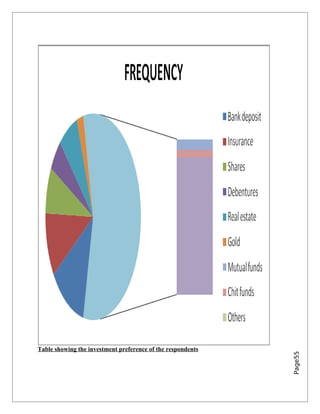
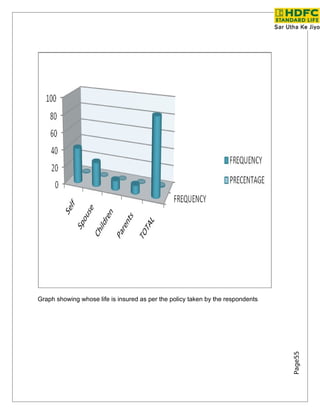
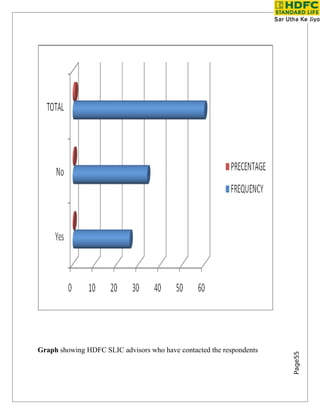
Growth in Insurance Sector
- 1. PROJECT REPORT ON SUMMER TRAINING NAME OF THE ORGANISATION: HDFC Standard Life Insurance PLACE : Dharamshala FIELD OF STUDY : Marketing TOPIC OF RESEARCH : Recruitment, growth and potential of HDFC Standard Life Insurance. Submitted to Institute of Engineering and Emerging Technology, Baddi. In partial fulfillment of the Requirements for the award of Degree of Masters of Business Administration. SUBMITTED BY: Name Sapna Sood Course MBA Year IInd year Roll No 98/08 HPU (roll no) 981 INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES, BADDI, DIST SOLAN, HIMACHAL PRADESH Page1
- 2. To whomsoever it may con This is to certify that Mr. / Miss SAPNA SOO Technologies, Baddi (IMS) titled “ Recruitment, Grow From 1- July-09 (Start date) Company Ltd, DHARAMSHA We wish her/ him good luck Page1
- 3. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I would like to extend my sincere thanks to HDFC Standard Life Insurance Company for providing me an immense opportunity for undertaking research in their esteemed organization and providing me with continuous support and guidance which was vital for the successful completion of the project. I would like to take this opportunity to express my gratitude to my project guide, Mr. Sunny Walia, Branch development manager, for a significant contribution made by him towards my learning, by way of making himself available, providing leads in course of the project and most importantly for the tremendous source of encouragement and inspiration he has bestowed on me throughout the project. He was my advisor in HDFC SLIC. I express my sincere gratitude to Mr. Varun Gandotra Branch Manager of HDFC Standard Life Insurance, Dharamshala, and also our training officer Mr. Sanjeev for their timely guidance and in providing the required facilities and information for completing the project. I am also very indebted to my parents and my brother who have been with me at every moment of my life. I also wish to thank Mr. Vivek Kapoor, channel development officer for his kind help and support during the tenure of the project. I also want to take this opportunity to express my sincere gratitude to all the faculty members of HDFC Standard Life Insurance, Dharamshala, my friends and all the people who encouraged me throughout the project. I am also thankfull to god for always being there. Page1
- 4. TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER NO. PAGE.NO. 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY…………………………………………………..…….7-8 2. INTRODUCTION TO INSURANCE………………………………………..……9 DEFINITION…………………………………………………………….…...10 CONCEPT OF INSURANCE………………………………………….…….10 KINDS OF INSURANCE……………………………………………..……..11-12 FUNCTIONS…………………………………………………………….……13-14 3. RECRUITMENT OF FC IN HDFC FINANCIAL CONSULTANT…………………………………………….….15 BENEFITS GIVEN TO FC…………………………………………………...15 PAYOUT TERMS……………………………………………………………..16 SPECIFICATIONS……………………………………………………………16 PAY OUT ELIGIBILITY……………………………………………………...17 CUMULATIVE LICENSING PAYOUT CHART…………………................18-19 TRAINING GIVEN TO FC……………………………………………………20 RATE OF COMMISION THAT FC WILL GET ON PLANS………..............21 QUALITY TRAINING IN HDFC SLIC……………………………………...22 CLUBS………………………………………………………………………….22 STAR PERFORMERS CLUB…………………………………………………22 FIELD WORK ON RECRUITMENT………………………………………....23 4. DIFFERENT PRODUCTS ON WHICH WE WERE TRAINED UNIT LINKED YOUNG STAR PLUS-II………………………………..24-29 UNIT LINKED ENDOWMENT PLUS-II………………………………..30-34 Page1 HDFC SIMPLILIFE……………………………………………………….35-38
- 5. UNIT LINKED ENDOWMENT –II……………………………………… 39-43 UNIT LINKED ENDOWMENT WINNER……………………………….44 HDFC’S SURGICARE PLAN……………………………………………..44 UNIT LINKED YOUNG STAR CHAMPION…………………………….45 UNIT LINKED WEALTH MAXIMISER PLUS…………………………..45 5. INSURANCE INDUSTRY’S PROFILE LIFE INSURANCE…………………………………………………………..46 HISTORY AND PRESENT STATUS OF INSURANCE MARKET………46 INSURANCE SECTOR REFORM…………………………………………..47-48 INDIAN INSURANCE MARKET…………………………………………...49-53 OVERVIEW OF INDIAN INSURANCE INDUSTRY……………………..54 LIFE INSURANCE IN INDIA……………………………………………….54-55 IRDA…………………………………………………………………………...56 DISTRIBUTION TIE UPS OF LIC……………………………………………58 FUNDWISE PATTERN OF INVESTMENT OF LIC…………………………59 MARKET SHARE OF PRIVATE INSURANCE COMPANIES……………..60 EXISTING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET…………………………………….60 PRODUCT MIX OF LIC……………………………………………………….61 6. INTRODUCTION OF HDFC SLIC OVERVIEW OF HDFC SLIC………………………………………………….62-63 KEY STRENGTH……………………………………………………………….64-67 PROFILE OF THE ORGANISATION………………………………………...68-69 COMPANY’S HISTORY……………………………………………………….70 • CODE OF CONDUCT AND ETHICS………………………………….71-76 • CORPORATE GOVERNANCE POLICY……………………………...77-78 Page1 RECENT ACHIEVEMENTS AND MILESTONES…………………………….79-80 PRODUCTS OF HDFC SLIC……………………………………………………81-87
- 6. INDUSTRIES OF HDFC SLIC…………………………………………………..88 VISION AND VALUES………………………………………………………….89 • RESPONSIBILITY OF BOARD OF DIRECTORS……………………90 • AUDIT AND RISK COMMITTEE OF DIRECTORS………………….91 7. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY………………………………………………………….92-95 8. DATA PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION……………………96-139 9. SUMMARY OF THE PROJECT……………………………………………………….140-149 FINDINGS……………………………………………………………………150-151 SUGGESTIONS………………………………………………………………152-158 CONCLUSION………………………………………………………………159 13. ANNEXURE AND BIBLIOGRAPHY……………………………………………..160-163 Page1
- 7. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Insurance is the pooling of fortuitous losses by transfer of such risk to insurers, who agreed to provide the pecuniary benefit on their occurrence, or to render service connected with risk. It is the transfer of financial responsibility for the risk at the point of occurrence and conventionally involves the insurer in a commitment to pay. The insurance service lead to efficient and productive allocation of capital resources, facilitate growth of trade and commerce. Globalization will certainly increase insurance penetration and all professionals shall equip themselves to exploit opportunities offered by this sector. The consumers are the largest economic group in any country and the present day business activities are because of consumers only. Thus, consumers are the pillars of the economy. The consumers are not only the heart of marketing system, but also the controller of marketing functions. But it the modern marketing system consumers sovereignty has become a myth on account of the variety of problems in the process of merchandising. The study of consumer behavior enables marketers to understand and predict consumer behavior in the market place; It also promote understanding of the role that consumption plays in the lives of individual. This gives me an opportunity to work on with this endeavor focusing on the recruitments and growth of the company with special reference to the insurance Page1 products’. The primary objective of the study is to understand the growth of the
- 8. company by studying the awareness of the financial products within the consumers and the number of consumers who take the policy from HDFC SLIC. Apart from this the project also mentions the necessity of recruitment of financial consultants. I have done field work regarding the recruitment. The introductory chapter gives and insight to the insurance industry. It briefly explains about the history of life insurance sector. It also contain the organizational profile of HDFC SLIC, stating about its mile stones, vision, products, protection solutions, advertising effectiveness and finally about its marketing strategies and challenges. The second chapter gives a glimpses idea about the area of dissertation i.e. theoretical background of the study. This part clearly explains the theoretical part of consumer behavior in general. It also includes statement of the problem, need and impotents of the present study and focal objectives of the dissertation undertaken. The third chapter explains about literature review. It briefly describes what all are the information source for the present study and what benefits has derived from the reference of those literatures. Next part explains about the research methodology. With the basic understanding of the study research design was formulated. To collect the data, questionnaires consisting of 24 questions were prepared. The necessary data were collected through personal interviews and interaction with both company personnel and holders of life insurance policies. This chapter specifically explains about the type of research, sample technique, sample size, actual collection of data and the tools used for the testing of hypothesis. The last but one chapter contains the analysis and interpretation of data collected. The collected data was coded through tally bars and presented in percentage wise and depicted in the form of graphical representation. It also includes the hypothesis test about the overall result of the present study. The last chapter is entirely the exploration of the research study giving all respondents opinion in nutshell as findings i.e. stating that around percentage of Page1 customers behave positively towards the HDFC SLIC’s products. The dissertation
- 9. ends up with the suggestions in order to modify the current system for a higher growth and progress. INTRODUCTION TO THE SUBJECT Introduction to Insurance Insurance is a complex mechanism & it is consequently difficult to define. Insurance is co-operative device for spreading over the loss suffered by one or more, caused by particular risk, over large number of persons who agree to share the loss collectively. We all are exposed to various risks in our daily life. Even the Wisest & Cleverest can't avoid all risks. Nobody can predict or foresee the calamity he may suffer in future. Everybody on the road, whether on foot or in a vehicle carries some risk.' of accident which may result into serious injury, loss of limb impairing ability to earn livelihood, or even death. One may take precautions against such risk, but the risk can't be eliminated. Similarly, there can be loss due to fire, earthquakes, illness etc. Every loss causes human suffering. A risk involves loss. Not all, but most of the losses can be expressed in term of money. A person exposed to some risk may incur a loss. If loss is small he may bear it alone. If loss is huge he may not be able to bear it alone. Society may've to render help to enable the sufferer to cope up with the situation. e.g., the help rendered to the victim of earthquake in Gujarat. However it will be better if a device or system is developed to provide help to those who happen to suffer a loss. Such a system is INSURANCE. INSURANCE is a Co-operative device, which spreads, the loss caused by a par- ticular risk to some person, over a number of person who are exposed to same or Page1 similar risk & who agree to 'insure' against that risk.
