Scientific Investigation and Mapping
- 2. Scientific Method A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world, based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experiment. Scientists create scientific theories from hypotheses that have been corroborated through the scientific method, then gather evidence to test their accuracy. A scientific law or scientific principle is a concise verbal or mathematical statement of a relation that expresses a fundamental principle of science, like Newton's law of universal gravitation. A scientific law must always apply under the same conditions, and implies a causal relationship between its elements. The law must be confirmed and broadly agreed upon through the process of inductive reasoning. Like theories and hypotheses, laws make predictions (specifically, they predict that new observations will conform to the law), and can be falsified if they are found in contradiction with new data.
- 3. Reading Graphs Independent variable goes on the x-axis, dependent on the y- axis Constants are things that stay the same in an experiment Control group is the group that you do not manipulate… independent variable is not applied
- 4. What is Density? Density is defined as the mass of an object per unit volume. It is the relationship between the mass and volume of a certain object So what does that mean? If the molecules are more compact or packed together, it is said to have more density. If they are loosely packed, they are said to be less dense.
- 5. How to Solve for Density It’s simple….D = m/v! Cover up what you want to solve for and go for it! If the values are on top of each other, you divide. If they are next to each other, you multiply.
- 6. Latitude & Longitude Lines of latitude run horizontally and are measured north and south of the equator (0o) Lines of longitude run vertically and are measured east and west of the prime meridian (0o) 180o longitude line is the International Date Line.
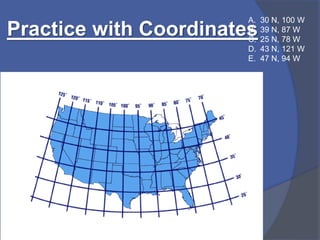
- 7. Practice with Coordinates A. 30 N, 100 W B. 39 N, 87 W C. 25 N, 78 W D. 43 N, 121 W E. 47 N, 94 W
- 8. Topographic Mapping Topographic maps show differences in the elevation of the Earth’s surface Lines connecting points of equal elevation are called contour lines; contour lines already marked with an elevation are called index contours; the distance between side by side contours is called the contour interval Contour lines that are close together indicate steep elevation, and contour lines farther apart indicate gentle elevation Benchmarks are located on the tops of mountains or hills that tell the exact elevation
- 9. Practice with Topo Maps