Research Report ppt (marketing)
- 1. B Y : K U M A R S A U R A V P R A S A D RESEARCH REPORT
- 2. Research Reports "Research reports are detailed and accurate accounts of the conduct of disciplined studies accomplished to solve problems or to reveal new knowledge." (Busha and Harter, 1988).
- 3. Functions of the Research Report It serves as a mean for presenting the problem studied, methods and techniques used for collecting and analyzing data, the findings, conclusions and recommendations in an organized manner. It provides factual base for formulating policies and strategies relating to the subject matter studied. It serves as a basic reference material for future use in developing research proposals in the same or related area. It is used to evaluate researchers ability and competence to do research. It is used for judging the quality of the completed research work/project
- 4. Characteristics of an ideal research report An ideal report should have the following characteristics: Report should be presented in a systematic and attractive manner. Titles, photographs and graphs should be used wherever necessary. Report should be clear, to the point and easily understandable. Proverbs and exaggerations should be avoided. The analysis of facts should have logical and scientific base so that no one should have the doubt that the report is based on assumption ideas.
- 5. Cont…. All the sources of information should be descried so that any person can verify the facts on the basis of described sources. Difficulties and problems faced during research work should necessarily be described to avoid any artificiality. Such guidelines are very helpful and advantageous for further and future researchers. An ideal report also indicates the points useful for research in future Suggestions provided should be unbiased, creative and useful.
- 6. Precautions for writing research reports While determining the length, one should keep in view the fact that it should be long enough to cover the subject but short enough to maintain interest. In fact , report should not be means to learning more and more about less and less. A research report should always sustain readers interest. Abstract terminology and technical jargon should be avoided in a research report. The report should be able to convey the matter as simply as possible. This, in the other words, means that report should be written in an objective style in simple language, avoiding expressions such as it seems, there may be and the like.
- 7. Appendices should be enlisted in respect of all the technical data in the report. Bibliography of sources consulted is a must for a good report and must necessarily be given. Index is also considered as an essential part of a good report and as such must be prepared and appended at the end. Report must be attractive in appearance, neat and clean. Calculated confidence limits must be mentioned and the various constraints experienced in conducting the research study may also be stated in the report.
- 8. Types of Research Report There are a variety of research reports. The audience to whom a research report is addressed has to be kept in view in the preparation of a research report. The research report may be divided into following types: Technical report Popular reports Interim reports Summary report
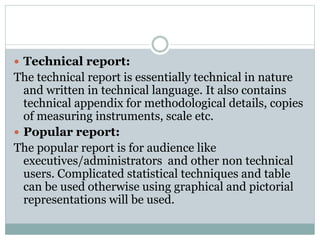
- 9. Technical report: The technical report is essentially technical in nature and written in technical language. It also contains technical appendix for methodological details, copies of measuring instruments, scale etc. Popular report: The popular report is for audience like executives/administrators and other non technical users. Complicated statistical techniques and table can be used otherwise using graphical and pictorial representations will be used.
- 10. Interim report: When there is a long time lag between data collection and the presentation of the results. Interim report will be a suitable kind of a report to present data as and when the phase of the project work gets completed. The interim report contains a narration of what has been done so far and what was the outcome. It presents a summary of the findings of that part if analysis which has been completed. Summary report: A summary report is generally prepared for the consumption of the lay audience. It is written in non-technical, simple language with a liberal use of pictorial charts. It just contains brief reference to the objectives of the study and major findings and their implications.
- 11. Steps in writing research report After the data analysis is over, report writing cannot be started abruptly. It requires careful pre- planning. The planning process involves the following consolidations and steps: The target audience ( Public/ Children/ Scientists etc.) The communication characteristics of the audience ( Level of Knowledge). The intended purpose of the report ( Award of Degree/Project/Diploma etc.)
- 12. The type and scope of report (M.Phil/ Ph.D/Scope and Limitations) The style of reporting ( simple/ Clear) The format of the report ( always varies according to the type of report) Outline of the contents ( what to cover and what not) Style of writing Proper footnotes and bibliography
- 13. Structure of research report Quantitative Format Title page Abstract Introduction Review of the Literature Methodology Timeline, Budget, and Preliminary Chapter Outline References Appendices Qualitative Format Title page Abstract Introduction Procedure Preliminary Findings Anticipated Outcomes Timeline, Budget, and Preliminary Chapter Outline References Appendices
- 14. Thank You !