- 10. DEFINITIONS: Functional definition: Insurance is an instrument of distributing the loss of a few among many. ALLEN C. MAYERSON, "Insurance is a device for the transfer to an insured of certain risks of economic loss that would otherwise be same by the insured." Contractual definition: JUSTICE TINDALL, "Insurance is a contract in which a sum of money is paid to the assured in consideration of insurer's incurring the risk of paying a large sum upon a given contingency." CONCEPT OF INSURANCE Insurance is always against the risk (Risk is a condition where there is a possibility of an adverse deviation from a desired outcome that is expected or hoped for). When risk is said to be exist, there must always be at least two outcomes: certain and uncertain. Risk arises out of uncertainty. Therefore Insurance is for the loss arising out of the uncertainty of an event. Page1
- 11. Insurance is a mechanism or device to reduce the risk through risk sharing and risk transfer. It is not the property, which is being insured. It is the person’s financial interest in the property. So, Insurance provides the financial service. However in simple terms, it has two characteristics: 1. Transferring or shifting of risk from one individual to a group; 2. Sharing losses, on some equitable basis, by all members of the Group. KINDS OF INSURANCE 1. Life Insurance: The subject matter of this type of insurance is human life. Most of insurance policies are combination of saving & security. The insured is promised by the insurance Co. that during the tenure of insurance in case of his death, his nominee will be paid the insurance amount. According to the SECTION 2 (ii) of Insurance Act 1938, "Life Insurance is the business of effecting contracts of insurance upon human life including any contract, whereby the payment of money is assured on death except death by accident on the happening of any contingency dependent on human life and any contract which is subject to the payment of premium for a team dependent on human life." 2. General Insurance: (a) Marine Insurance: It covers the sea or marine perils. Peril is the cause of loss or hazard, which is a condition that may increase the chance of the loss. Marine Insurance is protection against marine perils like loss or sinking of the ship, sea piracy, capture by enemy etc. Page1 (b) Fire Insurance:
- 12. It covers loss due to fire to the property like houses, shops, goods factories or go down etc. (c) Liability Insurance: Covers risk of liability against third party, which on insurer might have to pay under certain circumstances. E.g. injury to the property and/or person of a third person in road accident or employer's liability for an injury or death of a worker while performing duty etc. (d) Social Insurance: This is aimed at providing social security to the weaker sections of the society. It may take the shape of pension plans, disability or sickness benefits etc. The premium may come from government or employee and may also be shared by beneficiary. Life insurance is a contract that pledges payment of an amount to the person assured (or his nominee) on the happening of the event insured against. The contract is valid for payment of the insured amount during: 1. The date of maturity, or 2. Specified dates at periodic intervals, or 3. Unfortunate death, if it occurs earlier. Among other things, the contract also provides for the payment of premium periodically to the Corporation by the policyholder. Life insurance is universally acknowledged to be an institution, which eliminates 'risk', substituting certainty for uncertainty and comes to the timely aid of the family in the unfortunate event of death of the breadwinner. Reasons for investing in life insurance policies: 1. Protection for the Family The most important objective of life insurance is to provide financial protection for the family in case of an unexpected and premature death of its bread earner. The purpose Page1 is to protect the dependents against the loss of earning power of the insured through
- 13. death or disability. Those who have insured their lives for an adequate sum can live in peace and comfort, free of the worry of what would happen to their families in the event of their sudden and premature death. 2. Regular Savings Saving is not a physical need, unlike hunger or sleep. Many of us may not save unless there is compulsion to do so. For such people, life insurance is a compulsory, regular savings scheme, especially the monthly salary savings schemes. Even if you do not subscribe to the salary savings scheme, you can issue standing instructions to your bankers to pay the premium regularly without reference to you. The element of savings in a life insurance contract should be understood in a proper perspective. FUNCTIONS OF INSURANCE A). Primary Functions 1. Certainty of Compensation of Loss: Insurance provides certainty of payment at the uncertainty of loss. The element of uncertainty is reduced by better planning and administration. The insurer charges premium for providing certainty. Life is always full of risks. Life without risks and uncertainties is unthinkable. Man has always encountered risks of various types since the inception of civilization. Minor risks can be ignored but the major risks cannot be ignored and their avoidance is desirable. One of the ways or techniques of meeting the risks loss is prevention and insurance. Insurance removes all uncertainties and the assured is given certainty of payment of loss. The insurer charges premium for providing the said certainty. 2. Insurance provides protection: The risk will occur or not, when will occur, how much loss will be there is an uncertain? Page1 There are uncertainties of happenings of time and amount of loss. The main function of
- 14. the insurance is to provide protection against the probable chances of loss. The insurance cannot check the happening of risk. The insurer gives certainty of payment of loss to the assured by charging premium. 3. Risk sharing: Risk is uncertain and therefore loss arising from the risk is also uncertain. All business concerns face the problem of risk and if the concern is big enough the handling of risk become a specialized function. (B). SECONDARY FUNCTIONS 1. Prevention of loss: Prevention is always better than cure. Prevention of loss is by far the best solution to the problem of risk. When prevention fails other methods must be adopted. The insurance joins hands with those institutions, which are actively engaged in preventing the losses of the society. Reduction in loss causes lesser payment to the assured and so more saving is possible which will assist in reducing the premium 2. It provides capital: It provides capital to the society. For planned development of a country there is great need for huge amount of capital. The accumulated funds are invested in providing proper infrastructure and in investing in productive channel. Now a day, the insurance companies are rendering positive help in the development of trade, commerce and industries of a country through different scheme of investment. 3. Adequate Financial cover: The need of insurance is largely felt to give a cover to the rural areas and to the socially and economically backward classes with a view to Page1
- 15. reach all insurable person in the country and provide them adequate financial cover against death at a reasonable cost. 4. Mobilization of Savings: In insurance the savings of masses is collected by insurance corporations. 5. Investment: When funds are invested the interest of the community is kept in mind. RECRUITMENT AS FINANCIAL CONSULTANT IN HDFC STANDARD LIFE INSURANCE FINANCIAL CONSULTANT: A person who motivates other people to take different policies from the company. He is a mediator between the company and the people. He provides the people with all the necessary information regarding the different policies. There are certain benefits which are provided to financial consultants. Some of them are mentioned below: TIER/CLUB LICENSING NOS PAYOUT/LICENSE SILVER 1-3 1300 GOLD 4-10 1750 GOLD PLUS 11-25 2250 PLATINUM 26-40 2500 PLATINUM PLUS >=41 3000 RECRUITMENT NOS/ PER MONTH PAYOUT /RECRUITMENT 1-6 200 >=7 Page1 Bonus of rs.200/- per license if input/output ratio for the month is >= 33% will be paid quarterly.
