Research m sc(n)
- 1. A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY TO ASSESS THE ANXIETY & COPING MECHANISMOF CAREGIVERS OF CANCER PATIENTS ADMITTED IN SELECTED HOSPITAL, LUDHIANA, PUNJAB. Khushnasib Author’s affiliation:- Principal,MD Oswal College of Nursing,Ludhiana,Punjab. CorrespondingAuthor:- Khushnasib,AssistantProfessor,ArmyCollegeof Nursing,JalandharCantt, Punjab ABSTRACT Anxietyisanemotioncharacterizedbyfeelingsof tension,worriedthoughtsandphysical changeslike increasedbloodpressure. Materialsandmethods:- The Non- experimentalDescriptiveStudywas conductedtoassessthe level of anxiety&copingmechanismamongcaregiversof cancerpatients admittedinselected byNonRandomizedPurposive Sampling.Structuredquestionnaire(i) Standardized modifiedBurnAnxietyInventoryScale and(ii) Assessmentof copingmechanismtool usedfordata collection.The responsesare tabulated,organized,analyzedandinterpretedbyusingdescriptiveand inferential statisticsbasedonobjectivesof the study. Results:- Findingsrevealedthat5% of caregivers had minimal ornoanxiety,38%had mildanxiety,24% hadmoderate anxiety,8% hadsevere anxiety& 4% had extreme anxiety.Onassessingcopingmechanism,28% had maladaptive coping&72% had adaptive coping.Conclusion:- Oncomparisonof anxietyscoreswithcoping scoresitwasinterpreted that withincreasedseverityof anxiety,caregiversstartmovingtowardsfailure tocope withanxiety. Therefore,itisneedtoeducate caregiversadaptationmethodsof copingtoimprove copingmechanism. Introduction Anxietydisorderpresentsavarietyof physical symptoms& nonphysical symptomsi.e. excessive&unrealisticworrying,trembling, churningstomach,heartpalpitations,numbness inbody,restlessness,trouble concentrating, chestpain,shortnessof breathe anddizziness, flashbacksornightmares,avoidance of people, placesandthingsassociated withevent, difficultysleeping,closelywatching surroundings,irritability,diminishedfeelingsor aspirationsforfuture.Anxietyisof twotypes i.e.beneficial andharmful anxiety.Anxietyis “fightor flightresponse”thatkeepscaregivers safe fromstresses&tension.Itissaidthat adrenaline isbeneficial undertense circumstances.Itisreactionthat motivates, preparesforthingswe have to face and sometimesenergytotake actionwhenneeded. Thisis calledbeneficial anxiety.Incase of overwhelminganxietycaregiversfeel unableto make decisions,avoidingthings,unabletogoto occasion,can’t concentrate andcan’t stay focused,interference withtheirdayto day life. Thistype of symptomsproduce more anxiety problemandneedprofessionalhelp. Copingisto deal withstressesthata personwhile livingthroughstressesindailylife experience.Methodstocope withanxietyare to accept reality,separate outreal risksand changesthat situationspresent.Typesof coping are adaptive andmaladaptive coping.Adaptive
- 2. copingisask yourself inthisproductive thought, isit helpingme togo towardsmygoal,if its negative thoughtsay‘stop’.Maladaptive coping iswhencopingabilitiesbecome impairedi.e. personbecomesunable tocope i.e.person becomesunable tocope i.e.personknowsthat it isa negative thoughtbutcannotbe challenged.Differentmodalitiesof copingisto learnto relax,breathe retraining,yoga, meditation,exercise. Needofthe study While workinginclinical arearesearchermet manyof the relativesof cancerpatientswitha bigburden.Patient’srelativesfeltanxietyand were havingdeficitincopingability.Itwas causinginterference incaregivingandwas makingfamilymembersinefficienttoperform theirwork.Hence,needof attentioninthisarea of research. Studywas conductedtotestthe competingmodelsforhusbandandadult daughtercaregiversof breastcancerhospice patients.Datawas collectedwithtwomodels i.e ComplicatedGrief Model comprisingof empiricallyderivedanxietyanddepression symptomsandtheoreticallyderivedanxietyand depressionsymptomsandtheoreticallyderived psychological andhealthstrainformulations. Both predictedthathusbandsfeltmore difficult bereavementadjustmentsthandaughters. Neithermode wassupportedforadult daughters.The studypredictedbetter bereavementadjustmentinoldcaregiversfor bothhusbandsand daughters.Adultdaughters experiencedmore caregiverrole strain than husbandsdidi.e.adultdaughtersfeltmore difficulttoadjustwithcaergivingburden. Thisstudywas