Scrum Process For Offshore Team
- 1. Scrum Process For Offshore Team Thien Nguyen Email: thiennv1211@gmail.com
- 2. • Agile Methodologies, Waterfall vs Agile • Scrum Process - Overview • Scrum Process - Characteristics • Scrum Process - Criteria for Approach • Scrum Process - Rules • Scrum Process - Roles: Product Owner (PO); Scrum Master (SM); Project Manager (PM)(Offshore); Development Team (DEV Team); Business Analyst (BA); Onshore Manager (Engagement Manager/IT Head) • Scrum Process - Artifacts: The Product Backlog, Sprint log, Sprint Burndown Chart, Task Board, Velocity, Capacity • Scrum Process - Activities: Sprint 0, Release Planning, Sprint Planning, Daily Meeting, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective, … • Software Development Tools • Appendix: User Story Template, Definition Of Ready, Definition Of Done, Sprint Acceptance Criteria, Scrum vs Kanban vs Scrumban, Disadvantages of Scrum • Question & Answer Agenda
- 6. Scrum Process Overview (Cont.) 1. Sprint 0 (Pre-game): • Planning: Definition of a new release based on currently known backlog, along with an estimate of its schedule and cost. If a new system is being developed, this phase consists of both conceptualization and analysis. If an existing system is being enhanced, this phase consists of limited analysis. • Architecture: Design how the backlog items will be implemented. This phase includes system architecture modification and high level design. 2. Development Sprints (Game): Development of new release functionality, with constant respect to the variables of time, requirements, quality, cost, and competition. Interaction with these variables defines the end of this phase. There are multiple, iterative development sprints, or cycles, that are used to evolve the system. 3. Closure (Post-game ): Preparation for release, including final documentation, pre- release staged testing, and release.
- 7. Scrum Process Overview (Cont.)
- 8. Scrum Process - Overview (Cont.) Project Road Map
- 9. Scrum Process - Characteristics • Standard software development process for Offshore team • Embraced both standard Scrum process and others offshore team development process • Scrum deliverables in 2-4 weeks • Be quality implemented • Process can be tailored to match with each department and specific project when needed. • Add the best value to organization and client • Used by ODC (Offshore Development Center) team to work with client or Onshore team
- 10. Scrum Process - Criteria for Approach Scrum process is suitable for projects have following characteristics: • Project type is not fixed price, it should be T&M (Time & Material) or ODC (Offshore Development Center)/MRT(Managed Resource Team) • Project team members (Scrum team) have good awareness on SCRUM process • Stake Holders, Product Owner (PO), Scrum Master (SM), Development Team (DEV Team) are clearly defined • PO is representative of Client/IT Head and make sure they have time to stay with DEV team for queries and explanation on requirements and stories. (It’s should be at least 2 hours per day). If not the Business Analyst (BA) will take the role PO. • Development team are self-organising • Requirement is changed frequently
- 11. Scrum Process - Rules 1. Project Team & PO or Client/IT Head must be aware of project scrum process 2. The Sprints (0,1,2, …, N) are time-boxed, they end on a specific date whether the work has been completed or not, and Sprint duration should never be extended. Sprint duration is about 2-4 weeks will enabling fast verifications and corrections 3. Architecture/System design notes/documents must be done at Sprint 0 4. Sprint goal and scope of works must be finalized and sent out after Sprint planning 5. Communication channel to explain user story is clearly defined, Ex: document, tool, … 6. Daily stand-up meeting must be starts on time about 15 minutes. All are welcome, but normally only PO, DEV Team, SM speaks, and others should contribute ideas/suggestions after the meeting with SM and PM. The daily meeting should happen at the same time every day in the morning. 7. The PO is one person not two or a committee 8. Sprint planning is about 4-8 hours 9. Sprint demo/review is about 1-3 hours and Sprint retrospective is about 1-3 hours
- 12. Scrum Process - Roles • Product Owner (PO) • Scrum Master (SM) • Project Manager (PM) (Offshore) • Development Team (DEV Team) • Business Analyst (BA) • Onshore Manager (Engagement Manager/Client PM/IT Head) • Stakeholders (Architect, IT Director, …)