- 16. OTHER PAYOUT TERMS: 1. For licensing payouts, processing is done monthly based on slabs of cumulative count of license during the applicable period. 2. For recruitment payouts, payout cycle is on monthly basis. Each month FC recruitment count will start from zero. 3. For calculation of input/ output ratio, candidates recruited or licensed as life to life transfer cases will not be accounted. 4. Recruitments payouts to be made only on the completion of training of the candidates recruited. 5. PTs will be paid at the payout slab, based on cumulative number of licenses clocked by the recruited candidates during the applicable period. 6. Incase of recruitment of life to life transfer cases no recruitment payout to be considered to PTs. 7. If PT is recruitment inactive for 3 months continuously then he is declared terminated and he may not claim licensing payout post termination. 8. Recruit needs to be approved by the concerned BSM or AM-CD. 9. Payout shall not be paid on recruitments in case not accompanied by prescribed fees. 10. Payout will be done after 30 days of completion of project tenure by way of either gift cards or in such fashion. Page1 SPECIFICATION FOR RECRUITMENT OF FC Specifications are: (Q-score)
- 17. • Age of financial consultant should be in bracket of 25-55 years. • Family income of FC should be minimum of rs. 3 lacs /annum. • FC should be a graduate. • Fc should have spent a minimum of 3 years in the city of current residence. PAYOUT ELIGIBLE IS AS PER TABLE MENTIONED BELOW: Recruitmen 1200 1200 1000 1200 0 1200 t payout Licensing 7400 5250 10250 6750 11250 16500 payout Tier Gold Gold Gold plus Gold plus Gold plus Platinum attained Bonus at 1000 800 800 0 0 0 the end of 1st quarter Bonus at 200 0 400 1000 0 1400 the end of 2nd quarter IMPORTANT CALCULATIONS: • RC is eligible for max of 1200/- rs recruitment payout for a month in case of >=6 FC recruitment with training completion • Bonus payout is calculated on quarterly cycle. Page1
- 18. Page1
- 19. TIER COUNT PAYOUT INCREMENTAL INCREMENTAL CUMULATIVE COUNT OF LICENSE LIC PAYOUT FOR 2009(RS) SILVER 1 1300 1 1300 1300 SILVER 2 1300 1 1300 2600 SILVER 3 1300 1 1300 3900 GOLD 4 1750 1 1750 5650 GOLD 5 1750 1 1750 7400 GOLD 6 1750 1 1750 9150 GOLD 7 1750 1 1750 10900 GOLD 8 1750 1 1750 12650 GOLD 9 1750 1 1750 14400 GOLD 10 1750 1 1750 16150 GOLD 11 2250 1 2250 18400 PLUS GOLD 12 2250 1 2250 20650 PLUS GOLD 13 2250 1 2250 22900 PLUS GOLD 14 2250 1 2250 25150 PLUS GOLD 15 2250 1 2250 27400 PLUS GOLD 16 2250 1 2250 29650 PLUS GOLD 17 2250 1 2250 31900 PLUS GOLD 18 2250 1 2250 34150 PLUS GOLD 19 2250 1 2250 36400 PLUS GOLD 20 2250 1 2250 38650 PLUS GOLD 21 2250 1 2250 40900 PLUS GOLD 22 2250 1 2250 43150 PLUS GOLD 23 2250 1 2250 45400 Page1 PLUS GOLD 24 2250 1 2250 47650 PLUS GOLD 25 2250 1 2250 49900 PLUS PLATIN 26 2500 1 2500 52400 UM
- 20. CUMULATIVE LICENSING PAYOUT CHART BASED ON CUMULATIVE COUNT OF LICENSES FINANCIAL CONSULTANT Financial consultant is not an agent. The biggest difference is that an agent is not certified where as an FC is certified by a governing body of the insurance called the IRDA. An FC advice and recommend the best solution to meet a client’s financial requirement. Working as an FC brings an excellent growth opportunity as the FC himself can decide the amount of his own pay cheque. He can himself choose his working hours TRANINIG OF A FINANCIAL CONSULTANT Training Managers are appointed in major cities for the constant upgrading in providing service to a customer. Page1
- 21. Classroom sessions are conducted for all the trainees. 50 hours training is compulsory for every trainee. The examination is conducted by IRDA. If the FC is far away from the place of training then he can also opt for online training. They will have timely interactions with the company spokespersons. A special program is started to improve the selling skill of the FC which is known as the Professional Selling Skills Programme. The basic objective of the program is to: • Provide a lead • To increase the participation of FC in exhibitions and organizing events. • There are many Branch level contests which are started. If an FC works hard and smart and fulfills the criteria for being a winner then he is given certain gifts, benefits and free tours. RATE OF COMMISION THAT EVERY FC WILL GET ON THE FOLLOWING PLANS: Page1
- 22. Rate of commision Type of Plan First year 2nd year 3rd Year+ Bonus Endowment 25% 5% 5% 15% Money Back 25% 5% 5% 15% Term Assurance (RP) 20% 5% 5% 15% Loan Cover Term (RP) 20% 5% 5% 15% PPP (RP) 7.50% 2% 2% NIL SPWLP/ PPP (SP) 2% - - ULEP 12.50% 4% 1% NIL ULPP (RP) 7.50% 2% 1% NIL ULPP (SP) 1% HDFC SLIC gives the top quality training to all the FC. There are certain features which keeps the HDFC SLIC on the top when it comes to proper training of an FC. Some of them are mentioned below: • Support of a dedicated Sales Development Manager • First class pre and post sales support Page1 • Lead Generation Support
- 23. • Marketing Support • Recognition Programs - MDRT, Top Achievers Section • Reward Programs • Online Support CLUBS: There are certain clubs which are started to increase the healthy competition between the financial consultants. • Level 1: Star Centurion Club (upto 10% extra commission) • Level 2: Gold Star Performers Club (5% extra commission) • Level 3: Silver Star Performers Club (2.5% extra commission Star Performers Club • Periodic Branch Level Contests are started. • National Level Contests are started to increase the competition and urge to do better between the different FC’s. Prizes ranging from Foreign Trips, Consumer Durables, Mobile phones, Laptops, Palmtops, Handy-cams, Gold Coins etc. All Financial Consultants who qualify for National Level gets Certificate of Achievement from the Head - Retail Sales FIELD WORK IN HDFC SLIC Field work is of following two types: Policies Recruitment Page1
- 24. FIELD WORK POLICIES RECRUITMENT During my tenure in HDFC SLIC, we were only asked to do recruitments of financial consultants. TARGET received was of 4 recruitments. By the tenure of my training in HDFC SLIC I was able to complete 7 recruitments. The details of them are as follows: Name of the financial Educational qualification Profession consultant Arvind kumar Graduation Shop keeper Sumit kumar Graduation Shop keeper Sanjay kumar Graduation Clerk Tinkle Graduation Shop keeper Susheel Graduation Shop keeper Chander Graduation Teacher Narendra Graduation Teacher Page1
- 25. In HDFC SLIC, DHARAMSHALA, we were trained about different products. These are mentioned below: UNIT LINKED YOUNG STAR PLUS-II (Invest in your child’s dreams and secure your self respect) In young star plus policy, the investment risk in investment portfolio is borne by the policy holder. The HDFC Unit Linked Young Star Plus-II gives: • Valuable protection to your child in case you are not around. • An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investments. • Regular loyalty units to boost your fund value every year. • Flexible benefit combinations and premium payment options. • Flexible additional benefits options such as critical illness cover. • Flexible benefit payment preferences- double benefit and triple benefit. We can choose our investment funds and premium. We will then invest our premium, in our chosen funds, in the proportion we specify. In case of the person’s unfortunate demise during the policy term, we will: 1. Pay the sum assured he had chosen to the beneficiary. 2. For double benefit continue to pay 100% of the original regular premiums towards your policy. 3. For triple benefit continue to pay 50% of the original regular premiums towards your policy and pay the balance 50% of the premium to the beneficiary. This means that HDFC Standard Life Insurance will continue to make your savings on your behalf, in your absence. Four easy steps to your own plan: STEP 1 Choose the premium you wish to invest. STEP 2 Choose the amount of protection you desire. STEP 3 Choose the additional plan benefit you desire. STEP 4 Choose the investment fund you desire. Page55
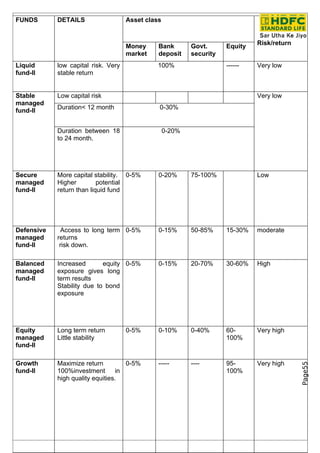
- 26. FUNDS DETAILS Asset class Risk/return Money Bank Govt. Equity market deposit security Liquid low capital risk. Very 100% ------ Very low fund-II stable return Stable Low capital risk Very low managed Duration< 12 month 0-30% fund-II Duration between 18 0-20% to 24 month. Secure More capital stability. 0-5% 0-20% 75-100% Low managed Higher potential fund-II return than liquid fund Defensive Access to long term 0-5% 0-15% 50-85% 15-30% moderate managed returns fund-II risk down. Balanced Increased equity 0-5% 0-15% 20-70% 30-60% High managed exposure gives long fund-II term results Stability due to bond exposure Equity Long term return 0-5% 0-10% 0-40% 60- Very high managed Little stability 100% fund-II Growth Maximize return 0-5% ----- ---- 95- Very high Page55 fund-II 100%investment in 100% high quality equities.
