 59% of the moon’s surface is visible from earth. •The moon is the only body that is in outer space that has been visited by humans and had samples taken from it. •The moon’s diameter is about ¼ the diameter of the Earth. About 49 moons would fit inside Earth.
- 37. Why do we only see one side of the moon? •The moon take 27.3 days to orbit the earth.
- 38. Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceSynchronous Rotation of the Moon.flv
- 39. Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceWhy does the moon change shape_.flv
- 40. Moon Phases: New Moon The moon is exactly in line between the earth and the sun and all the light is being reflected on the back side of the moon thus the part of the moon facing earth has no light hitting it and as a result we do not see a moon.
- 41. Waxing Crescent The moon is at a 45o angle from the earth, here just a sliver of brightness is visible on the right
- 42. First Quarter The moon is on the left of the earth and sun (moving anti-clockwise), here the sun’s rays shine on the half of the moon facing it, so now half of it is visible from earth. And thus we call this the half moon.
- 43. Waxing Gibbous Here it is the first time that there is a shift between the brighter side and the darker side. Here there is more of the bright side showing than the dark side.
- 44. Full Moon Here the sun, earth and moon are once again in line, but now the illuminated side of the moon is facing the earth, thus we see the entire moon.
- 46. Waning Gibbous Here the right edge of the moon appears to be invisible/dark. Moon is in the position opposite where it is during the waxing gibbous.
- 48. Last/Third Quarter The moon is to the right of the earth and sun, the sun’s light only falls on the side of the moon facing it and here there also appears to be a half moon. The side that is bright now is opposite where it was during the first quarter since now it is on the opposite side of the earth.
- 50. Waning Crescent This occurs just before the new moon, only a small slice of the bright side shows on the left edge closest to the sun.
- 52. HOMEWORK
- 53. Solar Eclipse What is an Eclipse?
- 54. What is the difference between a Solar and a Lunar Eclipse?
- 55. Are all eclipses dangerous? •Lunar Eclipses are not dangerous •Partial solar eclipses are the most dangerous. •During a full solar eclipse it is not dangerous.
- 56. Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceWhat Is A Solar Eclipse_.flv
- 57. •What makes it a Solar Eclipse? The moon orbit the earth every 27.3days, then why don’t we have 13 eclipses in a year? •This is due to the moon’s 5o tilt.
- 58. Can a solar eclipse be seen from all over the World? No
- 59. Solar Eclipse - Diagram
- 60. • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceThe Solar Eclipse In Varanasi - Wonders of the Solar System - Series 1 Episode 1 Preview - BBC Two.flv
- 61. Lunar Eclipse What is a lunar Eclipse? Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceWhat Is A Lunar Eclipse_.mp4
- 62. Lunar Eclipse Occurs when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and Moon, and the Moon is completely in the Earth’s shadow.
- 64. • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceNASA _ Lunar Eclipse Essentials.mp4
- 65. Lunar Eclipse - Diagram
- 67. The Solar System
- 69. • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceThe Solar System - Space School.mp4
- 70. Scavenger Hunt Rules • When you find a clue take only ONE. • Do not show your classmates where you found the clue. • Look carefully and responsibly! • No running! • No talking or screaming. • Leave everything the way you found it!
- 71. Is there life on other planets? • Water was detected in the atmosphere of 5 planets. • Water is a common constituent of other planet atmospheres. It has been found in the air of several other distant worlds. • A Planet sometimes called the Goldilocks zone for life has been found, this planet is not too hot or too cold, it is just right. • A single cell bacteria is considered life on other planets.
- 72. Gravity! • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceBest Idea Ever!.mp4 • All objects dropped, fall to the ground due to gravity! • Two objects dropped will hit the ground at the exact same time, independent of the weight. • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceGalileo's Gravity Demo.mp4
- 73. Gravity! • What happens when you decide to drop a sheet of paper and a ball? • What happens if the paper is crumpled? • What would happen if a sheet of paper and a ball are dropped from the same height in a vacuum? • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceFeather in Vacuum - Backstage Science.mp4
- 74. Gravity - Misconceptions • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceMisconceptions About Falling Objects.mp4
- 75. The Role of Gravity in the Solar System • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceWhy the solar system can exist.mp4 • How come planets orbit the Sun and not something else in our solar system? • The Sun is extremely large and has the biggest mass in the solar system. • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceWhat is Gravity_.mp4
- 76. Homework • Compare the gravity of the moon with that of earth and write down the effects of this difference. • Compare the gravity of other planets with that of earth and write down the effects of this difference. • Explain using gravity, how a rocket moves away from earth and stays in orbit.
