Re:invent 2016 Container Scheduling, Execution and AWS Integration
- 1. © 2016, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its Affiliates. All rights reserved. Andrew Spyker (@aspyker) 12/1/2016 Container Scheduling, Execution and AWS Integration
- 2. What to Expect from the Session • Why containers? • Including current use cases and scale • How did we get there? • Overview of our container cloud platform • Collaboration with ECS
- 3. About Netflix • 86.7M members • 1000+ developers • 190+ countries • > ⅓ NA internet download traffic • 500+ Microservices • Over 100,000 VM’s • 3 regions across the world
- 4. Why containers? Given our VM architecture comprised of … amazingly resilient, microservice driven, cloud native, CI/CD devops enabled, elastically scalable do we really need containers?
- 5. Our Container System Provides Innovation Velocity • Iterative local development, deploy when ready • Manage app and dependencies easily and completely • Simpler way to express resources, let system manage
- 6. Innovation Velocity - Use Cases • Media Encoding - encoding research development time • Using VM’s - 1 month, using containers - 1 week • Niagara • Build all Netflix codebases in hours • Saves development 100’s of hours of debugging • Edge Rearchitecture with NodeJS • Focus returns to app development • Simplifies, speeds test and deployment
- 7. Why not use existing container mgmt solution? • Most solutions are focused on the datacenter • Most solutions are • Working to abstract datacenter and cross-cloud • Delivering more than cluster manager • Not yet at our level of scale • Wanted to leverage our existing cloud platform • Not appropriate for Netflix
- 8. Batch
- 9. What do batch users want? • Simple shared resources, run till done, job files • NOT • EC2 Instance sizes, autoscaling, AMI OS’s • WHY • Offloads resource management ops, simpler
- 10. Historic use of containers • General Workflow (Meson), Stream Processing (Mantis) • Proven using cgroups and Mesos • With simple isolation • Using specific packaging formats Linux cgroups
- 11. Enter Titus Job Management Batch Resource Management & Optimization Container Execution Integration
- 12. Sample batch use cases • Algorithm Model Training
- 13. GPU usage • Personalization and recommendation • Deep learning with neural nets/mini batch • Titus • Added g2 support using nvidia-docker-plugin • Mounts nvidia drivers and devices into Docker container • Distribution of training jobs and infrastructure made self service • Recently moved to p2.8xl instances • 2X performance improvement with same CUDA based code
- 14. Sample batch use cases • Media Encoding Experimentation • Digital Watermarking
- 15. Sample batch use cases Ad hoc Reporting Open Connect CDN Reporting
- 16. Lessons learned from batch • Docker helped generalize use cases • Cluster autoscaling adds efficiency • Advanced scheduling required • Initially ignored failures (with retries) • Time sensitive batch came later
- 17. Titus Batch Usage (Week of 11/7) • Started ~ 300,000 containers during the week • Peak of 1000 containers per minute • Peak of 3,000 instances (mix of r3.8xls and m4.4xls)
- 18. Services
- 19. Adding Services to Titus Job Management Batch Resource Management & Optimization Container Execution Integration Service
- 20. Services are just long running batch, right?