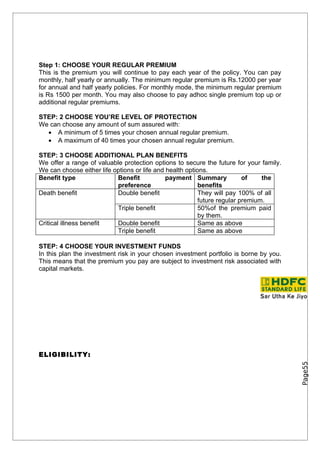
- 27. Step 1: CHOOSE YOUR REGULAR PREMIUM This is the premium you will continue to pay each year of the policy. You can pay monthly, half yearly or annually. The minimum regular premium is Rs.12000 per year for annual and half yearly policies. For monthly mode, the minimum regular premium is Rs 1500 per month. You may also choose to pay adhoc single premium top up or additional regular premiums. STEP: 2 CHOOSE YOU’RE LEVEL OF PROTECTION We can choose any amount of sum assured with: • A minimum of 5 times your chosen annual regular premium. • A maximum of 40 times your chosen annual regular premium. STEP: 3 CHOOSE ADDITIONAL PLAN BENEFITS We offer a range of valuable protection options to secure the future for your family. We can choose either life options or life and health options. Benefit type Benefit payment Summary of the preference benefits Death benefit Double benefit They will pay 100% of all future regular premium. Triple benefit 50%of the premium paid by them. Critical illness benefit Double benefit Same as above Triple benefit Same as above STEP: 4 CHOOSE YOUR INVESTMENT FUNDS In this plan the investment risk in your chosen investment portfolio is borne by you. This means that the premium you pay are subject to investment risk associated with capital markets. ELIGIBILITY: Page55
- 28. BENEFITS TIME PERIOD AGE AT ENTRY MAXIMUM MINIMUM MAXIMUM MINIMUM MAXIMUM AGE AT MATURITY LIFE 10 25 18 65 75 OPTIONS LIFE AND 10 25 18 55 65 HEALTH OPTIONS : Page55 ACCESSING YOUR MONEY 1. ON MATURITY: Your policy matures at the end of the policy term you have chosen and your death and other risk ceases. You may redeem your balance units at the then prevailing unit price and take the fund value with you.
- 29. SETTLEMENT OPTIONS: You have the option to take your fund in periodical installment over the period, this may extend to 5 years. 2. ON DEATH: Incase of your unfortunate demise during the policy Term, we will: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Double benefit payment: continue to pay 100% of the original regular premiums towards your policy as and when the premiums are due on an annual basis. • Triple benefit payment: continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy and pay the balance 50 % of the premium to the beneficiary on annual basis. 3. ON CRITICAL ILLNESS: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Continue to pay 100% of the original regular premium towards your policy as and when the premium is due, on an annual basis. • Continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy on annual basis. 4. ON SURRENDER Insurance plans are long term investments with significant tax advantages. If you do not pay the original regular premium due in the first 3 years your life cover will cease and the value of the units in the fund after the deduction of the surrender charge will cease to be invested and will be held separately by us. This amount will be paid out to you only at the end of the third year of your policy or the end of the two year after you stop paying premiums into your policy, whichever is later. Minimum withdrawal amount is 10000. Page55
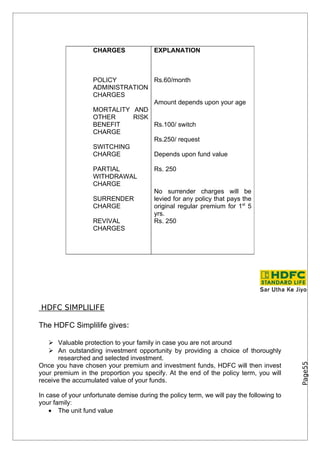
- 30. CHARGES EXPLANATION POLICY Rs.60/month ADMINISTRATION CHARGES Amount depends upon your age MORTALITY AND OTHER RISK BENEFIT Rs.100/ switch CHARGE Rs.250/ request SWITCHING CHARGE Depends upon fund value PARTIAL Rs. 250 WITHDRAWAL CHARGE No surrender charges will be SURRENDER levied for any policy that pays the CHARGE original regular premium for 1st 5 yrs. REVIVAL Rs. 250 CHARGES CHARGES on withdrawl Page55
- 31. UNIT LINKED ENDOWMENT PLUS-II The HDFC Unit Linked Endowment plus II gives: Valuable protection to your family in case you are not around. An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investments. Regular loyalty units to boost your fund value every year. Flexible benefit combinations and premium payment options. Flexible additional benefit options such as critical illness cover. You can choose your premium and the investment funds. HDFC will then invest your premium in your chosen funds. Incase of your unfortunate demise during the policy term, we will pay the greater of your sum assured and your total fund value to your family. 4 EASY STEPS TO YOUR OWN PLAN: STEP 1 Choose the premium you wish to invest. STEP 2 Choose the amount of protection you desire. STEP 3 Choose the additional plan benefit you desire. STEP 4 Choose the investment fund you desire. Step 1: CHOOSE YOUR REGULAR PREMIUM This is the premium you will continue to pay each year of the policy. You can pay monthly, half yearly or annually. The minimum regular premium is Rs.12000 per year for annual and half yearly policies. For monthly mode, the minimum regular premium is Rs 1500 per month. You may also choose to pay adhoc single premium top up or additional regular premiums. STEP: 2 CHOOSE YOU’RE LEVEL OF PROTECTION We can choose any amount of sum assured with: • A minimum of 5 times your chosen annual regular premium. • A maximum of 40 times your chosen annual regular premium. STEP: 3 CHOOSE ADDITIONAL PLAN BENEFITS We offer a range of valuable protection options to secure the future for your family. We can choose either life options or life and health options. Page55 Benefit type Benefit payment Summary of the preference benefits Death benefit Double benefit They will pay 100% of all future regular premium. Triple benefit 50%of the premium paid by them.