- 13. Scrum Roles – Product Owner (PO) The PO is representative of client or is BA, has responsible for: • Representing the interests of Client/IT Head and all the stakeholders • Ensuring business requirements & objectives are met, be responsible for the profitability of the product. Involved in the UAT (User Acceptance Testing) and Production phase. • Reviewing and signing off product specification requirements, project deliverables, the final design solution and business acceptance criteria. Accept or reject work results • Being available to answer project teams' questions and be ready to give advice. • Clearly expressing Product Backlog Items (PBIs), ensuring that the Product Backlog is visible, transparent, and clear to all, and shows what the DEV Team will work on next, ensuring the DEV Team understands items in the Product Backlog to the level needed. • Managing and prioritizing Product Backlog
- 14. Scrum Roles - PO (Cont.) • Leading the development effort towards the project's success and maximize projects‘ effectiveness by Creating the project's initial overall requirements, high-level feature requirements, user stories, etc.… Ordering the items in the Product Backlog, adjust features and priority every iteration as needed to best achieve goals and missions Defining the release plans after having rough relative size estimates, decide on release date and content The PO may represent the desires of a committee in the Product Backlog, but those wanting to change a backlog item’s priority must convince the PO
- 15. Scrum Roles – Scrum Master (SM) • Coaching the Project Team in self-organization and cross-functionality. Ensure that the team is fully functional and productive, leading the Project Team to create high-value products • Removing impediments to the Project Team’s progress • Responsible for enacting Scrum values and practices, ensures that the process is followed. Helping the project team and stakeholders understand and enact process and empirical product development. • Causing changes that increase the productivity of the Project Team and the effectiveness of the product • Shield the team from external interferences
- 16. Scrum Roles – Project Manager (PM) • Doing tailoring process for project. • Overall project delivery, building working environment, resource management and also facilitating the communication. • Planning and implementing the product so that it fits within our organization's culture and still delivers the expected benefits • Ensuring that the Project Team adheres to project approach, process activities, rules, policy, roles and responsibilities in project. • Performing project management activities (project planning, monitoring and control project, project scheduling, manage project quality and take care for project delivery, manage project risks and issues, reporting to client/IT Head or onshore manager/engagement manager)
- 17. Scrum Roles – Development Team • Perform the coding and follow project development process. • Create the Increment of “Done” product at the end of each Sprint. • Carries out unit testing • Self-managing, self-organizing to turn Product Backlog into Increments of potentially releasable functionality. • Cross-functional with all of the skills as a team necessary to create a product Increment • Individual DEV Team members may have specialized skills and areas of focus, but accountability belongs to the DEV Team as a whole; and • DEV Team do not contain sub-teams dedicated to particular domains like testing or business analysis. • Scrum recognizes no titles for DEV Team members other than Developer, regardless of the work being performed by the person Note: Although the best thing is to have cross-functional team, development team can be structured like below Developers: Perform the design, coding, unit test, review code. Testers: Plan to test, produce test case, execute test and test report
- 18. Scrum Roles – Business Analyst (BA) • Assist client/IT Head or PO in all initiatives related to define user stories. BA can play the role PO if PO is not available. • Work with client/IT Head or PO to discuss and collect all business and system requirements; Create Feature list, Mockup screen, Wireframe, Functional Specification and Use Case documents • Ensure all business requirements are fully understood and specified in a manner that will enable full understanding from DEV team • Assist Tester to verify that all requirements of the system are fulfilled by the implementation in the traceability manner among requirements, Change Request (CR) and development • Support client/IT Head or PO at UAT phase for testing, verifying bugs/issues and CRs • Join in all meetings of project and raise business requirements concerns/issues if any to SM, PM and PO
