Rhapsody Software
- 1. Improving software development with Telelogic Rhapsody
- 2. Systems and software lifecycle management Requirements definition and management Analysis and design Quality management Release management Construction Configuration and change mgmt Asset management and reuse Production Enterprise architecture/ architectural frameworks Measurement and reporting Product portfolio management System lifecycle process management
- 3. Combined portfolio in action For technical systems development Requirements definition and management Analysis and design Quality management Release management Construction Configuration and change mgmt Asset management and reuse Production Enterprise architecture/ architectural frameworks Measurement and reporting Product portfolio management System lifecycle process management IBM Rational ® Build Forge ® Telelogic DOORS® Telelogic Focal Point™ Eclipse Wind River Workbench, other integrated development environments (IDEs) Telelogic Rhapsody® IBM Rational Systems Developer Telelogic Tester™ IBM Rational Test RealTime IBM Rational PurifyPlus ™ IBM Rational ClearCase ® IBM Rational ClearQuest ® Telelogic Synergy™ Telelogic Change™ IBM Rational Asset Manager IBM Rational Method Composer, Telelogic Harmony™, IBM Rational Unified Process Systems Engineering plug-in IBM Rational ® ProjectConsole ™ Telelogic Dashboard™ Telelogic® System Architect™
- 4. Typical software development projects Typical software projects consist of new code, modifications to existing code, existing code not changing and third-party libraries Documentation for code is often out of date, if it exists at all Third-party libraries Existing code New features Modified code
- 5. Typical software development issues Increasing design complexity Reusing assets for product lines Nonmodular development of application makes makes product line reuse a key challenge. Constant time to market pressures Difficult to understand designs with no documentation Often the best or only documentation is the code alone Developer of code is often no longer at the company New developers are faced with a steep learning curve to understand existing code Reuse is difficult because of lack of understanding of existing code Testing performed late in the development cycle, resulting in finding defects when they are the most costly to fix Features dropped from product Product recalls
- 6. Key enablers for the software developer Dynamic model and code collaboration Rhapsody Reuse software assets Automated unit and integration testing Open development environment
- 7. Visualize existing and third-party code Visualizing code clarifies the structure and architecture of the application. Streamlined reverse engineering and visualization workflow Automatic generation of diagrams from code for documentation
- 8. Reuse software assets Rhapsody can incorporate external code to: Reuse code from other projects Integrate code developed by a third party Import code generated from another tool Such code can be: Viewed externally (code visualization) Provides easy referencing from the model Automatically allows graphical visualization of your IP Virtually seamless workflow between model and hand-written code Automatically reverse-engineered to become part of the model RTOS Legacy Code Rhapsody Real-Time Framework Rhapsody Generated Code
- 9. Integrating existing and third-party code More easily understand interfaces between existing code and new features New features External code
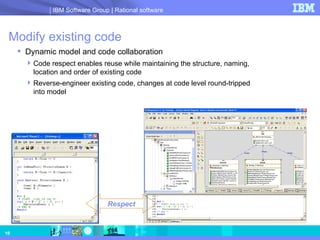
- 10. Modify existing code Dynamic model and code collaboration Code respect enables reuse while maintaining the structure, naming, location and order of existing code Reverse-engineer existing code, changes at code level round-tripped into model Respect
- 11. Working with code and models Increase developer productivity and ease model-driven development adoption Use tools familiar to coder Tight integration with IDE Changes in code need to be reflected in model Code respect helps ensure that the code and model have the same structure Multilanguage development allows designers to use the C, C++ and Java ™ languages in the same model
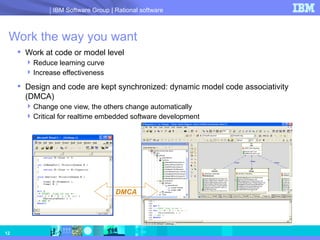
- 12. Work the way you want Work at code or model level Reduce learning curve Increase effectiveness Design and code are kept synchronized: dynamic model code associativity (DMCA) Change one view, the others change automatically Critical for realtime embedded software development DMCA
- 13. Rhapsody integration with Eclipse Integrated model-driven development within Eclipse environment Work in either the code or Rhapsody; both stay in sync Leverage Eclipse to tailor environment for your needs Eclipse code editor Rhapsody diagram editors