- 32. Critical illness benefit Double benefit Same as above Triple benefit Same as above STEP: 4 CHOOSE YOUR INVESTMENT FUNDS In this plan the investment risk in your chosen investment portfolio is borne by you. This means that the premiums you pay are subject to investment risk associated with capital markets. FUNDS DETAILS Asset class Risk/return Money Bank Govt. Equity market deposit security Liquid low capital risk. Very 100% ------ Very low fund-II stable return Stable Low capital risk Very low managed fund-II Duration< 12 month 0-30% Duration between 18 to 0-20% 24 month. Secure More capital stability. 0-5% 0-20% 75-100% Low managed Higher potential return fund-II than liquid fund Defensiv Access to long term 0-5% 0-15% 50-85% 15-30% moderate e returns managed risk down. fund-II Page55
- 33. Balanced Increased equity 0-5% 0-15% 20-70% 30-60% High managed exposure gives long fund-II term results Stability due to bond exposure Equity Long term return 0-5% 0-10% 0-40% 60-100% Very high managed Little stability fund-II Growth Maximize return 0-5% ----- ---- 95-100% Very high fund-II 100%investment in high quality equities. Page55
- 34. ACCESSING YOUR MONEY 1. ON MATURITY: Your policy matures at the end of the policy term you have chosen and your death and other risk ceases. You may redeem your balance units at the then prevailing unit price and take the fund value with you. SETTLEMENT OPTIONS: You have the option to take your fund in periodical installment over the period; this may extend to 5 years. 2. ON DEATH: In case of your unfortunate demise during the policy Term, we will: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Double benefit payment: continue to pay 100% of the original regular premiums towards your policy as and when the premiums are due on an annual basis. • Triple benefit payment: continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy and pay the balance 50 % of the premium to the beneficiary on annual basis. 3. ON CRITICAL ILLNESS: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Continue to pay 100% of the original regular premium towards your policy as and when the premium is due, on an annual basis. • Continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy on annual basis. 5. ON SURRENDER Insurance plans are long term investments with significant tax advantages. If you do not pay the original regular premium due in the first 3 years your life cover will cease and the value of the units in the fund after the deduction of the surrender charge will cease to be invested and will be held separately by us. This amount will be paid out to you only at the end of the third year of your policy or the end of the two year after you stop paying premiums into your policy, whichever is later. Minimum withdrawal amount is 10000. Page55
- 35. CHARGES on with drawl Page55
- 36. CHARGES EXPLANATION POLICY Rs.60/month ADMINISTRATION CHARGES Amount depends upon your age MORTALITY AND OTHER RISK BENEFIT Rs.100/ switch CHARGE Rs.250/ request SWITCHING CHARGE Depends upon fund value PARTIAL Rs. 250 WITHDRAWAL CHARGE No surrender charges will be SURRENDER levied for any policy that pays the CHARGE original regular premium for 1st 5 yrs. REVIVAL Rs. 250 CHARGES HDFC SIMPLILIFE The HDFC Simplilife gives: Valuable protection to your family in case you are not around An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investment. Page55 Once you have chosen your premium and investment funds, HDFC will then invest your premium in the proportion you specify. At the end of the policy term, you will receive the accumulated value of your funds. In case of your unfortunate demise during the policy term, we will pay the following to your family: • The unit fund value
- 37. • Sum assured 2 EASY STEPS TO YOUR OWN PLAN: STEP 1: Choose the premium you wish to invest This is the premium you will continue to pay each year of the policy. You can pay either annually or half yearly. Your policy will have a fixed sum assured of 5 times your chosen annualized premium. minimum maximum Annualized premium Rs. 20000 Rs. 100000 Sum assured Rs. 100000 Rs. 500000 STEP 2: Choose the investment fund or funds you desire. In this plan the investment risk in your chosen investment portfolio is borne by you. This means that the premiums you pay in this plan are subject to investment risks associated with the capital markets. So, to balance your level of risk and return, making the right investment choice is very important and you are responsible for the choice you make. FUNDS DETAILS Asset class Risk/return Money Bank Govt. Equity market deposit security Liquid low capital risk. Very 100% ------ Very low fund-II stable return Stable Low capital risk Very low managed fund-II Duration< 12 month 0-30% Duration between 18 to 0-20% 24 month. Secure More capital stability. 0-5% 0-20% 75-100% Low managed Higher potential return Page55 fund-II than liquid fund
- 38. Defensiv Access to long term 0-5% 0-15% 50-85% 15-30% moderate e returns managed risk down. fund-II Balanced Increased equity 0-5% 0-15% 20-70% 30-60% High managed exposure gives long fund-II term results Stability due to bond exposure Equity Long term return 0-5% 0-10% 0-40% 60-100% Very high managed Little stability fund-II Growth Maximize return 0-5% ----- ---- 95-100% Very high fund-II 100%investment in high quality equities. FLEXIBLE OPTIONS FOR YOUR NEEDS: Flexible options benefits Changing your investment decisions Switching Premium redirections Premium changes You can not increase or reduce your regular premiums at any time. After 3 years of regular premium Page55 your policy will be converted into a paid policy. ELIGIBILITY:
- 39. TERM PERIOD AGE AT ENTRY MAX AGE AT MATURITY MIN-15 YRS MIN-18 YRS 60 YRS MAX-20 YRS MAX- 45 YRS ACCESSING YOUR MONEY 1. ON MATURITY: Your policy matures at the end of the policy term you have chosen and your death and other risk ceases. You may redeem your balance units at the then prevailing unit price and take the fund value with you. SETTLEMENT OPTIONS: You have the option to take your fund in periodical installment over the period; this may extend to 5 years. 2. ON DEATH: In case of your unfortunate demise during the policy Page55 Term, we will: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Double benefit payment: continue to pay 100% of the original regular premiums towards your policy as and when the premiums are due on an annual basis.
- 40. •Triple benefit payment: continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy and pay the balance 50 % of the premium to the beneficiary on annual basis. 3. ON CRITICAL ILLNESS: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Continue to pay 100% of the original regular premium towards your policy as and when the premium is due, on an annual basis. • Continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy on annual basis. 6. ON SURRENDER Insurance plans are long term investments with significant tax advantages. If you do not pay the original regular premium due in the first 3 years your life cover will cease and the value of the units in the fund after the deduction of the surrender charge will cease to be invested and will be held separately by us. This amount will be paid out to you only at the end of the third year of your policy or the end of the two year after you stop paying premiums into your policy, whichever is later. Minimum withdrawal amount is 10000. UNIT LINKED ENDOWMENT II The HDFC Unit Linked Endowment II gives: Valuable protection to your family in case you are not around. An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investment. Page55 Flexible benefit combinations and premium payment options. Flexible additional benefit options such as critical illness cover. 4 EASY STEPS TO YOUR PLAN: STEP 1 Choose the premium you wish to invest.
- 41. STEP 2 Choose the amount of protection you desire. STEP 3 Choose the additional plan benefit you desire. STEP 4 Choose the investment fund or funds you desire. Step 1: CHOOSE YOUR REGULAR PREMIUM This is the premium you will continue to pay each year of the policy. You can pay monthly, half yearly or annually. The minimum regular premium is Rs.12000 per year for annual and half yearly policies. For monthly mode, the minimum regular premium is Rs 1500 per month. You may also choose to pay adhoc single premium top up or additional regular premiums. STEP: 2 CHOOSE YOU’RE LEVEL OF PROTECTION We can choose any amount of sum assured with: • A minimum of 5 times your chosen annual regular premium. • A maximum of 40 times your chosen annual regular premium. STEP: 3 CHOOSE ADDITIONAL PLAN BENEFITS We offer a range of valuable protection options to secure the future for your family. We can choose either life options or life and health options. Benefit type Benefit payment Summary of the preference benefits Death benefit Double benefit They will pay 100% of all future regular premiums. Triple benefit 50%of the premium paid by them. Critical illness benefit Double benefit Same as above Triple benefit Same as above STEP: 4 CHOOSE YOUR INVESTMENT FUNDS In this plan the investment risk in your chosen investment portfolio is borne by you. This means that the premiums you pay are subject to investment risk associated with capital markets. Page55 FUNDS DETAILS Asset class Risk/return Money Bank Govt. Equity market deposit security
- 42. Liquid low capital risk. Very 100% ------ Very low fund-II stable return Stable Low capital risk Very low managed fund-II Duration< 12 month 0-30% Duration between 18 to 0-20% 24 month. Secure More capital stability. 0-5% 0-20% 75-100% Low managed Higher potential return fund-II than liquid fund Defensiv Access to long term 0-5% 0-15% 50-85% 15-30% moderate e returns managed risk down. fund-II Balanced Increased equity 0-5% 0-15% 20-70% 30-60% High managed exposure gives long fund-II term results Stability due to bond exposure Equity Long term return 0-5% 0-10% 0-40% 60-100% Very high managed Little stability fund-II Growth Maximize return 0-5% ----- ---- 95-100% Very high fund-II 100%investment in Page55 high quality equities.
- 43. ACCESSING YOUR MONEY 1. ON MATURITY: Your policy matures at the end of the policy term you have chosen and your death and other risk ceases. You may redeem your balance units at the then prevailing unit price and take the fund value with you. Page55 SETTLEMENT OPTIONS: You have the option to take your fund in periodical installment over the period, this may extend to 5 years. 2. ON DEATH: Incase of your unfortunate demise during the policy Term, we will: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary.
