Review of Biomass Energy Sources
- 1. Review of Biomass Energy Sources Himanshu Paghdal 232825
- 2. ℍ Introduction ℍ Biomass and It’s Product ℍ Global energy potential ℍ Energy scenario in Europe ℍ Energy systems in Europe and the world ℍ Future technologies in energy production ℍ Energy storage ℍ conclusions Outlines
- 3. Introduction ⌘Several countries have adopted ambitious plan to obtain their power from renewable energy. ⌘Many people, the most familiar forms of renewable energy are the wind and the sun. But , Biomass (plant material and animal waste) is the oldest source of renewable energy, used since our ancestors learned the secret of fire. ⌘Biomass is one of the most plentiful resources available globally, and demand for it, is likely to increase substantially as the world looks to wean its dependence from fossil fuels and on-going commitments to reducing greenhouse gases and emissions.
- 4. Biomass and Process Ꙛ Biomass is the biological material derived from living, or recently living organisms. It is known as ‘natural material’. Biomass contains stored energy, in the form of chemical energy - that’s because plants absorb energy from the sun through the process of photosynthesis - as the plants died, the energy is trapped in the residue, so when biomass is burned, this stored energy is released as heat. Ꙛ In biomass, power plants, wood waste or other waste are burned to produce steam that runs a turbine to make electricity, or that provides heat to industries and homes. Fortunately, new technologies - including pollution controls and combustion engineering - have advanced to the point that any emissions from burning biomass in industrial facilities are generally less than emissions produced when using fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil).
- 5. To Generate Electricity,Boimass used
- 6. Sources of Biomass ꙚAnimal residues ꙚIndustrial Residues Ꙛ Forestry crops and residues ꙚAgricultural crops and residues ꙚSewage ꙚMunicipal solid waste
- 9. Applications of Biomass Ꙛ BIOFULES Converting biomass into liquid fuels for transportation. The two most common types of biofuels are ethanol and biodiesel. Ꙛ BIOPOWER Burning biomass directly, or converting it into a gaseous fuel or oil, to generate electricity. Types of biopower systems: direct- fired,cofiring, gasification, anaerobic digestion, pyrolysis, and small modular. ꙚBIOPRODUCTS Converting biomass into chemicals for making products that typically are made from petroleum.
- 10. Examples
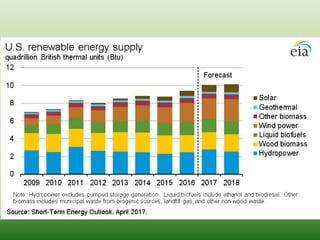
- 11. Projections production of energy in EU
- 12. Projections production of energy in EU
- 13. Projections production of energy in India
- 14. Projections production of energy in world wild
- 15. Advantages Disadvantages Advantages ∀ Cleaner/Renewable energy, 0% harmful emissions ∀ Funds and finance ∀ A fuel with a future- Readily available ∀ Reduce Dependency on Fossil Fuels ∀ Can be Used to Create Added value ∀ Can be Used to Create Different Products Disadvantages ∀ Investment levels ∀ Larger property/ land side & location ∀ Efficiency ∀ Air pollution ∀ Seasonality
- 16. Conclusion ₺ The use of biomass as an energy resource is sure to become more prominent in our world as we transition away from fossil fuels. ₺ However, the advantages and disadvantages, and therefore, the sustainability, of biomass energy are largely dependent upon which type of biomass is being utilized. ₺ The biomass feedstock's that we choose to rely upon should not compete with food production, should work in concert with the restoration of forests and other natural ecosystems, and should not place an unsustainable demand on natural resources.
- 17. Thank You