- 19. Scrum Roles – Onshore Manager • Plans, initiates and closes projects • Deals with risks, issues and dispute resolution • Tracks progress against plan (although some day to day operational matters are delegated to the offshore PM) • Receive the progress report from offshore PM • Focus on software development operations • Works with client/IT Head to plan for the medium and long term • Escalation point for Offshore PM • Escalation point for client/IT Head • To be chair the regular checkpoint meeting between client/IT Head and Offshore PM
- 20. Scrum Process - Artifacts • The Product Backlog • Sprint log • Sprint Burndown Chart • Task Board • Velocity • Capacity
- 21. Scrum Process Artifacts - The Product Backlog User Story Description: As a <user role> I want to be able to <user wish/goal>, so that I can <business value> Business Acceptance Criteria Current and Suggested Mock-up Screens Workflows
- 22. Scrum Process Artifacts - Sprint Log
- 23. Scrum Artifacts - Sprint Burndown Chart
- 24. Scrum Process Artifacts - Task Board
- 25. Scrum Process Artifacts - Velocity Velocity is the number of story points completed by a team in an iteration The velocity can be estimated as the average, over several recent sprints, of the sum of the estimates for the amount of work completed by a team per sprint — so in the chart above, the velocity = (37 + 47 + 50 +57) / 4 = 48. A team's recent velocity can be useful in helping to predict how much work can be completed by the team in a future sprint
- 26. Scrum Process Artifacts - Capacity
- 27. Scrum Process – Activities • Sprint 0 (Planning and Architecture) • Release Planning (Grooming) • Sprint Planning • Daily Meeting • Sprint Demo/Review • Sprint Retrospective • Cancel A Sprint • UAT (User Acceptance Testing) • Project Closure
- 28. Sprint 0 – Planning and Architecture Purpose: To plan and design architecture at high level, to prepare everything ready to getting start for next sprints 1. Planning: Duration is about 4-8 weeks Project manager is to prepare the following activities to getting start for next sprints: • Get Scope Of Works (SOW) from Onshore Manager or PO • Develop Project charter (resource, stakeholder, project approach, communication plan, role& responsibility.) • Define Tailoring process • Define Risk plan and Risk log • Define all sub-plan (Configuration Management Plan, Test strategy, Test Plan) • Define acceptance criteria • Conduct Kick-off Meeting to transfer the scope, vision, role & responsible, process approach, quality objectives, lesson learnt,… to project team.
- 29. Sprint 0 – Planning and Architecture (Cont.) Scrum Master is to prepare the following activities • Coach project team to understand Scrum process • Make sure the activities of planning are done and the management approval, funding are done • Create Configuration Management plan; prepare the development, test and deployment environments
- 30. Sprint 0 – Planning and Architecture (Cont.) 2. Requirement & Architecture Design Product Owner is to prepare the following activities • Gather the business requirements, produce the product backlog and be responsible for User Stories approval. Enough of the product backlog must be estimated and prioritized that the team can pick a reasonable amount of high value work from the backlog in the first Sprint planning • Share the high level vision of expected outcome and implementation (scope of project) • Define “Definition of Done” for each user stories • Estimation of release cost, including development, collateral material, marketing, training, and rollout
- 31. Sprint 0 – Planning and Architecture (Cont.) Development team is to prepare following activities: • Architecture vision should be initialized and discussed. First version of high level architecture should be discussed and documented down Key technical challenges, constraints High level system overview, high level architectural break down with requirement and solution High level components view, touch points, integration points between subsystems or sub components. • Design and coding standards, design and coding review check list need to be tailored and approved. They should includes Customized rules set for automatic design and coding metrics analyzing tools Design and code guidelines and review check list for each type of component or technologies used. For example: design guideline and check list for database, design and implementation guideline and check list for security … • Base framework and solution structure and related documents also need to be ready.
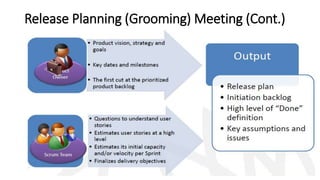
- 32. Release Planning (Grooming) Meeting
- 33. Release Planning (Grooming) Meeting (Cont.)
- 34. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Sprint Planning
- 35. Agreement what will be done in the sprint Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Sprint Planning (Cont.)