- 44. • Double benefit payment: continue to pay 100% of the original regular premiums towards your policy as and when the premiums are due on an annual basis. • Triple benefit payment: continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy and pay the balance 50 % of the premium to the beneficiary on annual basis. 3. ON CRITICAL ILLNESS: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary. • Continue to pay 100% of the original regular premium towards your policy as and when the premium is due, on an annual basis. • Continue to pay 50% of the original regular premium towards your policy on annual basis. 7. ON SURRENDER Insurance plans are long term investments with significant tax advantages. If you do not pay the original regular premium due in the first 3 years your life cover will cease and the value of the units in the fund after the deduction of the surrender charge will cease to be invested and will be held separately by us. This amount will be paid out to you only at the end of the third year of your policy or the end of the two year after you stop paying premiums into your policy, whichever is later. Minimum withdrawal amount is 10000. CHARGES on with drawl Page55
- 45. CHARGES EXPLANATION POLICY Rs.60/month ADMINISTRATION CHARGES Amount depends upon your age MORTALITY AND OTHER RISK BENEFIT Rs.100/ switch CHARGE Rs.250/ request SWITCHING CHARGE Depends upon fund value PARTIAL Rs. 250 WITHDRAWAL CHARGE No surrender charges will be SURRENDER levied for any policy that pays the CHARGE original regular premium for 1st 5 yrs. REVIVAL Rs. 250 CHARGES Page55 UNIT LINKED ENDOWMENT WINNER The HDFC Unit Linked Endowment Winner gives:
- 46. ⇒ Valuable protection to your family in case you are not around. ⇒ An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investments. ⇒ Bumper additions to the fund value at maturity ⇒ Access to your accumulated fund before maturity. ⇒ No need to go to for medicals. 3 EASY STEPS TO YOUR OWN PLAN: STEP 1 Choose the premium you wish to invest STEP 2 Choose the investment funds you desire. STEP 3 Fill the short medical questionnaire. SURGICARE PLAN The HDFC Surgicare Plan gives you: Valuable financial protection in case of surgical procedures. Increasing health cover every year. Lump sums benefit payment irrespective of actual medical cost. Flexible benefit options to choose from Flexible premium payment options 3 EASY STEPS TO YOUR PLAN: STEP 1 Choose the level of health cover you need STEP 2 Choose the benefit option you desire STEP 3 Work out the premium payable along with our financial consultant. Page55 UNIT LINKED YOUNGSTAR CHAMPION
- 47. The HDFC Unit Linked Young Star Champion gives: Valuable protection to your child in case you are not around. An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investments. Bumper addition to the fund value at maturity. Flexible premium options No need to go for medicals. In case of your unfortunate demise during the policy term, we will: • Pay the sum assured you had chosen to the beneficiary • Continue to pay 50% of the original regular premiums towards your policy. 3 EASY STEPS TO YOUR OWN PLAN: STEP 1 Choose the premium you wish to invest STEP 2 Choose the investment funds you desire STEP 3 Fill the short medical questionnaire UNIT LINKED WEALTH MAXIMISER PLUS The HDFC Unit Linked Wealth Maximiser Plus gives: An outstanding investment opportunity by providing a choice of thoroughly researched and selected investments. One time investment at the star of the policy Cover till age 99 years. Regular loyalty units to boost your fund value every year. No medicals 3 EASY STEPS TO YOUR OWN PLAN: STEP 1 Choose the premium you wish to invest STEP 2 Choose the level of protection you desire. STEP 3 Choose the investment fund you desire. Page55 INDUSTRY PROFILE
- 48. LIFE INSURANCE Life insurance is a contract providing for a payment of a sum of money to the person assured or failing him to the person entitled to receive the same on the happening of certain event. Uncertainty of death is inherent in human life. It is this risk, which gives rise to the necessity for some form of protection against the financial loss arising from death. Insurance substitutes this uncertainty by certainty. The objective of insurance is normally to provide: A. Family protection and B. Provision for old age. HISTORY AND PRESENT STATUS OF INSURANCE MARKET IN INDIA The insurance sector in India has come a full circle from being an open competitive market to nationalization and back to a liberalized market again. Tracing the developments in the Indian insurance sector reviles the 360-degre turn witnessed over a period of almost two centuries. A brief history of the insurance sector The business of life insurance in India in its existing form started in India in the 1818 with the establishment of Oriental Life Insurance Company in Calcutta. Some of the important milestones in the life insurance business in India are: 1912: The Indian Life Assurance Companies Act enacted as the first statute to regulate the life insurance business. 1928: The Insurance Companies Act enacted to enable the government to collect statistical information about both life and non – insurance business. 1938: earlier legislation consolidated and amended to by the Insurance Act with the objective of protecting the interest of the insuring public. 1956: 245 Indian and foreign insurers and provident societies are taken over Page55 by the central government and nationalized. LIC found by an Act of Parliament, viz. LIC Act 1956, with a capital contribution of rupees Five Crore from the Government of India. Insurance sector reforms
- 49. In 1993, Malhotra Committee, headed by former Finance Secretary and RBI Governor R.N. Malhotra, was formed to evaluate the Indian insurance industry and recommend its future direction. The Malhotra committee setup with the objective of complimenting the reforms initiated in the financial sector. The reforms where aimed at “creating a more efficient and competitive financial system suitable for the requirements of the economy keeping in mind the structural changes currently underway and recognizing that insurance is an important part of the overall financial system where it was necessary to address the need for similar reforms…”In 1994, the Committee submitted the report and some of the key recommendations included: i. Structure • Government stake in the insurance companies to be brought down to 50%. • Government should take over the holdings of GIC and its subsidiaries so that these subsidiaries can act as independent corporations. • All the insurance company should be given greater freedom to operate. ii. Competition • Private companies with a minimum paid up capital of Rs. 1bn should be allowed to enter the industry. • No company should dealing both the life and general insurance through a single entity. • Foreign companies may be allowed to enter the industry in collaboration with the domestic companies • Postal Life Insurance should be allowed to operate in the rural market. • Only one State Level Life Insurance Company should be allowed to Page55 operated in each state. iii. Regulatory body
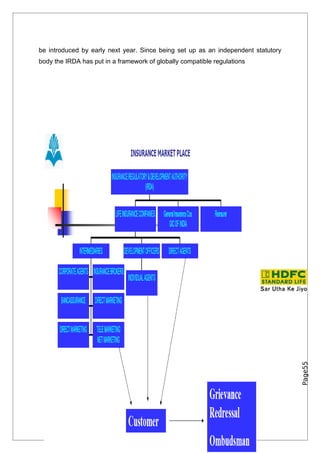
- 50. • The Insurance Act should be changed. • An insurance regulatory body should be setup. The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Reforms in the Insurance sector were initiated with the passage of the IRDA Bill in Parliament in December 1999. The IRDA since its incorporation as statutory body in April 2000 has fastidiously stuck to its schedule of framing regulations and registering the private sector insurance companies. The other decisions taken simultaneously to provide the supporting systems to the insurance sector and in particular the life insurance companies was the launch of the IRDA’s online service for issue and renewal of license to agents. The approval of institutions for imparting training to agents has also ensured that the insurance companies would have trained work force of insurance agents in place to sell their products, which are expected to be introduced by early next year. Since being set up as an independent statutory body the IRDA has put in a framework of globally compatible regulations. In the private sector 12 life insurance and 6 general insurance companies have been registered. Page55 INDIAN INSURANCE MARKET
- 51. Insurance is an Rs 400 billion business in India, and together with banking services adds about 7% to India’s GDP. Gross premium collection is about 2% of GDP and has been growing by 15 to 20% per annum. India also has the highest number of life insurance policies in force in the world, and total investable funds with the LIC are almost 8% of GDP. Yet more than three fourth of India’s insurable population has no life insurance or pension cover. Health insurance of any kind is negligible and other forms of non life insurance are much below international standards. To tap the vast insurance potential and to mobilize long term savings we need reforms with include revitalizing and restructuring of the public sector companies, and opening up the sector to private players. A statutory body needs to be made to regulate The market and promote a healthy market structure. Insurance Regulatory Authority (IRA) is one such body, which checks on these tendencies. IRA role comprises of following three functions: a. Protection of consumer’s interest b. To ensure financial soundness and solvency of the insurance industry c. To ensure healthy growth of insurance market. An insurance policy protects the buyer at some cost against the financial loss arising from a specified risk. Different situations and different people require a different mix of risk – cost combinations. Insurance companies provide these by offering schemes of different kinds. Page55
- 52. Unfortunately the concept of insurance is not popular in our country. As per the latest estimates, the total premium income generated by life and general insurance in India is estimated at around 1.95% of GDP. However India’s share of world insurance market has shown an increase of 10% from 0.31% in 1996-97 to 0.34% in 1997-98. India’s market share in the life insurance business showed a real growth of 11% there by outperforming global average of 7.7%. Non life insurance business grew by 3.1% against global average of 0.20%. In India insurance pending per capita was among the last in the world at $7.6 compared to $7 in the previous year. Amongst the emerging economies, India is one of the least insured countries but the potential for further growth is phenomenal, as a significant portion of its population is in services and the life expectancy also increased over the years. The nationalized insurance industry has not offered consumers a variety of products. Opening of the sector to private firms will foster competition, innovation and variety of products. It would also generate greater awareness on the need for buying insurance as a service and not merely for tax exemption, which is currently done on the demand side, a strong correlation between demand for insurance and per capita income level suggests that high economic growth can spur growth in demand for insurance. Also there exists a strong correlation between insurance density and social indicators such as literacy. With social development, insurance demand will grow. Page55
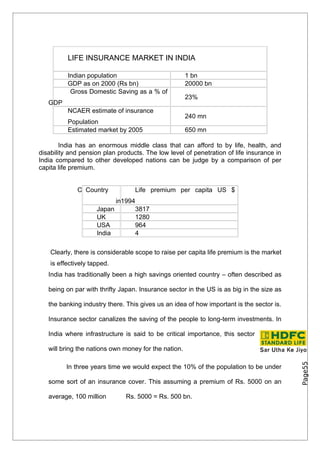
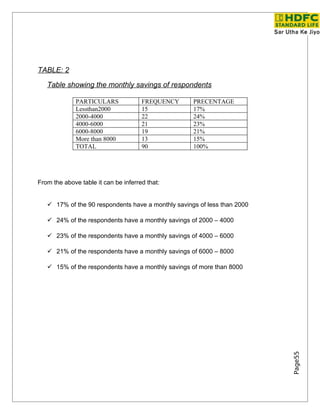
- 53. LIFE INSURANCE MARKET IN INDIA Indian population 1 bn GDP as on 2000 (Rs bn) 20000 bn Gross Domestic Saving as a % of 23% GDP NCAER estimate of insurance 240 mn Population Estimated market by 2005 650 mn India has an enormous middle class that can afford to by life, health, and disability and pension plan products. The low level of penetration of life insurance in India compared to other developed nations can be judge by a comparison of per capita life premium. C Country Life premium per capita US $ in1994 Japan 3817 UK 1280 USA 964 India 4 Clearly, there is considerable scope to raise per capita life premium is the market is effectively tapped. India has traditionally been a high savings oriented country – often described as being on par with thrifty Japan. Insurance sector in the US is as big in the size as the banking industry there. This gives us an idea of how important is the sector is. Insurance sector canalizes the saving of the people to long-term investments. In India where infrastructure is said to be critical importance, this sector will bring the nations own money for the nation. Page55 In three years time we would expect the 10% of the population to be under some sort of an insurance cover. This assuming a premium of Rs. 5000 on an average, 100 million Rs. 5000 = Rs. 500 bn.
