Resins
- 1. RESINS K.Sudheer Kumar, Assistant professor. Dept.of Pharmacognosy Chilkur Balaji college of Pharmacy Hyderabad. E-mail:sudheer.y2k8@gmail.com
- 2. INTRODUCTION Resins are amorphous products of complex chemical nature. They are transparent or translucent solids, semi-solids or liquid substances containing large number of carbon atoms. They are hard, electrically non-conductive and combustible masses. They are usually formed in schizogenous or schizolysigenous cavities or ducts as end products of metabolism. Most of the resins are heavier than water. They are insoluble in water, but soluble in alcohol, volatile oils, fixed oils, chloral hydrate and non-polar organic solvents like benzene and ether.
- 3. The composition of resins varies with the species. The most common terpenes in resin are the bicyclic terpenes, monocyclic terpenes and smaller amount of tricyclic sesquiterpene. The resin produced by most plants is a viscous liquid, composed mainly of terpenes, with lesser components of dissolved non-volatile solids, which make resin thick and sticky. The individual components of resin can be separated by fractional distillation.
- 4. CLASSIFICATION Based on occurrence, it is classified into five types. They are 1.Oleo resin 2.Gum resin 3.Oleo-gum resin 4.Glucoresin/ Glycoresins 5.Balsam Based on chemical constituents, it is classified as: 1.Resin Acids/ Resinolic Acids 2.Resin Alcohols/ Resin Esters 3.Resenes/ Inert Resins
- 5. METHODS OF EXTRACTION 1. Extraction by using solvents 2. Extraction by Distillation 3. Extraction by making Incisions 4. Extraction by heating the plant part containing resin 5. Extraction of resin from Encrustations
- 6. 1.Physical properties: (a)Resins in purified form are amorphous, brittle and hard solids. (b)Their specific gravity is more than one; hence they are heavier than water. (c)They dissolve in organic solvents. PROPERTIES 2. Chemical properties: (a)Chemically, resins are terpenes. (b)Resins upon heating soften and melt. (c)Resins when burnt produce smoky flame
- 7. USES • It reflects light. This decreases the heat on the flowers, thereby protecting them. • They are used in the preparation of emulsions. • Solid resenes are available as adhesives. • They are used externally as mild antiseptic agents in the form of ointments and plasters. •Animals do not chew the leaves of resinous plants. Hence, they can be used as outdoor plants. • Resinous drugs possess the action of anthelmintic, counter-irritant, expectorant, hydragogue, laxative, and sedative.
- 8. GINGER •Syn: Adarak, Zingiber, Sunthi •Source: Scraped or unscraped rhizomes of Zingiber officinale •Family: Zingiberaceae Specification: •Size: 7-15 cm long, 1-1.5 cm broad •Colour: Buff •Odour: Agreeable •Taste: Pungent
- 9. Microscopy (a) Schematic diagram (T.S) & (b) Transverse section of ginger rhizome
- 10. Chemical Constituents: Ginger consists of volatile oil (1-4%), starch (40-60%), fat (10%), fibre (5%), inorganic material (6%), residual moisture (10%) and acrid resinous matter (5-8%), Sesquiterpene: zingiberene, ar-curcumene. Uses: •Stomachic, Aromatic, Carminative, Stimulant & Flavouring agents. •Mouth washes, Ginger beverages & Liquors. •It is effective in motion sickness.
- 11. CAPSICUM •Syn: Chillies, Pepper, Red pepper, Mirch •Source: Dried, ripe fruits of the Capsicum minimum & C.annum •Family: Solanaceae Characteristics: •Size: 5-12 cm long & 2-4 cm wide •Colour: Orange-red •Odour: Characteristic •Taste: Intense & pungent
- 12. Uses: •Carminative •Appetizer •Counter-irritant •Lumbago •Neuralgia •Spices •Yellow fever, Sore throat Chemical Constituents: •Fixed oil (4-16%), Oleo-resin, Carotenoids, Capsacutin, Capsico, Thiamine, Volatile oil (1.5%), Ascorbic acid (0.2%).
