Psychosomatic for CME
- 1. DR. ASHOK SHARMA D.H.M.S. N.H.M.C.H. DLI M.D.(HOM) CHIEF MEDICAL OFFICER VIVEK VIHAR DISPENSARY VIVEK VIHAR B – BLOCK DELHI - 95 DIRECTORATE OF I.S.M AND HOMOEOPATHY G.N.C.T DELHI E-MAIL: homoeodrashok@gmail.com
- 2. 30.011.2013
- 3. LEARNING IS A PECULIAR “ TREE” ON WHICH GROWS THE “FRUIT” KNOWN AS – EDUCATION.
- 4. Knowledge is like a field and action is the sowing of seeds. So the conclusion is that while knowledge is limitless and transcends the flight of human thought, we should pick up the knowledge pertaining to our immediate needs and apply it into practice for , to derive full benefit.
- 5. RELATIONSHIP BEWEEN SOMA AND PSYCHE. WHAT ARE PSYCHOSOMATIC DISORDERS. HOW THEY ARE CLASSIFIED. WHAT ARE THEIR CAUSES. THEIR UNDERSTANDING FROM HOMOEOPATHIC POINT OF VIEW. WHAT IS PSYCHOSOMATIC MEDICINE REFERENCES IN REPERTORY AND MAT.MED. CASES.
- 9. Psychologically will is linked to intentionality. Will has been described as the mental agency that transforms awareness and knowledge into action, as the bridge between desire and action.
- 10. “The progressive explorations of psychological and pathological science develop intimate bonds of union between mind and body hitherto undiscovered, and not even supposed to exist. The mind and body are inseparable, at least during life; they are mutually dependent for energy; the strength of the one is the power of the other; the weakness of one is the impotence of the other.” Dr.Garth Wilkinson
- 11. Psychosomatic illness is any physical dysfunction where the primary cause is emotional. All illnesses can be psychosomatic because the body reflects our mental, emotional and spiritual health.
- 12. The term psychosomatic refers to the connection between body and mind. Therefore a psychosomatic illness refers to a physical dysfunction that is primarily caused by some form of emotional and mental stress.
- 14. Traditionally , the medical profession has been concerned with physical illness and has concentrated research efforts on understanding the organic factors in disease. In psychopathology, on the other hand, interest has centered primarily on uncovering the psychological and emotional factors that led to the development of mental disorders.
- 15. The interdisciplinary approach to all disorderswhich fits relevant biological, psychosocial, and sociocultural data into a coherent picture- is referred to as the psychosomatic approach.
- 16. Arousal of the negative emotions in response to stress situation- nature of stress and individual’s perception. Failure of these emotions to be dealt with adequately. Response stereotype- the damaging effects of chronic arousal becoming concentrated in a specific organ.
- 17. Psychosphysiologic skin disorders-, etc. neurodermatosis,atopic dermatitis eczema Musculoskeletal disorders- backaches, muscular cramps, tension headache. Respiratory disorders- bronchial asthma, hiccoughs, recurring bronchitis. Gastrointestinal disorders- peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, colitis. Genitourinary disorders- menstrual disturbances etc. Endocrine disorders- hyperthyroidism, obesity etc. Organs of special senses- chronic conjunctivitis. Other types- disturbances in the nervous system in which emotional factors play a major role – multiple sclerosis.
- 18. BIOLOGICAL FACTORS PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS. SOCIOCULTURAL FACTORS. .Genetic . . Personality characteristics. . Differences in autonomic activity. . Inadequate coping patterns. . Somatic weakness. . Alteration in corticovisceral control mechanism. . Kinds of stress. . Interpersonal relationship.
- 20. REACTION EQUATION CONNECTING VARIOUS LEVELS OF ENERGY IN NATURE THAT INFLUENCE HUMAN KIND Structure Function Positive Space/Time energy Spirit - Chemistry Negative Space/Time energy. Mind Divine William A. Tiller Department of Material Science and Engineering Stanford University.
