The Project Management Framework
- 1. The project management framework
- 2. What is a project? • “A Project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.” The definition of the Project contains two things: • a project is temporary in nature • a project is undertaken to produce a unique output.
- 3. Examples Some of the examples of the projects are: • Developing a new product or service. • Designing a new transportation vehicle. • Developing or acquiring a new or modified information system. • Constructing a building. • Building a water system for a community in a developing country
- 4. Why are the projects Implemented? • Projects are often implemented as a mean of achieving an Organization’s strategic plan. • For many Organization’s, projects are the means to respond to those requests that can not be addressed with in the Organization’s normal operational limits.
- 5. Similarities between Projects and Operation • • • Performed by people. Constrained by limited resources. Planned, executed, and controlled.
- 6. Difference between Projects and Operations are: Projects Operations • Temporary • Ongoing • Output :unique • Output: Repetitive • Purpose: Attain its objective and then terminate • Purpose: Sustain the business • Concludes when its specific objectives have been attained • Adopts a new set of objectives and the work continues
- 7. Temporary • One of the properties of the project • Every project has a definite beginning and a definite end. • End is when the objectives are achieved or not. • Duration of project is finite • It does not apply to the services made by the projects (some projects may create a lasting result)
- 8. Temporary contd. • The objective of projects and operations are fundamentally different • The objective of a project is to attain the objective and close the project • The objective of operation is to sustain the business
- 9. Temporary contd. • Temporary nature may also affect other aspects: The opportunity is temporary: Most projects have limited time frame to produce their desired product The project team rarely survives the project: Most projects are performed by the team created for performing the project but it is broken up at the end of the project
- 10. Unique product, service or result • A project involves doing something that has not been done before which is ‘unique’. • A product or service may be unique even if the category to which they belong is large.(e.g. each individual facility in the office is unique)
- 11. Unique product, service or result contd. • The presence of repetitive elements does not change the uniqueness of the project. Examples are Project to develop new commercial airliner(requires many prototypes) Project to build new drug market(thousands of doses of drugs are requires) Real estate development project(includes many individual units) Development project(can be implemented in many areas)
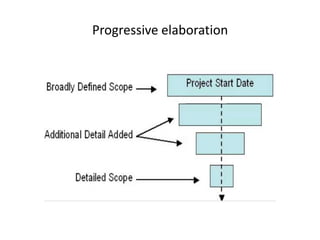
- 12. Progressive Elaboration • Progressive :“ proceeding in step, continuing steadily in increments” • Elaboration : “ worked out with care and detail ,develop thoroughly” • A characteristic of project • Means to development in increments as the project moves forward • Is planned • Not considered scope creep
- 13. Scope Creep • Progressive Elaboration is not considered to be Scope Creep as it is done with coordinated and planned intent. • additional scope added to the project after the project's objectives has been defined. • It affects the project's - cost - resources - time. • This is one of the top reasons that the projects frequently are over budgeted.
- 15. Examples of Progressive Elaboration: • Projects where research plays important role in determining the project scope • A project affected my research findings • Defining characteristic of a process • Elaborated based on testing results
- 16. Project Management • Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, managing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals. we can also define as : • Project management is the science (and art) of organizing the components of a project, whether the project is development of a new product, the launch of a new service, a marketing campaign, or a wedding.
- 19. Components of project management • Time • Money • Scope