- 13. •Syn: Haridra, Haldi, Indian saffron, Curcuma •Source: Dried rhizomes of Curcuma longa, C.domestica •Family: Zingiberaceae Characteristics: •Size: 4-7 cm long, 1-1.5 cm wide, called as Finger •Colour: Deep yellow-orange •Odour: Indistinct •Taste: Aromatic, pungent, bitter •Shape: Ovate, pear shaped, oblong or cylindrical
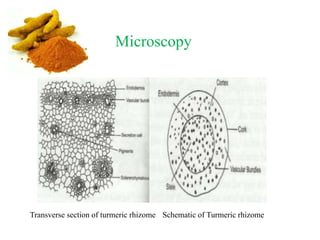
- 14. Microscopy Transverse section of turmeric rhizome Schematic of Turmeric rhizome
- 15. Chemical Constituents: •It contains volatile oils, starch grains and curcuminoids. •The chief components of curcuminoids is called as Curcumin. Chemical test: •Powder + conc.H2SO4 →Red colour •Powder + Alkali solution → Red-violet colour Uses: •As Condiment or spice, colouring agent, for ointments & creams. •Chemically, it is used for detection of boric acid. •Curcumin is used as anti-inflammatory agent. •Common house hold remedy for cough & cold.
- 16. ASAFOETIDA •Syn: Hing, Devil’s dung, Gum asafoetida •Source: Obtained from incision of rhizome & root of Ferula foetida & other species of Ferula. •Family: Umbelliferae Characteristics: •Colour: Golden yellowish brown •Odour: Strong •Taste: Bitter & acrid •Forms: 2 types- Tears & Masses. Tears are rounded or flattened.
- 17. Chemical Constituents: • It contains gum, resins & volatile oil. • The resin consists of asaresinotannol in the free or combined form of ferulic acid. •Powder + water trituration Milky white emulsion •Fractured surface + HNO3 Green colour Uses: •Carminative, expectorant, nerve stimulant, flavouring curry, sauce & pickles, sedative. Chemical test:
- 18. PERU BALSAM •Syn: China oil, Black balsam, Peruvian balsam •Source: Obtained from trunk of Myroxylon balsamum •Family: Leguminosae Characteristics: •Colour: Dark brown-reddish brown •Odour: Aromatic vanilla like •Taste: Bitter & acrid •Solubility: Soluble in alcohol, gl. acetic acid, insoluble in water.
- 19. Chemical Constituents: •It contain 50-65% volatile oil with cinnamein & 25- 28% resin, traces of styrene, vanillin & coumarin. Uses: •Treatment of wounds, ulcers; in feminine hygiene sprays, soaps & cosmetics. •As flavor for food items candy, dairy desserts, alcoholic & non- alcoholic beverages.
- 20. COLOPHONY •Syn: Rosin, Amber resin, Gum-rosin, Colophonium •Source: Solid residue obtained after distillation of volatile oil (turpentine) from oleo-gum resin of various species of Pinus like P.palustris, P.pinaster, P.carribacea. •Family: Pinaceae •GS: America, France, Italy, Spain, India(Himalaya)
- 21. Characteristics: •Colour: Pale yellow-yellowish brown •Odour: Faint •Burn at 100 degree C & produce smoky flame •Soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene & insoluble in water Chemical Constituents: •90% abietic acid, 0.5% volatile oil, 5-6% resenes, sapinic acid & pimaric acid.
- 22. •Powder +Acetic anhydride → dissolve in a dry test tube → Conc. HCl → Purple colour. Chemical test: •Stimulant •Diuretic •Preparation of ointments, soaps, printing inks •Anti-microbial property •Anti-ulcer property Uses:
- 23. LONG PEPPER •Syn: Pippali large, catkins •Source: Dried fruiting spikes of climbing vine, Piper longum •Family: Piperaceae Characteristics: •Colour: Pale-dark brown •Odour: Aromatic spicy •Taste: Hot & sweet •Size: 2-5 cm length & 0.4-0.5 cm diameter •Shape: Circular & elongated. Spikes are cylindrical, erect & blunt.
- 24. Chemical Constituents: •Alkaloids piperine, piplartine & piplasterol (6%), essential oil(1%), pungent resin. Uses: •Ayurvedic & Unani medicines, diseases of respiratory tract. •Roots are used for bronchitis, stomach-ache, diseases of spleen & tumours. •Improves appetite & used in pickles.
- 25. Thank you