reverse logistic and compititiveness : A brief relationship
- 1. REVERSE LOGISTICS AND COMPETITIVENESS: A BRIEF REVIEWOF THIS RELATIONSHIP -SUDIP MITRA PGDMABPM 53
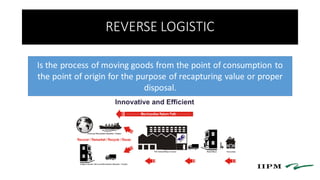
- 2. REVERSE LOGISTIC Is the process of moving goods from the point of consumption to the point of origin for the purpose of recapturing value or proper disposal.
- 3. INTRODUCTION Presently logistic seen by companies as a way to increase their competitiveness. In the past treated just as cost drivers. Reverse Logistic is the return of products into the production process. It is for recycling or for reintegration, considering both post-consumerlogistics and aftermarket logistics. The growing concerns about the environment, coupled with the volume and variety of products manufactured by companies.
- 4. 1. Reuse 2. Product update, 3. Material recovery 4. Waste management
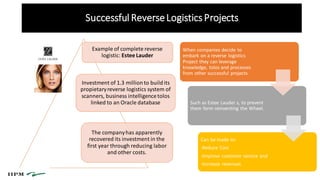
- 6. Successful ReverseLogistics Projects Example of complete reverse logistic: Estee Lauder Investment of 1.3 millionto buildits propietaryreverse logistics system of scanners, business intelligencetolos linked to an Oracle database The companyhas apparently recovered its investment in the first year through reducing labor and other costs. When companies decide to embark on a reverse logistics Project they can leverage knowledge, tolos and processes from other successful projects Such as Estee Lauder s, to prevent them form reinventing the Wheel. Can be made to: -Reduce Cost -Improve customer service and -Increase revenues
- 7. ReturnReasons • when the product is not what is expected • when the product does not arrive in a defined period Customer NOT Satisfied • The consumer assumes that the product is damaged but really that was installed improperly due to lack of instructions.Installationor Usage Problems • when the product does not work properly • when the product has physical damage • - when the product is repaired by warranty Warranty Claims
- 8. ReturnReasons •Incompleteorders •Misguided amounts •Prematuredelivery and duplicate Faulty Order Processing •Excessivequantities of products •New orders atthe end of trimesterRetail Overstock •Productlife finished •New producttrends •Old products areeliminated End of product life cycle or product replacement • Installation by the manufacturer • Standards of product safety • Corrective measures Manufacture recall programs
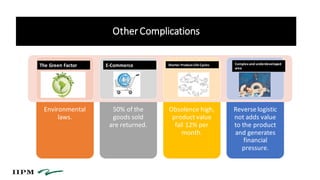
- 9. OtherComplications Environmental laws. 50% of the goods sold are returned. Obsolence high, product value fall 12% per month. Reverse logistic not adds value to the product and generates financial pressure. The Green Factor E-Commerce Shorter Product Life Cycles Complexand underdeveloped area
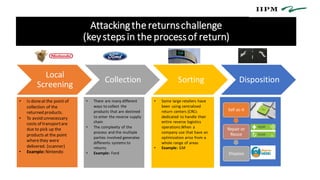
- 10. Attackingthe returnschallenge (keystepsin the processof return) Local Screening Collection Sorting Disposition • Is doneat the point of collection of the returned products. • To avoid unnecessary costs of transportare due to pick up the products at the point wherethey were delivered. (scanner) • Example: Nintendo • There are many different ways to collect the products that are destined to enter the reverse supply chain • The complexity of the process and the multiple parties involved generates differents systems to returns • Example: Ford • Some large retailers have been using centralized return centers (CRCs dedicated to handle their entire reverse logistics operations.When a company use that have an optimization arise from a whole range of areas • Example: GM Sell as-it Repair or Reuse Dispose
- 11. Reverse Logistics - the driving forces Many companies use reverse logistics in-house or through outsourced specialized companies ……..WHY??? To recapture economic value, To increase competitiveness, To demonstrate corporate responsibility To clean distribution channels through inventory management To demonstrate compliance with legislation.
- 12. Reverse Logistics – the restrictive forces The life cycle of a product does not end when it is discarded. The lack of involvement and commitmentof the entire supply chain caused by the mismatch of objectives The lack of complete studies to ensure and prove the efficiency of reverse logistics processes Absence of clear legislation.
- 13. Competitiveness and Reverse Logistics Chaves; Martins (2005) inform that: Compliance with environmental demand Reduced costs Customer Loyalty Positive Corporate image Improvement in the level of service offered to the customer
- 14. CONCLUSION Reverse logistics is an important tool for organizations to differentiate themselves from their competitors. Organizations that adopt reverse logistics have processes well structured. For the customer this means ensuring capacity to meet their needs, generating customer loyalty and making it difficult for competitors to imitate simple services that are geared towards value creation and the environment.