Scrum methodology
- 1. Scrum Methodology Andrey Elkin, PMP, C.T.Co March 12, 2013
- 2. Scrum in 100 words • Scrum is an agile process that allows us to focus on delivering the highest business value in the shortest time. • It allows us to rapidly and repeatedly inspect actual working software (every two weeks to one month). • The business sets the priorities. Teams self- organize to determine the best way to deliver the highest priority features. • Every two weeks to a month anyone can see real working software and decide to release it as is or continue to enhance it for another sprint.
- 3. Scrum has been used by: •Microsoft •Intuit •Yahoo •Nielsen Media •Google •First American Real Estate •Electronic Arts •BMC Software •Lockheed Martin •Ipswitch •Philips •John Deere •Siemens •Lexis Nexis •Nokia •Sabre •IBM •Salesforce.com •Capital One •Time Warner •BBC •Turner Broadcasting
- 4. Scrum has been used for: • Commercial software • Video game development • In-house development • FDA-approved, life-critical systems • Contract development • Fixed-price projects • Satellite-control software • Financial applications • Websites • ISO 9001-certified • Handheld software applications • Mobile phones • Embedded systems • Network switching applications • 24x7 systems with 99.999% • ISV applications uptime requirements • Some of the largest • the Joint Strike Fighter applications in use
- 5. Characteristics • Self-organizing teams • Product progresses in a series of month-long “sprints” • Requirements are captured as items in a list of “product backlog” • No specific engineering practices prescribed • Uses generative rules to create an agile environment for delivering projects • One of the “agile processes”
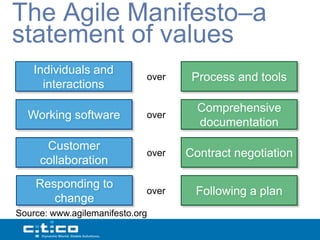
- 6. The Agile Manifesto–a statement of values Individuals and over Process and tools interactions Comprehensive Working software over documentation Customer over Contract negotiation collaboration Responding to over Following a plan change Source: www.agilemanifesto.org
- 7. Project noise level Far from Agreement Anarchy Requirements Complex Source: Strategic Management and Organizational Dynamics by Ralph Stacey in Agile Software Development with Scrum by Ken Schwaber and Mike Close to Simple Beedle. Agreement Certainty Close to Certainty Far from Technology
- 8. Scrum 24 hours Sprint 2-4 weeks Sprint goal Return Sprint Potentially shippable Cancel Return backlog product increment Coupons Gift wrap Gift wrap Cancel Coupons Product backlog
- 9. Putting it all together
- 10. Sprints • Scrum projects make progress in a series of “sprints” • Analogous to Extreme Programming iterations • Typical duration is 2–4 weeks or a calendar month at most • A constant duration leads to a better rhythm • Product is designed, coded, and tested during the sprint
- 11. Sequential vs. overlapping development Requirements Design Code Test Rather than doing all of one thing at a time... ...Scrum teams do a little of everything all the time
- 12. No changes during a sprint Change • Plan sprint durations around how long you can commit to keeping change out of the sprint
- 13. Scrum framework Roles •Product owner •ScrumMaster •Team Ceremonies •Sprint planning •Sprint review •Sprint retrospective •Daily scrum meeting Artifacts •Product backlog •Sprint backlog •Burndown charts
- 14. Scrum framework Roles •Product owner •ScrumMaster •Team Ceremonies •Sprint planning •Sprint review •Sprint retrospective •Daily scrum meeting Artifacts •Product backlog •Sprint backlog •Burndown charts
- 15. Product owner • Define the features of the product • Decide on release date and content • Be responsible for the profitability of the product (ROI) • Prioritize features according to market value • Adjust features and priority every iteration, as needed • Accept or reject work results
- 16. The ScrumMaster • Represents management to the project • Responsible for enacting Scrum values and practices • Removes impediments • Ensure that the team is fully functional and productive • Enable close cooperation across all roles and functions • Shield the team from external interferences
- 17. The team • Typically 5-9 people • Cross-functional: • Programmers, testers, user experience designers, etc. • Members should be full-time • May be exceptions (e.g., database administrator) • Teams are self-organizing • Ideally, no titles but rarely a possibility • Membership should change only between sprints
- 18. Scrum framework Roles •Product owner •ScrumMaster •Team Ceremonies •Sprint planning •Sprint review •Sprint retrospective •Daily scrum meeting Artifacts •Product backlog •Sprint backlog •Burndown charts
