Protists
- 1. Protists
- 2. Alteration of generations-requires two structures Conjugation- direct exchange of DNA Differentiate two ways Protists reproduce sexually Sexual- alteration of generations Asexual-Mitosis Distinguish a sexual and sexual reproduction in Protists Appear similar to PA&F, but lack complex organization Identify unifying features of Protists fresh water, salt water (marine), damp soil List three environments where Protists are found Eukaryotic, some autotrophic, some heterotrophic. Live in water List characteristics of Protists
- 3. Dino- marine, plankton, two flagella Zoo- one flagellum at least, parasitic species, Euglenoids- some auto some hetero, light sensitive, flexible pelicle Differentiate three types of Flagellates Classified according to their pigments: Green, Red and Brown Contrast thee kinds of algae Silicon shelled photoautotrophs, divide in half until too small, sharp shells Describe the structure of diatoms Using pseudopodia, and cytoplasm streaming Identify how amoebas and forams move
- 4. Medicines works some, but developing resistance Control mosquito population, works but can cause other problems if too widespread Evaluate methods of controlling malaria Infected mosquito bites, sporozites got to liver, make merozoites these enter RBC’s and burst them in 24-48 hr cycles Summarize how malaria is transmitted Giradasis, Malaria, Toxoplasmosis, African sleeping sickness Name three diseases caused by Protists Human disease, livestock disease Identify two ways that Protists affect human health
- 5. Common Features of Protists Eukaryotic Mostly unicellular No specialized cells Similar to modern organisms Found any place there is water
- 6. Three Major Phyla Protozoa Alga Slime Molds
- 7. Protozoa Animal-like Heterotrophic Three modes of movement Pseudopodia Flagella Cilla Free living and parasitic species
- 8. Amoeba Move with pseudopodia Engulf food via endocytosis
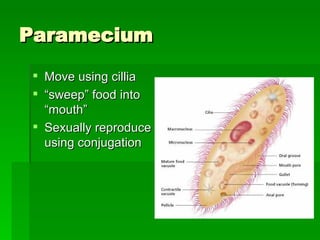
- 9. Paramecium Move using cillia “ sweep” food into “mouth” Sexually reproduce using conjugation
- 10. Zooflagellates Move using a eukaryotic flagellum Most free living Pathogenic ones cause dysentery, sleeping sickness, Chagas disease
- 11. Classify the following Organism is autotrophic Unicellular Contains no Cellulose in its cell wall Contains chloroplasts
- 12. Classify the following Organism is heterotrophic Has no cell wall Moves using pseudopodia Eats using phagocytes Contains mitochondria
- 13. Classify the following Organism is autotrophic Contains Chlorophyll Undergoes photosynthesis Cell wall contains peptidoglycan Responsible for Oxygen in atmosphere Does not contain chloropplasts
- 14. Classify the following Organism undergoes sexual and asexual reproduction Heterotrophic Unicellular, but condenses to a multicelular organism in stress Saprophotic