- 21. Services more complex Services resize constantly and run forever • Autoscaling • Hard to upgrade underlying hosts Have more state • Ready for traffic vs. just started/stopped • Even harder to upgrade Existing well defined dev, deploy, runtime & ops tools
- 22. Real Networking is Hard
- 23. Multi-Tenant Networking is Hard • IP per container • Security group support • IAM role support • Network bandwidth isolation
- 24. Solutions • VPC Networking driver • Supports ENI’s - full IP functionality • With scheduling - security groups • Support traffic control (isolation) • EC2 Metadata proxy • Adds container “node” identity • Delivers IAM roles
- 25. VPC Networking Integration with Docker Titus Executor Titus Networking Driver - Create and attach ENI with - security group - IP address create net namespace
- 26. VPC Networking Integration with Docker Titus Executor Titus Networking Driver - Launch ”pod root” container with - IP address - Using “pause” container - Using net=none Pod Root Container Docker create net namespace
- 27. VPC Networking Integration with Docker Titus Executor Titus Networking Driver - Create virtual ethernet - Configure routing rules - Configure metadata proxy iptables NAT - Configure traffic control for bandwidth pod_root_id Pod Root Container
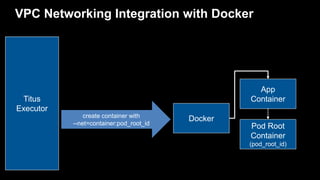
- 28. VPC Networking Integration with Docker Titus Executor Pod Root Container (pod_root_id) Docker App Container create container with --net=container:pod_root_id
- 29. Metadata Proxy container Amazon Metadata Service (169.254.169.254) Titus Metadata Proxy What is my IP, instanceid, hostname? - Return Titus assigned What is my ami, instance type, etc. - Unknown Give me my role credentials - Assume role to container role, return credentials Give me anything else - Proxy veth<id> 169.254.169.254:80 host_ip:9999 iptables/NAT
- 30. Putting it all together Virtual Machine Host ENI1 sg=A ENI2 sg=X ENI3 sg=Y,Z Non-routable IP IP1 IP2 IP3 sg=X sg=X sg=Y,ZNonroutable IP, sg=A Metadata proxy App container pod root veth<id> App container pod root veth<id> App container pod root veth<id> App container pod root veth<id> Container 1 Container 2 Container 3 Container 4 Linux Policy Based Routing + Traffic Control 169.254.169.254 NAT
- 31. Additional AWS Integrations • Live and rotated to S3 log file access • Multi-tenant resource isolation (disk) • Environmental context • Automatic instance type selection • Elastic scaling of underlying resource pool
- 32. Netflix Infrastructure Integration • Spinnaker CI/CD • Atlas telemetry • Discovery/IPC • Edda (and dependent systems) • Healthcheck, system metrics pollers • Chaos testing
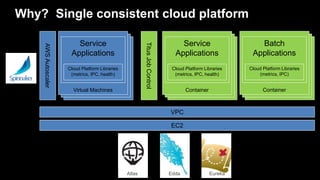
- 33. VM’s VM’s Why? Single consistent cloud platform VPC EC2 Virtual Machines AWSAutoscaler Service Applications Cloud Platform Libraries (metrics, IPC, health) TitusJobControl VM’s VM’s Container Service Applications Cloud Platform Libraries (metrics, IPC, health) VM’s VM’s Container Batch Applications Cloud Platform Libraries (metrics, IPC) Edda EurekaAtlas
- 35. Deploy Based On New Docker Registry Tags
- 36. Deployment Strategies Same as ASG’s IAM Roles and Sec Groups Per Container Basic Resource Requirements
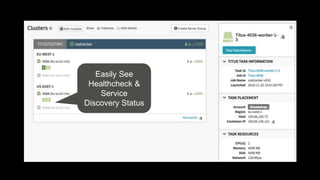
- 37. Easily See Healthcheck & Service Discovery Status
- 40. Fenzo – The heart of Titus scheduling Extensible Library for Scheduling Frameworks • Plugins based scheduling objectives • Bin packing, etc. • Heterogeneous resources & tasks • Cluster autoscaling • Multiple instance types • Plugins based constraints evaluator • Resource affinity, task locality, etc. • Single offer mode added in support of ECS
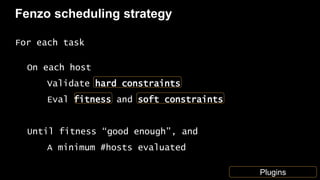
- 41. Fenzo scheduling strategy For each task On each host Validate hard constraints Eval fitness and soft constraints Until fitness “good enough”, and A minimum #hosts evaluated Plugins
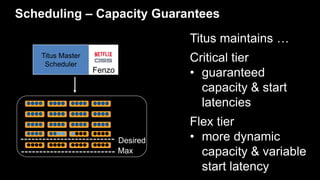
- 42. Scheduling – Capacity Guarantees Desired Max Titus maintains … Critical tier • guaranteed capacity & start latencies Flex tier • more dynamic capacity & variable start latency Titus Master Scheduler Fenzo
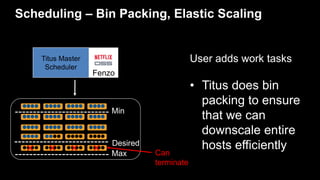