- 14. Integrated design and debug environment Natural workflow for code-centric developers Perform design or code-level debugging in single environment Use Eclipse Intellisense View build errors View Rhapsody diagrams View model information
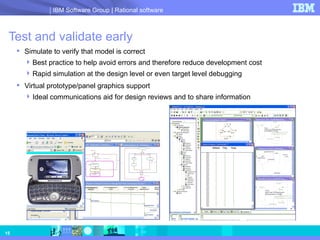
- 15. Test and validate early Simulate to verify that model is correct Best practice to help avoid errors and therefore reduce development cost Rapid simulation at the design level or even target level debugging Virtual prototype/panel graphics support Ideal communications aid for design reviews and to share information
- 16. Traditional code-centric testing process Coding test benches manually ... Error prone; no fun Coding test cases manually ... Difficult; poor coverage is the norm Code on host ... Puzzling; time consuming Code on target ... Frustrating; expensive
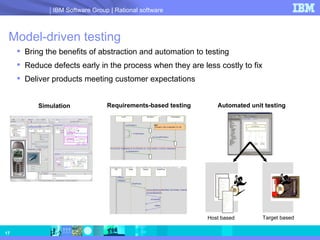
- 17. Model-driven testing Bring the benefits of abstraction and automation to testing Reduce defects early in the process when they are less costly to fix Deliver products meeting customer expectations Simulation Finding & Correcting Errors Sequence Diagrams Requirements-based testing Automated unit testing Host based Target based
- 18. Design and test process integration Virtually seamless integrated process, based on UML 2.0 testing profile Requirements linked to test cases Easier navigation between design and test artifacts Design and test — in sync Automatically generated test execution reports Design artifacts Test artifacts Test execution reports
- 19. Creating a Graphical Test Architecture A Test Architecture is a model of a code-based TestBench Automatically generated Updates as model gets updated
- 20. Test Cases Behaviors as Sequence Diagrams Use Sequence Diagrams as graphical test scripts to capture the required behavior Record and ReUse Animated Sequence Diagrams as test cases for regression testing purposes Use ATG to automatically generate test cases from the design
- 21. Test Cases Behaviors as Flowcharts and Code
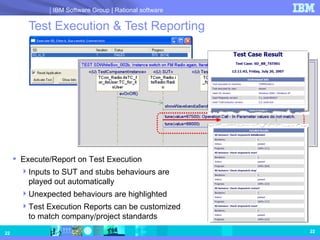
- 22. Test Execution & Test Reporting Execute/Report on Test Execution Inputs to SUT and stubs behaviours are played out automatically Unexpected behaviours are highlighted Test Execution Reports can be customized to match company/project standards
- 23. Structural Testing with Rational Test RealTime Static Analysis Metrics Reporting MISRA-C:2004 compliance review Runtime Analysis Code Coverage Memory Profiling Performance Profiling Analyze user code blocks to ensure quality of the application.
- 24. Runtime Analysis: Code Coverage Get insights into program execution Identify unused and/or untested code MC/DC Coverage levels for C/C++ Directly correlate all analysis results to test cases and code
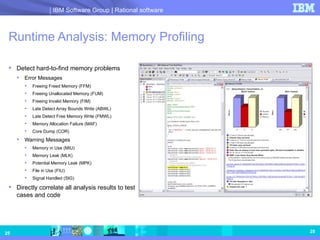
- 25. Runtime Analysis: Memory Profiling Detect hard-to-find memory problems Error Messages Freeing Freed Memory (FFM) Freeing Unallocated Memory (FUM) Freeing Invalid Memory (FIM) Late Detect Array Bounds Write (ABWL) Late Detect Free Memory Write (FMWL) Memory Allocation Failure (MAF) Core Dump (COR) Warning Messages Memory in Use (MIU) Memory Leak (MLK) Potential Memory Leak (MPK) File in Use (FIU) Signal Handled (SIG) Directly correlate all analysis results to test cases and code
- 26. Runtime Analysis: Performance Profiling Graphically see where your application is consuming the most time Top functions graph Performance summary report
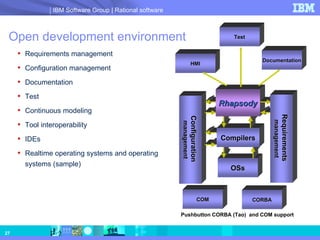
- 27. Open development environment Requirements management Configuration management Documentation Test Continuous modeling Tool interoperability IDEs Realtime operating systems and operating systems (sample) Configuration management OSs Compilers Rhapsody Requirements management Documentation Test HMI CORBA COM Pushbutton CORBA (Tao) and COM support
- 28. Open development environment Reuse existing IP Work with existing development tools and processes Open configuration management Interface Interface to any compiler or IDE Work with any realtime operating system or target Continue to use existing development tools Code coverage Static analysis Simulink integration Application programming interface (API) to create custom scripts
- 29. Summary Rhapsody’s model-driven development environment lets you work the way you want to Model code associativity synchronizes the model and code Rhapsody supports reuse of software assets Visualize legacy code to provide clarity View structure and architecture of the current design Better understand code that is in “maintenance mode” Leverage external code into your application Move forward with model-driven testing to help improve quality and productivity Integrated Verification and Validation with TestConductor & Test RT integration Rhapsody provides an open environment that allows you to continue to use existing tools