conductedtoexamine predictorsof psychological stressforcaregivers of cancerpatientsfollowingbereavement.It was basedonfactors identifiedatthe time of referral topalliative care agency.Sample consistedof 178 caregiversof 178 caregiversof cancer patients.The chief predictorsof caregiver’spsychological symptomsand severityof grief were scoresof psychological symptomsduringreferral.Theywere also measuredatthe time of adverse life events aboutcaregivers’copingresponses,post bereavementandseparationexperiences, caregivers’relationshipduringandgreater severityof patient’s illnessatthe time of referral.These findingsindicate thatclinical risk factors foradverse shorttermbereavement outcome can be usedto identifythe psychological needsof caregiverstoformthe potential basisforinterventions&toenhance the psychological outcome of familycaregivers. Objectives 1. To identifythe anxietyof caregiversof cancer patients. 2. To identifythe copingmechanismof caregiversof cancerpatients. 3. To analyze the correlationof anxiety and copingmechanismof caregiversof cancer patients. 4. To findthe associationbetweenanxiety withselectedvariables suchassex,age, education,income,occupation,length of hospital stay,massmediaexposure and residential area. 5. To findthe associationbetweencoping mechanismswithselected variables such as age,sex,education,lengthof hospital stay,massmediaexposureand residentialarea. 6. To identifythe anxietyandcoping mechanismdeficitinordertoprepare healthguidelines.
- 3. Hypothesis Cancer patients’caregivershave anxietyand deficitincopingmechanismondiagnosisof familymemberwithcancer. Conceptual framework The presentstudywasbasedon RoyAdaptation Model.The RAMsuggeststhe methodof adaptationwithstressesandanxietiesinlife.It include 3components:- Input,Output&Control Processes. 1) INPUT:- Inputsare stimuli orfactorsof personinfluencingadaptation.These can be external orinternal factors. Accordingto the presentstudy, caregiversof cancerpatientsdevelop anxiety due tofamilymember diagnosedwithcancer.Itsinputswere of 3 typesthat were influencinganxiety of caregivers:- a) Independentvariables(understudy):- Gender,age,education,income, occupation,lengthof hospital stay, mass mediaexposure,residential area. b) Internal factors(Notunderstudy):- Knowledge,selfesteem, outlook, relationshipwithpatient,skillsof caregiving. c) External factors:- Social role changes, financial role change,lackof communication,patient’s characterstics,patient’sfunctional ability,social pressures. 2) OUTPUT:- Accordingto stimulus, responseswere produced.These canbe adaptive ornon adaptive. 3) Control Processes:- Control Processes are adaptive system.Inthisstep,coping strategieswere minddiversion, introspection,introjections,behavior modification.Accordingtoadaptation of caregivers,itcanbe adaptive or ineffective.Accordingtolevel of
- 4. adaptation,assessmentof anxiety& copingwas done.Nursinginterventions giventoimprove copingmechanismi.e. healthguidelinesforknowledgeof anxiety&coping.Evaluationwasdone whichrevealedthatcaregiverswere betterable tocope upwithanxiety, showeddecreasedanxiety,showed decreasedanxiety&increasedcoping scores. RESEARCH DESIGN:- Nonexperimental researchdesignwasapplied to assessthe level of anxietyandcoping mechanismamongcaregiversof cancer patients.The independentvariablesinclude gender,age,education,income,occupation, lengthof hospital stay, massmediaexposure and residential areaof caregiversof cancer patientsadmittedinselectedhospital, Ludhiana,Punjab. Reviewof Literature:- The Reviewof Literature forthe presentstudyis gatheredandorganizedunderthe following headings:- 1. Literature relatedtoanxietyandits effects 2. Literature relatedtocopingmechanism MATERIALS AND METHODS Research approach & design A quatitative approachwithnon-experimental descriptive researchdesignwasusedtoconduct the study. Independependentvariables:- Gender,age, education,income,occupation,lengthof hospital stay,massmediaexposureand residentialarea. Dependentvariables:- Anxietyandcoping mechanismof caregivers of cancerpatients. Research setting Differentwardsof cancerinMD Oswal MultispecialityandCancerHospital,Ludhiana, Punjab.
