Python Programming | JNTUK | UNIT 1 | Lecture 5
- 2. UNIT 1 : SYLLABUS • Conceptual introduction: topics in computer science, algorithms; • Modern computer systems: hardware architecture, data representation in computers, software and operating system; • Installing Python; basic syntax, interactive shell, editing, saving, and running a script. • The concept of data types; variables, assignments; immutable variables; numerical types; • arithmetic operators and expressions; comments in the program; understanding error messages;
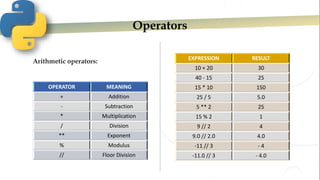
- 5. Operators Arithmetic operators: EXPRESSION RESULT 10 + 20 30 40 - 15 25 15 * 10 150 25 / 5 5.0 5 ** 2 25 15 % 2 1 9 // 2 4 9.0 // 2.0 4.0 -11 // 3 - 4 -11.0 // 3 - 4.0 OPERATOR MEANING + Addition - Subtraction * Multiplication / Division ** Exponent % Modulus // Floor Division
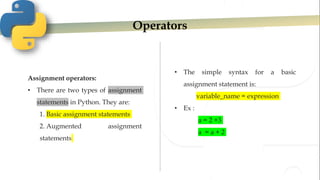
- 6. Operators Assignment operators: • There are two types of assignment statements in Python. They are: 1. Basic assignment statements 2. Augmented assignment statements • The simple syntax for a basic assignment statement is: variable_name = expression • Ex : a = 2 +3 a = a + 2
- 7. Operators • There are two types of assignment statements in Python. They are: 1. Basic assignment statements 2. Augmented assignment statements • We can combine arithmetic operators in assignments to form an augmented assignment statement. a = a + b is written as a + = b • Here the left-hand side i.e., a is evaluated first, then value of b is evaluated and then addition is performed, and finally the addition result is written back to a x = x * 2 is written as x * = 2
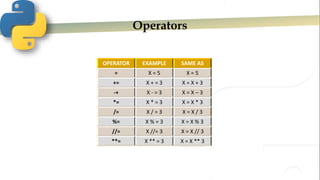
- 8. Operators OPERATOR EXAMPLE SAME AS = X = 5 X = 5 += X + = 3 X = X + 3 -+ X - = 3 X = X – 3 *= X * = 3 X = X * 3 /= X / = 3 X = X / 3 %= X % = 3 X = X % 3 //= X //= 3 X = X // 3 **= X ** = 3 X = X ** 3
- 9. Operators Comparison operators: • Comparison operators are used to compare two values: EX: X = 3, Y = 4, Z = 4 X == Y Output: False Y == Z Output: True OPERATOR MEANING EXAMPLE == Equal X == Y != Not Equal X != Y > Greater than X > Y < Less Than X < Y >= Greater than or Equal to X > = Y <= Less Than or Equal to X < =Y
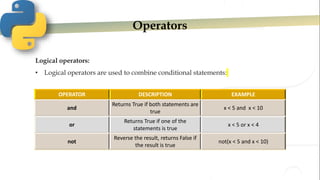
- 10. Operators Logical operators: • Logical operators are used to combine conditional statements: OPERATOR DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE and Returns True if both statements are true x < 5 and x < 10 or Returns True if one of the statements is true x < 5 or x < 4 not Reverse the result, returns False if the result is true not(x < 5 and x < 10)
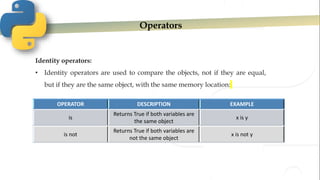
- 11. Operators Identity operators: • Identity operators are used to compare the objects, not if they are equal, but if they are the same object, with the same memory location: OPERATOR DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE is Returns True if both variables are the same object x is y is not Returns True if both variables are not the same object x is not y
- 12. Operators Membership operators: • Membership operators are used to test if a sequence is presented in an object: OPERATOR DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE in Returns True if a sequence with the specified value is present in the object x in y not in Returns True if a sequence with the specified value is not present in the object x not in y
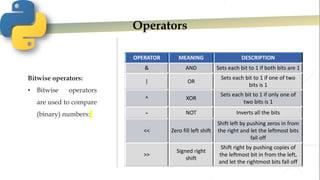
- 13. Operators Bitwise operators: • Bitwise operators are used to compare (binary) numbers: OPERATOR MEANING DESCRIPTION & AND Sets each bit to 1 if both bits are 1 | OR Sets each bit to 1 if one of two bits is 1 ^ XOR Sets each bit to 1 if only one of two bits is 1 - NOT Inverts all the bits << Zero fill left shift Shift left by pushing zeros in from the right and let the leftmost bits fall off >> Signed right shift Shift right by pushing copies of the leftmost bit in from the left, and let the rightmost bits fall off
- 16. Expressions • An expression is a combination of values(Constants), variables and operators. • Instructions that a Python interpreter can execute are called statements. For example, a = 1 is an assignment statement. • a = 10 # This is an assignment statement • b = 10 # This is an assignment statement • print(a + b) o # a + b is an expression o print(a + b) is a statement • a = b * 5 + c o # b * 5 + c is an expression o a = b * 5 + c is a statement
- 17. Consider a=1, b=5, c=6, d=3. Evaluate b – a * c / d + 10 Answer : 13
- 18. Expressions
- 20. Comments • A comment is a piece of program text that the computer ignores but that provides useful documentation to programmers. • # symbol is used to add comments. a = 10 # a value assigned b = 20 # b value assigned c = a + b # sum of a and b assigned to c
- 22. Error Messages How Python Works: • In python there are three types of errors; o Syntax errors o Semantic errors o Exceptions
- 23. Error Messages • The most common reason of an error in a Python program is when a certain statement is not in accordance with the prescribed usage. Such an error is called a syntax error. • When Python encounters a syntax error in a program, it halts execution with an error message.
- 24. Error Messages • A semantic error is detected when the action that an expression describes cannot be carried out, even though that expression is syntactically correct.
- 26. UNIT 1 : SYLLABUS • Conceptual introduction: topics in computer science, algorithms; • Modern computer systems: hardware architecture, data representation in computers, software and operating system; • Installing Python; basic syntax, interactive shell, editing, saving, and running a script. • The concept of data types; variables, assignments; immutable variables; numerical types; • arithmetic operators and expressions; comments in the program; understanding error messages;