Refraction lecture
- 1. OBJECTIVES: Explore the refraction property of light. Determine what causes bending of light. Relate refraction of light to real life experiences.
- 4. REFRACTION Is the BENDING of light as it passes OBLIQUELY from one medium to another of different optical density. Examples: Air to water Water to air Water to glass
- 5. Why does LIGHT bend?
- 6. Light bends because…. 1. Of the change in MEDIUM. Light bends as it moves from one medium to another like from air to water.
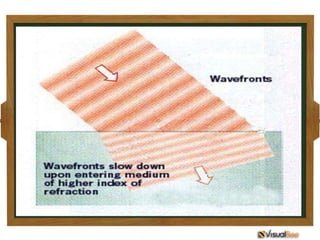
- 7. Light bends because…. 1. It changes speed as it encounters a different medium.
- 9. Light does not bend when it enters the medium perpendicularly, however it slows down.
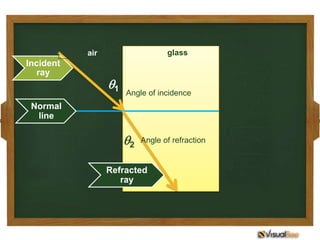
- 10. air glass Incident ray 1 Angle of incidence Normal line 2 Angle of refraction Refracted ray
- 11. What determines the bending of light?
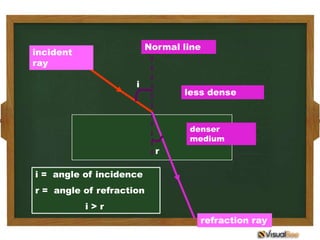
- 12. When light enters a medium of greater optical density, it bends towards the normal.
- 13. Normal line incident ray i less dense denser medium r i = angle of incidence r = angle of refraction i>r refraction ray
- 14. Normal line cident y i less dense air water denser medium r Light rays bend angle of incidence towards the normal angle of refraction air when the rays travel glass from a less dense medium to a denser refraction ray medium Light rays travel much slower in a denser medium
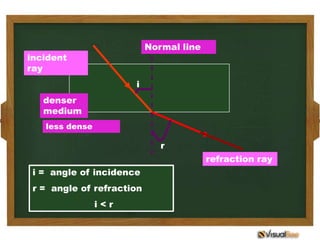
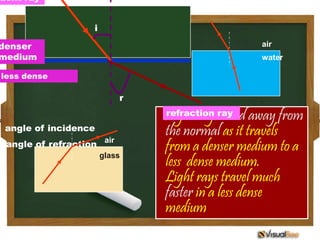
- 16. When light enters a medium of lesser optical density, it bends away from the normal.
- 17. Normal line incident ray i denser medium less dense r refraction ray i = angle of incidence r = angle of refraction i<r
- 18. dent ray i denser air medium water less dense r Light raysray away from refraction bend angle of incidence the normal as it travels = angle of refraction air from a denser medium to a glass less dense medium. Light rays travel much faster in a less dense medium
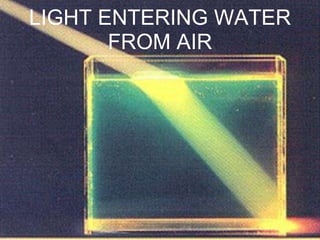
- 19. LIGHT ENTERING WATER FROM AIR
- 20. INDEX OF REFRACTION (n). The ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the material. n Speed of light in vacuum = C = Speed of light in material v