- 30. Appendix
- 31. Aerospace/defense applications Aerospace/defense applications Air traffic control Avionics Displays Navigation Autopilot Cabin systems Communications Wireless Secure Engine controls Flight controls Fuel systems Hydraulic systems Landing gear Flight controls Aerospace/defense applications Landing systems Lighting systems Maintenance systems Military vehicles Manned Unmanned Missiles Mission software Power management Radar Satellites Training systems Weapons systems Stores management Fire control
- 32. Automotive applications Automotive applications Body/cabin systems Air bag Communications - buses (Can and J1850) Communication gateways Displays (dashboard) Digital tachography systems GPS HVAC (climate control) Keyless entry Lighting (interior/exterior) Occupant position Power seat Power tilt Power seat belts Power mirrors Power roofs Automotive applications Body/cabin systems Power windows Power sliding doors Power locks Radios Security/anti-theft Telematics Tire deflation indicator Windshield wipers Chassis control systems ABS Power train systems Cruise control GlowPlug Transmission/gear box
- 33. Medical applications Medical applications Medical imaging IMRT Computed tomography (CT) scanners Implantable therapeutic devices Blood oxygenation Heart lung machines Pacemakers Defibrillators Medical applications Blood glucose monitors PAP test Blood analyzer Incubator Oncology care Infusion pumps and systems Dental treatment centers
- 34. Industrial automation applications Industrial automation applications Air-conditioning systems Elevator controls Home heating systems Pick and place systems Semiconductor manufacturing Industrial automation applications Wafer inspection systems Letter sorting systems Semiconductor component handlers Industrial process engineering
- 35. Telecommunications applications Telecom applications EVDO IMS (IP multimedia subsystem) Intelligent networks Radio access network for 3G Routers/switches Telecom applications Set-top boxes Terminal devices (handsets) Telephony modems Ultra mobile broadband Wi-MAX
- 36. Consumer electronics/office automation applications Consumer/office applications Copiers DECT with SMS/MMS Faxes Hard drives Image processing Multifunction copiers Printers Consumer/office applications Copiers Printer drivers Security systems Industrial printers TV applications Cashless point of sale Mobile data capturing terminals
- 37. IBM services Customer services Technical support Client center Administrative support Consulting Best practices assessment Process and methodology Consulting and mentoring Training Tool training: dedicated for systems engineers Dedicated for software engineers Process training, including Harmony process training and modeling guidelines handbook UML / SysML training Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) training Rapid deployment package Custom courses Tools Consulting Customer service Training
- 38. Rapid deployment package Provides a roadmap for a successful and on-time project Supports enhanced productivity Helps reduce risks Specifically designed for new Telelogic Rhapsody users or existing users beginning a new project IBM experts work directly with your team Based on extensive experience in helping users develop systems and software with Rhapsody Contents customized based on your project needs Includes a customized methodology handbook with plus version
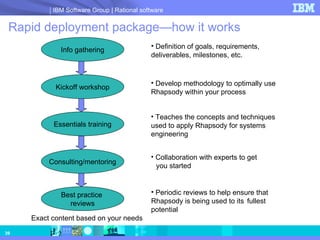
- 39. Rapid deployment package—how it works Info gathering Definition of goals, requirements, deliverables, milestones, etc. Kickoff workshop Develop methodology to optimally use Rhapsody within your process Essentials training Teaches the concepts and techniques used to apply Rhapsody for systems engineering Consulting/mentoring Collaboration with experts to get you started Best practice reviews Periodic reviews to help ensure that Rhapsody is being used to its fullest potential Exact content based on your needs
- 40. Rapid development package—the handbook Customized for your goals Tailored to your process Includes Process description Modeling guidelines Traceability guidelines Content management guidelines Illustrations Completed by the end of rapid development package Info gathering Kickoff workshop Essentials training Consulting/mentoring Best practice reviews Modeling guidelines handbook Exact content based on your needs