- 21. COMPARISON BETWEEN THE TWO CONVENTIONAL SYSTEM • Deals directly with chemical and structural components of the body . • It can be classed as an objective medicine and thus has much laboratory evidence. . HOMOEOPATHIC SYSTEM • Deals indirectly with the chemistry and structure of the physical body by dealing directly with the substance and energy at the next more subtle level. • It can be classed as subjective medicine as it deals with energy that can strongly perturbed by the mental and emotional activity of the individual.
- 22. Three general group of patients. With comorbid psychiatric and general medical illnesses complicating each other. . With somatoform and functional disorders. . With psychiatric disorders that are direct consequence of a primary medical condition or treatment.
- 23. . In OPD practice we witness tremendous diversity of emotional and behavioral responses to illness. . Clinical experience and research demonstrates that illness variable such as severity, chronicity or organ system involvement cannot predict an individual’s response to any given medical illness. . Rather, it is in the realm of the individual’s subjective experience of an illness that can begin to understand his or her emotional and behavioral responses.
- 24. . . . . Concepts of stress. Personality types. Coping strategies. Defense mechanisms.
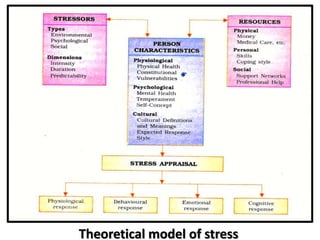
- 25. Theoretical model of stress
- 26. “The dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his characteristic behavior and thought.” It sees as an organization within the individual. Gordon Allport.
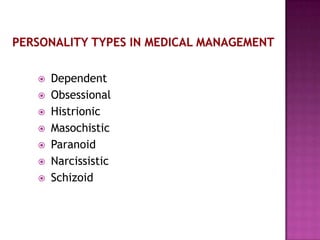
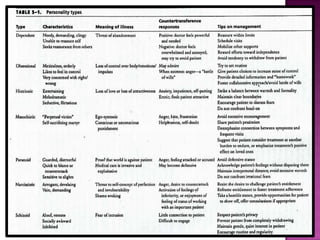
- 27. Most patients do not fit into one type but may exhibit characteristics of a number of personality types. Personality type is ignored because of the current emphasis on biological treatment.
- 30. Can be defined as “ thoughts and behaviors that the person uses to manage or alter the problem that is causing distress( problem-focused coping) and regulate the emotional response to the problem ( emotion- focused coping).”
- 31. Confronting coping Distancing coping Self controlling Seeking social support Accepting responsibilities escape avoiding Planful problem solving
- 32. illness as challenge illness as an enemy Illness as punishment illness as weakness illness as relief illness as strategy illness as irreparable loss or damage illness as value.
- 33. Defense mechanisms are automatic processes by which the mind confronts a threat or conflict between a wish and the demands of reality or the dictates of conscience.
- 35. ASPECTS OF DEFENSE MECHANISM . Defenses are generally outside of awareness of the individual or unconscious. . Defenses by nature distort inner and outer reality. . Defense can appear strange or overt to the observer while going unnoticed by the subject. . Defense are creative. . Defenses involve psychological conflict. . Defense are adaptive and are not at all pathological.
- 38. A central task of a physician working with the medically ill is- To understand patient’s subjective experiences. In order to design therapeutic intervention that: . Modulate the patient’s behavioral and emotional responses. . Decrease their distress and . Improve their medical out comes.
- 39. CASES
- 40. That there is no royal road to a perfect understanding of Materia Medica. It is at its worst a tedious drudgery. It seems and appears to be very fascinating and yet an exasperating subject. No other system of therapeutics possesses such a large number of books on Materia Medica. Each author has tried to present the drugs as he understood them. One can only imagine the plight of a homoeopath.