- 54. This has made the sector the hottest one in India after IT. With social security and security to the public at large being the agenda for opening the sector, the role of the regulator becomes all the more serious and one that would be carefully watched at every step. The Insurance Regulator and Development bill is now an Act. With this India in now the cynosure of all the global insurance players. Numerous player, both Indian and foreign have announced their intention to start their insurance shops in India. IRDA, under chairman ship of Mr. RANGACHARI, opened the window for applying license in India. One of the main deference between the developed economies and the emerging economies is that insurance products are bought in the former while these are sold in later. Focus of insurance industry is changing towards providing a mix of both protection/risk cover and long-term investment opportunities. Page55 Who’s going with whom? Indian company Foreign partner Kotak Mahindra Chubb
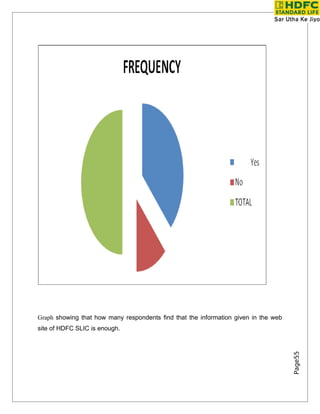
- 55. Tata Group AIG Sundaram Finance Winterthur Sanmar Group GIO of Australia Spic Met Life ILFS Cigna Alpic Finance Allianz 20th Century Canada Life Vysya Bank ING Cholmandalan Axa SBI Allince Capita HDFC Standard Life ICICI Prudential Hindustan Times Commercial Union IDBI Principal Max India New York Why life insurance? Life Insurance cover is essential for it provides the following benefits: • A lump sum payment to the nominees at the time of the death of the policy holder; • A regular payment to the nominees in the event of the death of the policy holder; • Tax benefits, as premiums paid reduce the liability of tax; • Relieves economic hardships in the family on the uneventful death of the sole income holder; • Inculcates the habit of saving. AN OVERVIEW OF INDIAN INSURANCE INDUSTRY Indian Insurance Industry Page55 With a large population and untapped market, insurance happens to be a big opportunity in India. The insurance business (measured in the context of first year premium) grew at 47.93 per cent in 2005-06, surpassing the growth rate of 32.49 percent achieved in 2004-05. However, insurance penetration in the country
- 56. continues to be low. Insurance penetration or premium volume as a share of a country’s GDP, for the year 2005 stood at 2.53 per cent for life insurance and 0.62 per cent for non-life insurance. The level of penetration tends to rise as income increases, particularly in life insurance. India, with its huge middle class households, has exhibited potential for the insurance industry. Saturation of markets in many developed economies has made the Indian market even more attractive for global insurance majors. The insurance market has witnessed dynamic changes which includes presence of a fair number of insurers in both life and non-life segment. Life Insurance in India Life insurance industry recorded a premium income of Rs.105875.76 crore during 2005-06 as against Rs.82854.80 crore in the previous financial year, recording a growth of 27.78 per cent. The contribution of first year premium, single premium and renewal premium to the total premium was Rs.21275.75 crore (20.09 per cent); Rs.17509.78 crore (16.54 per cent); and Rs.67090.21 crore (63.37 per cent), respectively. In the year 2000-01, when the industry was opened up to the private players, the life insurance premium was Rs.34,898.48 crore which constituted of Rs.6996.95 crore of first year premium, Rs.25191.07 crore of renewal premium and Rs.2740.45 crore of single premium. Post opening up, single premium had declined from Rs.9, 194.07 crore in the year 2001-02 to Rs.5674.14 crore in 2002-03 with the withdrawal of the guaranteed return policies. Though it went up marginally in 2003-04 to Rs.5936.50 crore (4.62 per cent growth) the year 2004-05 witnessed a significant shift with the single premium income rising to Rs.10336.30 crore showing 74.11 per cent growth over 2003-04, accounting for 12.74 per cent of the total premium underwritten in that year. Page55 As against 34.62 percent in 2005-06.While the number of single premium individual policies underwritten by the private insurance companies grew by 103 percent, the non-single premium individual policies grew by 64 percent. The new insurers have
- 57. improved their market share from 9.33 per cent in 2005-06 to 14.25 percent in 2006- 07. It reflects increase in their persistency ratio and enables insurers to bring down overall cost of doing business. The renewal premium underwritten by the life insurance industry, during 2006-07 recorded a growth of 18.46 per cent as against 20.85 per cent in 2005-06. The private insurers and LIC reported growths of 122.56 per cent and 14.32 per cent respectively during the year. Segregation of the first year premium reflects a definite consolidation towards linked products with premium underwritten at Rs.16060.67 crore in 2006-07 as against Rs.8247.74 crore in 2005-06, i.e., a growth of 95 per cent. The non-linked premium was Rs.19804.33 crore as against Rs.17069.37 crore in 2004-05, i.e., a growth of 16 per cent. The linked and non-linked business accounted for 44.78 and 55.22 per cent as against 32.54 and 67.46 per cent respectively in the year 2005-06. The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority. Reforms in the Insurance sector were initiated with the passage of the IRDA Bill in Parliament in December 1999. The IRDA since its incorporation as a statutory body in April 2000 has fast stuck to its schedule of framing regulations and registering the private sector insurance companies. The other decision taken simultaneously to Page55 provide the supporting systems to the insurance sector and in particular the life insurance companies was the launch of the IRDA online service for issue and renewal of licenses to agents. The approval of institutions for imparting training to agents has also ensured that the insurance companies would have a trained workforce of insurance agents in place to sell their products which are expected to
- 58. be introduced by early next year. Since being set up as an independent statutory body the IRDA has put in a framework of globally compatible regulations Page55
- 59. Page55 Distribution Tie Ups of Life Insurance Companies: (up to July 07)
- 60. Page55
- 61. Fund Wise Pattern of Investments of Life insurance companies Page55
- 62. Page55
- 63. Product mix of Life insurance companies: Source=IRDA Page55
- 64. INTRODUCTION TO HDFC STANDARD LIFE INSURANCE Over view of the HDFC Standard Life Insurance Established on 14th August 2000, HDFC Standard Life Insurance Co. Ltd. is a joint venture between Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC Limited), India's leading housing finance institution, and a Group Company of the Standard Life Plc, UK. The Company is one of leading private insurance companies, offering a range of individual and group insurance solutions, in India. Being a joint venture of top financial services groups, HDFC Standard Life has adequate financial expertise to manage long-term investments safely and resourcefully. HDFC Standard Life Insurance offers a range of individual and group solutions, which can be easily personalized to specific needs. Its group solutions have been planned to offer complete flexibility, together with a low charging structure. As on 31 December, 2008, the Company's new business premium income stood at Rs. 1,839.70 Crores; it has covered over 812,811 lives so far. Given below is a comprehensive list of policies and products on offer by HDFC Standard Life Insurance: Protection Plans • HDFC Term Assurance Plan • HDFC Loan Cover Term Assurance Plan • HDFC Home Loan Protection Plan Children's Plans • HDFC Children's Plan • HDFC Unit Linked Young Star II • HDFC Unit Linked Young Star Plus II • HDFC Unit Linked Young Star Champion Retirement Plans • HDFC Personal Pension Plan • HDFC Unit Linked Pension II • HDFC Unit Linked Pension Maximiser II • HDFC Immediate Annuity Page55
- 65. Savings & Investment Plans • HDFC Unit Linked Endowment Plus II • HDFC SimpliLife • HDFC Unit Linked Endowment II • HDFC Unit Linked Enhanced Life Protection II • HDFC Unit Linked Wealth Maximiser Plus • HDFC Unit Linked Endowment Winner • HDFC Endowment Assurance Plan • HDFC Money Back Plan • HDFC Single Premium Whole of Life Insurance Plan • HDFC Assurance Plan • HDFC Savings Assurance Plan Health Plans • HDFC Critical Care Plan • HDFC SurgiCare Plan Group Plans • Group Term Insurance Plan • Group Variable Term Insurance Plan • Group Unit Linked Plan - Gratuity • Group Unit Linked Plan - Superannuation • Group Unit Linked Plan - Leave Encashment Page55
- 66. INTRODUCTION OF HDFC SLIC Introduction HDFC Standard Life Insurance Company Limited. is one of India's leading private insurance companies, which offers a range of individual and group insurance solutions. It is a joint venture between Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC Limited), India's leading housing finance institution and a Group Company of the Standard Life Plc, UK. As on February 28, 2009 HDFC Ltd. holds 72.43% and Standard Life (Mauritius Holding) 2006, Ltd. holds 26.00% of equity in the joint venture, while the rest is held by others. Our Key Strengths Financial Expertise As a joint venture of leading financial services groups, HDFC Standard Life has the financial expertise required to manage your long-term investments safely and efficiently. Range of Solutions We have a range of individual and group solutions, which can be easily customized to specific needs. Our group solutions have been designed to offer you complete flexibility combined with a low charging structure. Track Record So Far Our gross premium income, for the year ending March 31, 2009 stood at Rs. 5,564.69 crores. The company has covered over 8, 33,070 lives as on March 31, 2009. HDFC Standard Life believes that establishing a strong and ethical foundation is an essential prerequisite for long-term sustainable growth. To ensure this, we have concentrated our focus on expansion of branch network, organizing an efficient and well trained sales force, and setting up appropriate systems and processes with optimum use of technology. As all these areas form the basic infrastructure for establishing the highest possible customer service standards. Page55