- 41. Open, extensible and configurable framework Goal: customizable framework so that users have greater control The framework is delivered as a Rhapsody model Provides a clear understanding of its component structure and functionality, to support fine-tuning Includes requirements and design rationale so it’s easily understood Validation suite can be made available through professional services Facilitates scaling down for smaller footprint applications Pick and choose only the necessary components Customize components Facilitates certification of the framework such as DO-178B Scalable—helps ensure that you include only the components you need; no dead code Customizable—you can fine-tune the implementation to help meet the safety-critical standards
- 42. Agile and model-driven development for development of realtime or embedded systems
- 43. Agile software principles Implementation versus exhaustive planning and documentation Iterative, incremental development and testing of working parts of the design completed quickly Team collaboration with customers and business stakeholders Responsiveness to ever-changing requirements, virtually anytime in the development cycle
- 44. Challenges facing developers Poor communication with customer on code level alone Some documentation is still required Valuable diagrams are created during meetings that are discarded and later needed Target hardware may not be available for early prototyping Managing changing requirements Increasing productivity while design complexity increases More documentation required for embedded systems Collaboration with large teams, often located globally Long learning curve for new team members Maintenance of long life products is difficult with staff changes
- 45. Rhapsody Model-Driven Development Rhapsody Model-Driven Development ™ helps developers to capture the design using graphical models Visualizing design concepts helps increase understandability Use Object Management Group (OMG) UML or a domain-specific language (DSL) Achieving the benefits of both Model-Driven Development and Agile requires the model and code to be the same
- 46. Agile and model-driven development with Rhapsody Rhapsody supports graphical programming of the working application while documentation is automatically generated Empowers individuals to work the way they want to get the job done the way they know how at either the code or model level Work in an iterative, incremental development fashion producing working parts of the design in short time frames while executing and validating each part on target or host Support team collaboration with customers and business stakeholders via graphical models and prototypes as opposed to code based designs Ability to respond to ever-changing requirements, virtually anytime in the development cycle using dynamic links to requirements and automatic graphical differencing and merging
- 47. Iterative development Deliver prototypes often with increasing functionality Customers and stakeholders provide feedback Helps ensure that final product meets expectations Prototype 1 Prototype 2 Prototype 3 Name: Hello World Mission: • Subsystem architecture • Data acquisition • Basic user interface for monitoring Name: Revision 1 Mission: • Basic distribution architecture • Data waveform display • User setting of control values • Data logging Name: 'Customer Review Prototype' Mission: • Reliable Distribution Architecture • Reliable transport protocol • Sockets • Closed Loop Control Analysis Design Implementation Testing Increment review
- 48. For more information To learn more about Telelogic Rhapsody, please visit: http://modeling.telelogic.com/products/rhapsody/index.cfm
- 49. © Copyright IBM Corporation 2008 IBM Corporation Route 100 Somers, NY 10589 U.S.A. Produced in the United States of America October 2008 All Rights Reserved IBM, the IBM logo, ibm.com, Rational, and Telelogic are trademarks or registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. If these and other IBM trademarked terms are marked on their first occurrence in this information with a trademark symbol (® or ™), these symbols indicate U.S. registered or common law trademarks owned by IBM at the time this information was published. Such trademarks may also be registered or common law trademarks in other countries. A current list of IBM trademarks is available on the Web at "Copyright and trademark information" at ibm.com/legal/copytrade.shtml Java and all Java-based trademarks and logos are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States, other countries, or both. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both. Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others. References in this publication to IBM products or services do not imply that IBM intends to make them available in all countries in which IBM operates. Copyright information RAP14031-USEN-00