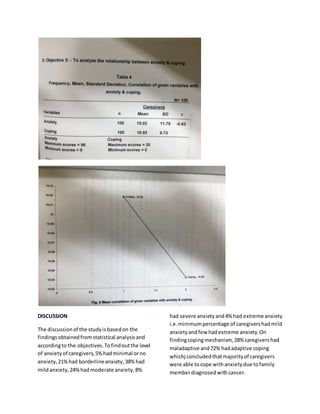
- 5. Population The populationcomprisedof caregiversi.e. bloodrelatedrelatives/familymembersof cancer patientsprovidingcare tothe patients providingcare to the patientsfordurationof 3- 7 daysin hospital andfacinganxietyandaltered copingmechanismwhilecaringforthe patient. Sample and samplingTechnique Sample size was100 caregiversof cancer patients.NonRandomizedpurposive and Convinience samplingwasused. Developmentoftool The tool forthe presentstudywasStandardized Burn AnxietyInventorytool andNon Standardizedstructuredquestionnaire for assessinglevel of copingbasedonreviewof literature andobjectivesof the study. Descriptionof the tool The tool consistsof 3 sections:- SectionI:- Sample characterstics:- Itcontain8 demographicvariablesincludinggender,age, education,income,occupation,lengthof hospital stay,massmediaexposureand residentialarea. SectionII:- BurnAnxietyInventoryScale:- It contained32 itemsrelatedtoanxiety symptoms. SectionIII:- A structuredquestionnaire with32 itemsrelatedtocopingsymptoms. Data collection The data collectionwascarriedoutby investigatorbypersonallyadministering questionnaire tostudysubjects.The responses of caregiverswastabulated,organized, analyzedandinterpretedbydescriptive and inferential statisticsbasedonobjectivesof the study. Ethical clearance Ethical clearance wastakenfrom Ethical Committee. RESULTS In the presentstudy,in sample of 100 subjects 54% were malesand46% were females, accordingto age in20-40 yrs of age were 57%, 41-60 yrsof age were 41% & <61 yrs of age were 2%,18% were illiterates,43% were matriculationpassed,39% were graduates, income>5000 were 45%, 5001-10,000 were 28%, 10,000-15,000 were 16% &<15,000 were 11%, 71% were employed,29% unemployed,3- 5 dayshospital staywere 39%, 5-7 days hospital stay were 31%, 7 or above days were 30%,mass mediaexposure dailywere 18%,sometimes 47%, neverwere 35% & rural 19%, semi urban 46% andurban were 35%. On assessinglevel of anxiety,38% had mildanxiety,24% had moderate anxiety,21% had borderline anxiety, 8% had severe anxiety,51% hadminimal orno anxiety,4% hadextreme anxiety.Itconcluded that majorityof caregiverswere able tocope withanxiety. On findingthe associationandlevelof variance,there issignificantassociationof anxietywitheducation(F=4.16),occupation (t=1.42) and gender(t=0.04). Onanalyzingco- relationwithlevel of anxiety andcopingof caregivers,there wasnegativerelationbetween anxietyandcopingmechanismi.e.asthe level of one increases,the otherdecreasesandvice versa. Hence,Hypothesis(H) suggestingcancer patients’caregivershave anxietyanddeficitin
- 8. DISCUSSION The discussionof the studyisbasedon the findingsobtainedfromstatistical analysisand accordingto the objectives.Tofindoutthe level of anxietyof caregivers,5%hadminimal orno anxiety,21%had borderlineanxiety,38% had mildanxiety,24%hadmoderate anxiety,8% had severe anxietyand4% had extreme anxiety i.e.minimumpercentage of caregivershadmild anxietyandfew hadextreme anxiety.On findingcopingmechanism, 28% caregivershad maladaptive and72% hadadaptive coping whichj concludedthatmajorityof caregivers were able tocope withanxietydue tofamily memberdiagnosedwithcancer.