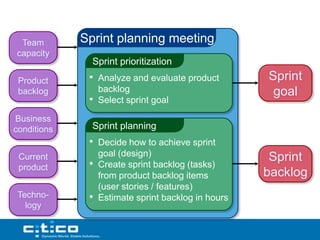
- 19. Team Sprint planning meeting capacity Sprint prioritization Product • Analyze and evaluate product Sprint backlog backlog goal • Select sprint goal Business conditions Sprint planning • Decide how to achieve sprint Current goal (design) Sprint product • Create sprint backlog (tasks) from product backlog items backlog (user stories / features) Techno- • Estimate sprint backlog in hours logy
- 20. Sprint planning • Team selects items from the product backlog they can commit to completing • Sprint backlog is created • Tasks are identified and each is estimated (1-16 hours) • Collaboratively, not done alone by the ScrumMaster • High-level design is considered As a vacation Code the middle tier (8 hours) planner, I want to Code the user interface (4) see photos of the Write test fixtures (4) hotels. Code the foo class (6) Update performance tests (4)
- 21. The daily scrum • Parameters • Daily • 15-minutes • Stand-up • Not for problem solving • Whole world is invited • Only team members, ScrumMaster, product owner, can talk • Helps avoid other unnecessary meetings
- 22. Everyone answers 3 questions 1 What did you do yesterday? 2 What will you do today? 3 Is anything in your way? • These are not status for the ScrumMaster • They are commitments in front of peers
- 23. The sprint review • Team presents what it accomplished during the sprint • Typically takes the form of a demo of new features or underlying architecture • Informal • 2-hour prep time rule • No slides • Whole team participates • Invite the world
- 24. Sprint retrospective • Periodically take a look at what is and is not working • Typically 15–30 minutes • Done after every sprint • Whole team participates • ScrumMaster • Product owner • Team • Possibly customers and others
- 25. Start / Stop / Continue • Whole team gathers and discusses what they’d like to: Start doing Stop doing This is just one of many ways to Continue doing do a sprint retrospective.
- 26. Scrum framework Roles •Product owner •ScrumMaster •Team Ceremonies •Sprint planning •Sprint review •Sprint retrospective •Daily scrum meeting Artifacts •Product backlog •Sprint backlog •Burndown charts
- 27. Product backlog • The requirements • A list of all desired work on the project • Ideally expressed such that each item has value to the users or customers of the product • Prioritized by the product owner • Reprioritized at the start of This is the each sprint product backlog
- 28. A sample product backlog Backlog item Estimate Allow a guest to make a reservation 3 As a guest, I want to cancel a 5 reservation. As a guest, I want to change the dates of 3 a reservation. As a hotel employee, I can run RevPAR 8 reports (revenue-per-available-room) Improve exception handling 8 ... 30 ... 50
- 29. The sprint goal • A short statement of what the work will be focused on during the sprint Life Sciences Support features necessary Database Application for population genetics studies. Make the application run on SQL Server in addition to Oracle. Financial services Support more technical indicators than company ABC with real-time, streaming data.
- 30. Managing the sprint backlog • Individuals sign up for work of their own choosing • Work is never assigned • Estimated work remaining is updated daily • Any team member can add, delete or change the sprint backlog • Work for the sprint emerges • If work is unclear, define a sprint backlog item with a larger amount of time and break it down later • Update work remaining as more becomes known
- 31. A sprint backlog Tasks Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Code the user interface 8 4 8 Code the middle tier 16 12 10 4 Test the middle tier 8 16 16 11 8 Write online help 12 Write the foo class 8 8 8 8 8 Add error logging 8 4
- 32. A sprint burndown chart Hours
- 33. Tasks Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Code the user interface 8 4 8 Code the middle tier 16 12 10 7 Test the middle tier 8 16 16 11 8 Write online help 12 50 40 30 Hours 20 10 0 Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri
- 34. Scalability • Typical individual team is 7 ± 2 people • Scalability comes from teams of teams • Factors in scaling • Type of application • Team size • Team dispersion • Project duration • Scrum has been used on multiple 500+ person projects
- 35. Scaling through the Scrum of scrums
- 36. Scrum of scrums of scrums
- 37. Where to go next • www.scrumalliance.org
- 38. Q&A? Thank you!