- 67. Our core values are drilled down to all levels of employees, as these are inviolable. We continue to promote high integrity in business practices and shun short cuts and unethical practices, as we wish to be perceived as an institution with high moral standing. Since our inception in 2000, when the Indian insurance space was opened for private participation, we have consistently focused on setting benchmarks in all aspect on insurance business. Being the first private player to be registered with the IRDA and the first to issue a policy on December 12, 2000, our differentiators are: Strong promoter: HDFC Standard Life is a strong, financially secure business supported by two strong and secure promoters – HDFC Ltd and Standard Life. HDFC Ltd’s excellent brand strength emerges from its unrelenting focus on corporate governance, high standards of ethics and clarity of vision. Standard Life is a strong, financially secure business and a market leader in the UK Life & Pensions sector. 1. PREFFERED AND TRUSTED BRAND Our brand has managed to set a new standard in the Indian life insurance communication space. We were the first private life insurer to break the ice using the idea of self-respect instead of ‘death’ to convey our brand proposition (Sar Utha Ke Jiyo). Today, we are one of the few brands that customers recognize, like and prefer to do business. Moreover, our brand thought, SAR Utha Ke Jiyo, is the most recalled campaign in its category. 2. INVESTMENT POLICY We follow a conservative investment management philosophy to ensure that our customer’s money is looked after well. The investment policies and actions are regularly monitored by a formal Investment Committee comprising non-executive directors and the Principal Officer & Executive Director. As a life insurance company, we understand that customers have invested their savings with us for the long term, with specific objectives in mind. Thus, our investment focus is based on the primary objective of protecting and generating good, consistent, and stable investment returns to match the investor’s long-term objective and return expectations, irrespective of the market condition. Page55
- 68. 3. NEED BASED SELLING APPROACH Despite the criticality of life insurance, sales in the industry have been characterized by over reliance on tax benefits and limited advice- based selling. Our eight-step structured sales process ‘Disha’ however, helps customers understand their latent needs at the first instance itself without focusing on product features or tax benefits. Need-based selling process, 'Disha', the first of its kinds in the industry, looks at the whole financial picture. Customers see a plan not piecemeal product selling. 4. RISK CONTROL FRAMEWORK HDFC Standard Life has fully implemented a risk control framework to ensure that all types of risks (not just financial) are identified and measured. These are regularly reported to the board and this ensures that the company management and board members are fully aware of any risks and the actions taken to ensure they are mitigated. 5. FOCUS ON TRAINING Training is an integral part of our business strategy. Almost all employees have undergone training to enhance their technical skills or the softer behavioral skills to be able to deliver the service standards that our company has set for itself. Besides the mandatory training that Financial Consultants have to undergo prior to being licensed, we have developed and implemented various training modules covering various aspects including product knowledge, selling skills, objection handling skills and so on. 6. FOCUS ON LONG TERM VALUE HDFC Standard Life does not focus in the business of ramping up the topline only, but to create maximisation of stakeholder's value. Today, we are extremely satisfied with the base that we have created for the long-term success of this company. 7. TRANSPARENT DEALING We are one of the few companies whose product details, pricing, clauses are clearly communicated to help customers take the right Page55 decision.
- 69. 8. STRICT COMPLIANCE WITH REGULATIONS We have initiated and implemented many new processes, some of which were found useful by the IRDA and later made mandatory for the entire industry. The agents who successfully completed this training only, were authorized by the company to sell ULIPs. This has now been made compulsory by IRDA for all insurance companies under the new Unit Linked Guidelines. DIVERSIFIED PRODUCT PORTFOLIO HDFC Standard Life’s wide and diversified product portfolio help individuals meet their various needs, be it: • Protection: Need for a sound income protection in case of your unfortunate demise • Investment: Need to ensure long-term real growth of your money • Savings: Save for the milestones and protect your savings too • Pension: Need to save for a comfortable life post retirement • Health: Cover for health related exigencies Page55
- 70. PROFILE OF THE ORGANISATION Name of the company: HDFC Standard Life Insurance Address of Head office: City : Dharamshala Pin Code: 176215 State : Himachal Pradesh Status : Private Telephone number : 1892222913 STD Code : 1800-227/6000 9191 Fax no : Email : life@hdfcinsurance.com Website : www.hdfcinsurance.com Chief executive Contact person (H.R Manager/ Personnel manager) Mobile no Company’s year of establishment: 14th August, 2000 Company’s product range/ services/business area 1. Products Protection Plans • HDFC Term Assurance Plan • HDFC Loan Cover Term Assurance Plan • HDFC Home Loan Protection Plan Children's Plans • HDFC Children's Plan • HDFC Unit Linked Young Star II • HDFC Unit Linked Young Star Plus II • HDFC Unit Linked Young Star Champion Retirement Plans • HDFC Personal Pension Plan • HDFC Unit Linked Pension II • HDFC Unit Linked Pension Maximiser II • HDFC Immediate Annuity Page55
- 71. Savings & Investment Plans • HDFC Unit Linked Endowment Plus II • HDFC SimpliLife • HDFC Unit Linked Endowment II • HDFC Unit Linked Enhanced Life Protection II • HDFC Unit Linked Wealth Maximiser Plus • HDFC Unit Linked Endowment Winner • HDFC Endowment Assurance Plan • HDFC Money Back Plan • HDFC Single Premium Whole of Life Insurance Plan • HDFC Assurance Plan • HDFC Savings Assurance Plan Health Plans • HDFC Critical Care Plan • HDFC SurgiCare Plan Group Plans • Group Term Insurance Plan • Group Variable Term Insurance Plan • Group Unit Linked Plan - Gratuity • Group Unit Linked Plan - Superannuation • Group Unit Linked Plan - Leave Encashment Name of Related Party/ Nature of Relationship: • HDFC Limited Holding Company • Standard Life Assurance Company Investing Party • Standard Life (Mauritius Holdings) 2006 Limited Investing Party • HDFC Asset Management Company Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Developers Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Holdings Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Trustee Company Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Realty Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Investments Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC ERGO General Insurance Company Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Sales Private Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Venture Capital Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Ventures Trustee Company Limited Fellow Subsidiary • HDFC Property Ventures Limited Annual turnover Number of employees Page55 Date Signature Course Branch Semester Roll No
- 72. COMPANY’S HISTORY Established on 14th August 2000, HDFC Standard Life Insurance Co. Ltd. is a joint venture between Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC Limited) - India's leading housing finance institution, and a Group Company of the Standard Life Plc, UK. The Company is one of leading private insurance companies, offering a range of individual and group insurance solutions, in India. Being a joint venture of top financial services groups, HDFC Standard Life has adequate financial expertise to manage long-term investments safely and resourcefully. HDFC Standard Life Insurance offers a range of individual and group solutions, which can be easily personalized to specific needs. Its group solutions have been planned to offer complete flexibility, together with a low charging structure. As on 31 December, 2008, the Company's new business premium income stood at Rs. 1,839.70 Crores; it has covered over 812,811 lives so far. HDFC Standard Life Insurance Company Limited. is one of India's leading private insurance companies, which offers a range of individual and group insurance solutions. It is a joint venture between Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC Limited), India's leading housing finance institution and a Group Company of the Standard Life Plc, UK. As on February 28, 2009 HDFC Ltd. holds 72.43% and Standard Life (Mauritius Holding) 2006, Ltd. holds 26.00% of equity in the joint venture, while the rest is held by others. Page55