- 9. To determine the relationshipbetween anxietyandcopingof caregiversof cancer patients,there isnegativecorrelationi.e.with increase inmeananxietyscores,the mean copingscoresdecreasesandvice versa i.e.as the anxietyincreasesthe personstartsfailingto cope.The analysisrevealedthatthere is significantassociationof anxietyandcoping witheducation,occupationandgender. RECOMMENDATIONS The followingstudiescanbe made basedon presentresearch. 1. The study can be replicated ona large sample. 2. A comparative studycanbe done to assessthe effectivenessof different copingmechanism 3. A quasi experimental studycanbe conductedtoassessthe anxietyand copingusingcontrol & experimental group. 4. The study can be conductedon differentpopulationandindifferent settings. 5. An exploratorystudycanbe conducted to detectpredisposingfactorsof anxiety instudentnurses. 6. A comparative studycanbe conducted to identifymeasurestakenbystudent nursesto reduce anxiety. CONCLUSION The data collected&statistical analysisof researchand interpretationhasclearlyshown that anxietyoccursincaregiversof cancer patientswhichdeclinescopingmechanism.The statistical analysisindicatednegative correlationbetweenanxietyandcopingamong caregivers.Byprovidinghealthinstructionsor enhancingthe life styleordietwe maybe able to reduce anxietyandcopingmechanism amongcaregiversof cancer patients. Source of finding:Self Conflictof interest:- None REFERENCES 1. Ross (2007), AmericanJournal of Cervical CancerStudyGroup,“ImprovingQualityof lifeandlife style”,School of Psychology,VolIV,3rd edition,112-115. 2. Yuji Ichikawa,Oxfordtextbookof Psychiatry,“Studiesrelatedtoanxietyandvariouscoping strategies”,HarperColins,Pubmed,VolI,Pp- 106-110. 3. Andrewes,AmericanJournal of Nursing,“TherapeuticStudyof anxiety,whatisanxiety,Distress managementinnursing,Vol III,Pp-532-541. 4. Ross (2009), Centre forMedical PsychologyJournal,“Signs&featuresof anxiety,Anxietyand DepressionmanagementinNursing”,Vol II,Pp-19-32. 5. Yu F, Journal of IndianPsychology,Universal Publishers,Bangalore University,Vol V,Pp-119- 121. 6. ChenM (2000), OxfordBookof Psychology,AnxietyandCoping,cliniciancompletereferenceto psychological interventions,JacobsonPublishers,Mosby,2000, Vol III,2nd edition104-109. 7. Ross (2001), NursingTimes,whatiscopingandit management,IndianJournalof Nursing Education,Pp-110-114.
- 10. 8. Speilberger(2003),OncologyNursingForums,“Anxietytypesandcopingtypes”,Universityof Nebraska,Vol I,Pp-49-56. 9. Belderetal,Textbookof behavioraltherapy,Blackwell Publication,March2006, 321-330. 10. KurtzME, (2007), Predictorsof postbereavementdepressivesymptomatologyamongfamily caregiversof cancerpatients,October20-25 (30) 482-85.