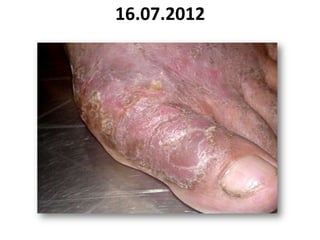
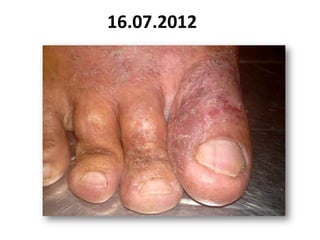
- 42. 16.07.2012
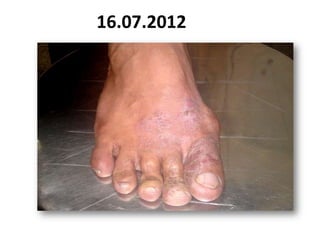
- 43. 16.07.2012
- 44. 16.07.2012
- 45. 16.07.2012
- 46. 16.07.2012
- 47. 16.07.2012
- 48. 16.07.2012
- 49. 16.07.2012
- 50. 16.07.2012
- 51. • • • • K.No (41) Excitement swallows continually while talking. K.No. (51) Grief condition about his. K.No. (15) Confusion talking while. K.No. (79) Sensitive rudeness to. K.No. (55) Indignation bad effects following. STAPHISGARIA.
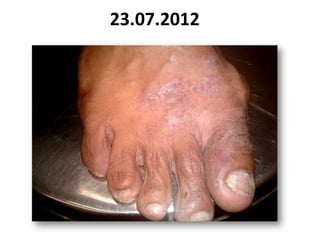
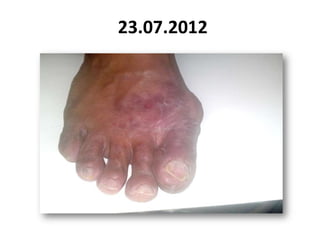
- 52. 23.07.2012
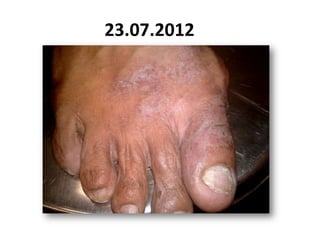
- 53. 23.07.2012
- 54. 23.07.2012
- 55. 23.07.2012
- 56. 23.07.2012
- 57. 23.07.2012
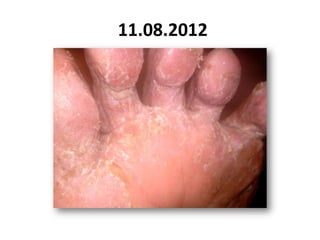
- 58. 11.08.2012
- 59. 11.08.2012
- 60. 11.08.2012
- 61. 11.08.2012
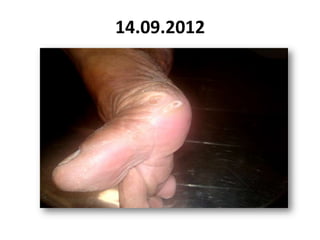
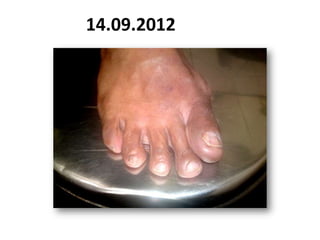
- 62. 14.09.2012
- 63. 14.09.2012
- 64. 14.09.2012
- 65. 14.09.2012
- 66. 14.09.2012
- 67. 14.09.2012
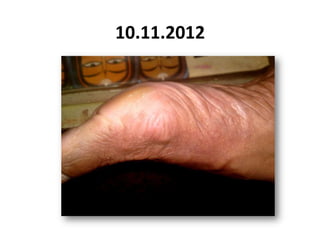
- 68. 10.11.2012
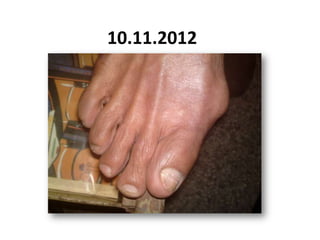