- 77. Mass VS Weight MASS • Mass represents the quantity of an object. • The material plays a very big part in mass. • Mass is often measured in kilos and grams. • Mass is a measure of how much matter (material, particles) there is in an object. • Your mass is the same wherever you are—on earth, on the moon, floating in space-- because the amount of stuff you're made of doesn't change.
- 78. Mass VS Weight WEIGHT • Weight is a measure of how hard gravity is pulling on that object. • You would weigh less on the moon (smaller gravity) • In interstellar space you would weigh almost nothing (No Gravity). • If you stay on Earth, gravity is always the same.
- 79. Mass VS Weight
- 80. Why are MASS and WEIGHT both measured in Kgs? • Mass is measured in KGs but weight is measured in a unit called Newtons. • Newton is a unit of force/weight were 1 Newton is 1kgms-2 it is abbreviated to N. • Gravity makes a 1 kilogram mass exert about 9.8Newtons of force. So a 100kg mass really weighs about 980N on earth. • http://education.ssc.nasa.gov/video/mvw/intr oduction_nc.mp4
- 81. Why do home balances show Kilograms? • That is what people understand best, but it is really just an estimate of the mass above them. Ideally scales should show Newtons. • To find out how much force your body is exerting on the scales, multiply by 9.8(to convert kg into Newtons). • Online balance: http://mrmont.com/games/scale.html
- 82. Light
- 83. • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceInside our Sun a deeper look.mp4 • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceMind- blowing Ancient Solar Calender - Wonders of the Universe w_ Brian Cox - BBC.mp4
- 84. Light - Sun • Light from the sun takes about 8 minutes to arrive on earth. • What is the distance between the earth and the sun? • d = sxt = 8x3x10^8 = 144000000km
- 85. Stars • Our sun is a star. • At night we see a lot of other starts in sky, and these are all suns of different planets/Solar Systems all of which are also light sources. • Stars appear as fixed luminous points in the sky at night. • The most popular stars have been placed into collections known as constellations and where given names according to the shape they take.
- 86. Constellations
- 87. Constellations • Pictures and videos - Earth and SpaceSCIENCE SCREEN REPORT FOR KIDS - Night Sky_ Navigating the Constellations - Volume 22 Issue 5.mp4 • Planet are not stars. • Stars are luminous planets are not. • The stars are still there during the day however we do not see them because they are outshined by the sun.
- 88. Light Years • What are LIGHT YEARS? • A light year is the distance between stars and galaxies in the universe since this distance is so large. • Light year might sound like time but it is in fact a distance it is the distance that light travels in one year.
- 89. Light Years • How far is a light year? • Light travels 3x10^8 m/s. Now there are 60s in a minute and 60 minutes in an hr and 24hr in a day and 365 days in a year. If we multiply all these we get 31500000s in a year if u multiply by 3x10^8 m/s you get 9450000000000000meters!!!!!
- 90. Light Years • The speed of light: if one had to drive nonstop to the sun at 60MILESper hr it would take 180 years. Light makes the same trip in eight minutes. So the sun is about 8 light minutes away from earth.
- 91. Light Years • The distance of a light year • How long would it take the space shuttle to go one light-year? The shuttle orbits the earth at about 5miles per second. Light travel at 186000 miles per second thus 37200 times faster than the shuttle. So the shuttle would need 37200years to go a distance of one light year.
- 92. Why is it important for us humans to explore space?
- 93. TimeLine Space Exploration 1. first animals (fruitflies) in space 2. first rocket launch 3. first human in space 4. first Venus flyby 5. first space tourist 6. use of Space Shuttle ; construction of first space station and ISS 7. First Mars flyby 8. first monkey in space 9. first dog in space 10. first landing on the Moon 11. first landing on Venus 12. first human being on the Moon 13. first satellite in space
- 94. TimeLine Space Exploration • 2 • 1 • 8 • 13 • 9 • 3 • 4 • 7 • 10 • 11 • 6 • 5 http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/space/space-exploration- timeline/
- 95. Why are satellites useful?
- 96. Satellites • Weather Satellites: orbit the earth to give weather information •
- 97. Satellites • Information satellites: manage the processing and distribution of the millions of bits of data and images that these satellites produce daily.
- 98. Satellites • Geostationary Satellites: GOES satellites provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. • They circle the Earth in an orbit, at a speed matching the Earth's rotation. • Since they stay above a fixed spot on the surface, they provide for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms, and hurricanes.
- 99. Satellites • Polar Orbiting Satellites: • Daily global coverage, by making nearly polar orbits roughly 14.1 times daily. • Currently in orbit we have a morning and afternoon satellite, which provide global coverage four times daily. • These satellites are able to collect global data on a daily basis for a variety of land, ocean, and atmospheric applications. SatellitesSatellites
- 100. Satellites