- 43. Scheduling – Bin Packing, Elastic Scaling Max User adds work tasks • Titus does bin packing to ensure that we can downscale entire hosts efficiently Can terminate Desired Min ✖ ✖ ✖ ✖ Titus Master Scheduler Fenzo
- 44. Availability Zone B Availability Zone A Scheduling – Constraints including AZ Balancing User specifies constraints • AZ Balancing • Resource and Task affinity • Hard and softDesired Min Titus Master Scheduler Fenzo
- 45. ASG version 001 Scheduling – Rolling new Titus code Operator updates Titus agent codebase • New scheduling on new cluster • Batch jobs drain • Service tasks are migrated via Spinnaker pipelines • Old cluster autoscales down Desired Min ASG version 002 Min Desired ✖ ✖ Titus Master Scheduler Fenzo
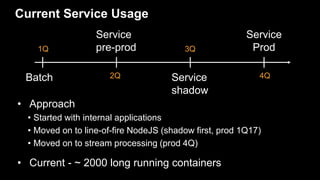
- 46. Current Service Usage • Approach • Started with internal applications • Moved on to line-of-fire NodeJS (shadow first, prod 1Q17) • Moved on to stream processing (prod 4Q) • Current - ~ 2000 long running containers 1Q Batch 2Q Service pre-prod 3Q Service shadow Service Prod 4Q
- 48. Why ECS? • Decrease operational overhead of underlying cluster state management • Allow open source collaboration on ECS Agent • Work with Amazon and others on EC2 enablement • GPUS, VPC, Sec Groups, IAM Roles, etc. • Over time this enablement should result in less maintenance
- 49. Titus Today Container Host mesos- agent Titus executor container container containerMesos master Titus Scheduler EC2 Integration Outbound - Launch/Terminate Container - Reconciliation Inbound - Container Host Events (and offers) - Container Events
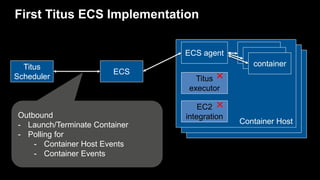
- 50. First Titus ECS Implementation Container Host ECS agent Titus executor container container container ECS Titus Scheduler EC2 integrationOutbound - Launch/Terminate Container - Polling for - Container Host Events - Container Events ✖ ✖
- 51. Collaboration with ECS team starts • Collaboration on ECS “event stream” that could provide • “Real time” task & container instance state changes • Event based architecture more scalable than polling • Great engineering collaboration • Face to face focus • Monthly interlocks • Engineer to engineer focused
- 52. Current Titus ECS Implementation Container Host ECS agent Titus executor container container container ECS Titus Scheduler EC2 Integration Outbound - Launch/Terminate Container - Reconciliation Inbound - Container Host Events - Container Events ✖ ✖ Cloud Watch Events SQS
- 53. Analysis - Periodic Reconciliation For tasks in listTasks describeTasks (batches of 100) Number of API calls: 1 + num tasks / 100 per reconcile 1280 containers across 40 nodes
- 54. Analysis - Scheduling • Number of API calls: 2X number of tasks • registerTaskDefinition and startTask • Largest Titus historical job • 1000 tasks per minute • Possible with increased rate limits
- 55. Continued areas of scheduling collaboration • Combining/batching registerTaskDefinition and startTask • More resource types in the control plane • Disk, Network Bandwidth, ENI’s • To fit with existing scheduler approach • Extensible message fields in task state transitions • Named tasks (beyond ARN’s) for terminate • Starting vs. Started state
- 56. Possible phases of ECS support in Titus • Work in progress • ECS completing scheduling collaboration items • Complete transition to ECS for overall cluster manager • Allows us to contribute to ECS agent open source Netflix cloud platform and EC2 integration points • Future • Provide Fenzo as the ECS task placement service • Extend Titus Job Management features to ECS
- 58. Future Strategy of Titus • Service Autoscaling and global traffic integration • Service/Batch SLA management • Capacity guarantees, fair shares and pre-emption • Trough / Internal spot market management • Exposing pods to users • More use cases and scale
- 60. Thank you!
- 61. Remember to complete your evaluations!
Editor's Notes
- Will talk how this led to rate limiting: com.amazonaws.services.ecs.model.AmazonECSException: Rate exceeded (Service: AmazonECS; Status Code: 400; Error Code: ThrottlingException; Request ID: xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx)
- Talking point: We were able to do this with our existing scheduler and task placement service (Fenzo) due to our architecture.