- 69. 10.11.2012
- 70. 10.11.2012
- 71. 10.11.2012
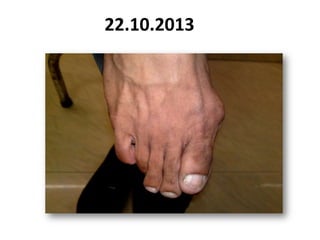
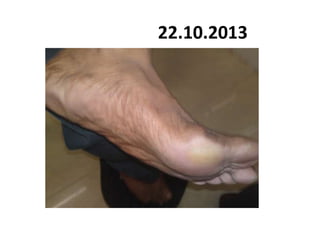
- 72. 22.10.2013
- 73. 22.10.2013
- 74. 22.10.2013
- 75. 22.10.2013
- 76. 22.10.2013
- 77. 22.10.2013
- 78. 22.10.2013
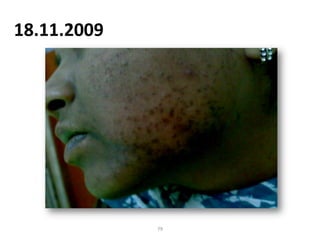
- 79. 18.11.2009 79
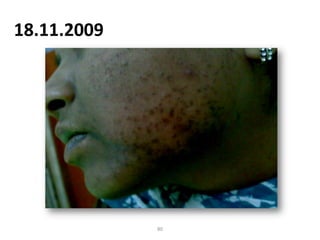
- 80. 18.11.2009 80
- 81. Extravagance- K.No(41) Excitement- thinking of the things others have done to displease her. K.No.(40). Ammonium .Carb.
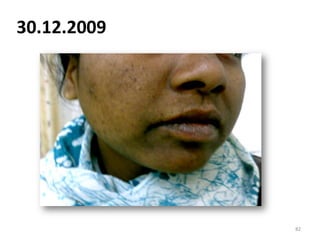
- 82. 30.12.2009 82
- 83. 30.12.2009 83
- 84. 30.12.2009 84
- 85. 30.12.2009 85
- 86. 30.12.2009 86
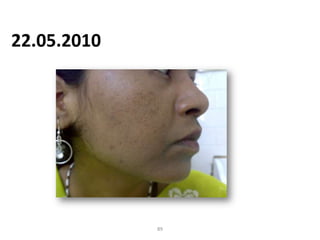
- 87. 22.05.2010 87
- 88. 22.05.2010 88
- 89. 22.05.2010 89
- 90. 90
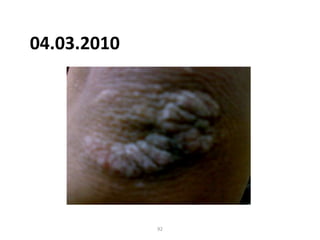
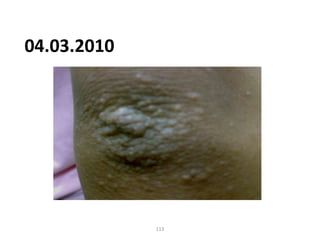
- 91. 04.03.2010 91
- 92. 04.03.2010 92
- 93. Obstinate – against whatever proposed she had the queerest objection. K.No(69) Talks- one subject . K.No.(87) Undertakes- nothing, lest he fails.K.no(91) Delusions- succeed, that he cannot does everything wrong. K.No.(33) Fear- undertaking anything. K.No(47) ARG.NIT.
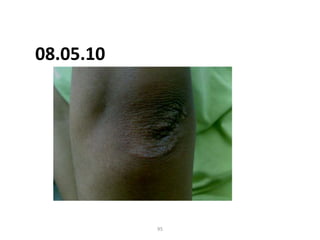
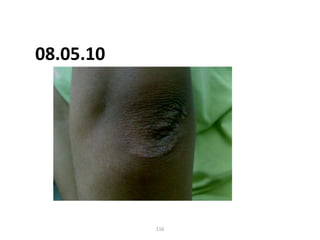
- 94. 08.05.2010 94
- 95. 08.05.10 95
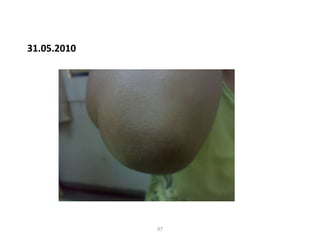
- 96. 31.05.2010 96
- 97. 31.05.2010 97
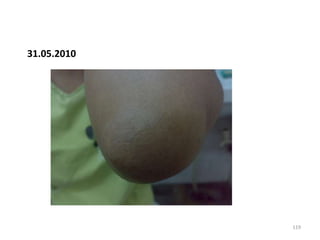
- 98. 31.05.2010 98
- 99. 11.06.2010
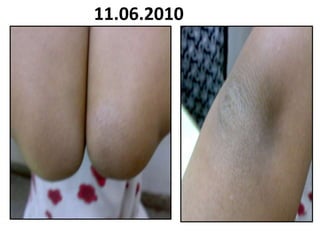
- 100. 11.06.2010
- 101. 11.06.2010
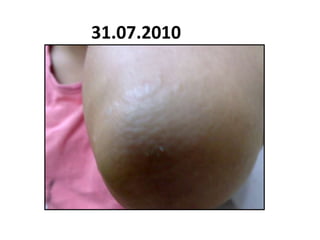
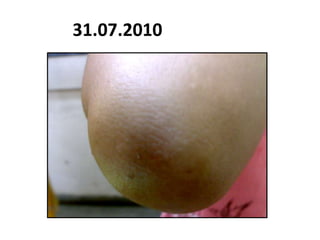
- 102. 31.07.2010
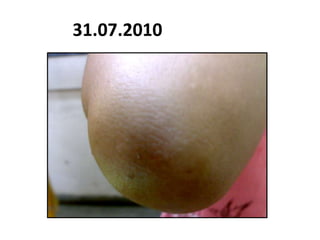
- 103. 31.07.2010
- 104. 31.07.2010
- 105. 12.02.2011
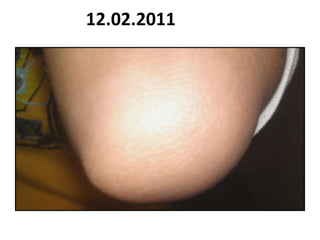
- 106. 12.02.2011
- 107. 12.02.2011
- 108. 27.07.2011
- 109. 27.07.2011
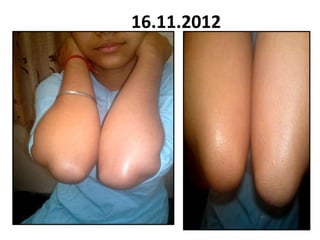
- 110. 16.11.2012
- 111. 21.06.2013
- 112. 112
- 113. 04.03.2010 113
- 114. 04.03.2010 114
- 115. 08.05.2010 115
- 116. 08.05.10 116
- 117. 31.05.2010 117
- 118. 31.05.2010 118
- 119. 31.05.2010 119
- 120. 11.06.2010
- 121. 11.06.2010
- 122. 11.06.2010
- 123. 31.07.2010
- 124. 31.07.2010
- 125. 31.07.2010
- 126. 12.02.2011
- 127. 12.02.2011
- 128. 12.02.2011
- 129. 27.07.2011
- 130. 27.07.2011
- 131. 16.11.2012
- 132. 21.06.2013
- 133. Do not confuse the instrument with the user of the instrument. The instrument is the brain; the user of the instrument is the infinite Being expressing itself in different disguises.
- 134. Thank You