- 36. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Sprint Planning (Cont.) At the beginning of each Sprint, the Sprint Planning Meeting takes place. Purpose: Team works to forecast the functionality that will be developed during the Sprint. PO presents ordered PBIs and for how to implement the items that the Team decides to take on. Input: Make sure all the followings are ready for sprint planning The product backlog User stories, design notes/documents, Question & Answer The latest product increment Capacity of DEV Team Previous performance of DEV Team (Sprints burn down chart and productivity or velocity)
- 37. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Sprint Planning (Cont.) Discussion in meeting: Clarify the selected PBIs : Discuss the goals and context for the high-priority items on the Product Backlog, providing the DEV Team with insight into the PO thinking. The PO and DEV Team also review the “Definition of Done” and the Acceptance Criteria Break down PBI into development task and estimate task The DEV Team should explain to the PO and SM how PBI intends to work as a self- organizing team to accomplish the Sprint Goal and create the anticipated Increment Plan to study and review user stories, requirements for the next sprint Output PBIs will be delivered in the Sprint The DEV team understand the Sprint goal Updated Product Backlog (included the additional tasks for review code, review requirement, testing, …) Updated Sprint log and Updated Acceptance Criteria if any
- 38. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Daily Meeting
- 39. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Daily Meeting (Cont.) • Purpose: to review the Sprint Goal and to synchronize activities and create a plan for the next 24 hours • Discussion in the meeting: each DEV Team member will answers/explains 3 questions: 1. What has been accomplished yesterday? 2. What will be done today? 3. What obstacles are in the way? • Output: Improve communications Identify and remove impediments/obstacles to development, highlight and promote quick decision-making Improve the DEV Team’s level of project knowledge The issue, risk log are updated by Scrum Master
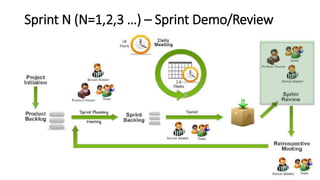
- 40. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Sprint Demo/Review
- 41. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) - Sprint Demo/Review (Cont.)
- 42. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) - Sprint Demo/Review (Cont.) • Purpose: To inspect the Increment To adapt the Product Backlog if needed and To elicit feedback and foster collaboration • Input: End of the Sprint Scrum Master is to baseline the package and release note. Test report from Tester • Discussion in the meeting: The PO identifies what has been “Done” and what has not been “Done”; The DEV Team demonstrates the “Done” work and answers questions about the Increment; The entire group collaborates on what to do next, so that the Sprint Done provides valuable input to subsequent Sprint Planning Meetings. • Output: Revised Product Backlog that defines the probable PBIs for the next Sprint. Release note The issue, risk log are updated by Scrum Master. Meeting minutes
- 43. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) – Sprint Retrospective
- 44. Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) - Sprint Retrospective (Cont.) • Purpose: Inspect how the Sprint went with regards to people, process, and tools Identify and order the major items that went well and potential improvements Create a plan for implementing improvements • Input: Occurs after the Sprint Review and prior to the next Sprint Planning Meeting Sprint report is completed by SM Lesson learnt, best practice • Discussion in the meeting: What’s done good and What’s done need to improve The Scrum Team plans ways to increase product quality • Output: The Scrum Team identified improvements that will implement in the next sprint Updated lesson learn, best practice, improvements plan
- 45. • Lessons Learnt ID Area Description of Event/Situation Root Cause Lesson Learned 1 2 3 ID Process Area Description of Event/Situation Best Practice 1 2 3 ID Action Description Owner Due date 1 2 3 • Best Practice • Action Need Sprint N (N=1,2,3 …) - Sprint Retrospective (Cont.)
- 46. Cancel A Sprint • Input: The Sprint Goal becomes obsolete such as changes direction or if market or technology conditions change. It no longer makes sense given the circumstances Only PO has authority to cancel the Sprint • Discussion in the meeting Review the work items are completed or done All incomplete PBIs are re-estimated/prioritized and put back on the Product Backlog Resource plan and re-allocation • Output: Updated PBIs Updated team capacity
- 47. UAT (User Acceptance Testing) Make sure the following items are ready before UAT: • Package release (include release note) and test report from Test leader • Process, plan and acceptance criteria for UAT • Scope, tools and environment for UAT • Test scenarios for UAT (PO, BA, Client/IT Head) • Jira/TFS workflow for handling bugs/CRs logged on Jira for UAT • Testing and bug fixing process for UAT • Change Requests process for UAT • Specify roles and responsibilities before UAT starts (PO, BA, Tester, DEV)
- 48. UAT (User Acceptance Testing) (Cont.) Best Practice for UAT: • PO prepares UAT plan early in the project life cycle and PO should also confirms the date to start UAT. • PO should prepares a checklist before the UAT starts • PO sets the expectation and defines the scope of UAT clearly • Testers should conduct pre-UAT session during Regression Testing phase itself • PO tests end to end business flow • Tests the system or application with real world scenarios and data • Thinks as an unknown user in the system • Conduct feedback session and meeting between the PO and development team before project end and moving to production
- 49. Project Closure • Input: Client/Onshore PM has sent the Acceptance Agreement for the final release or The project is cancelled by the client/onshore PM. • Activities: PM work with the Scrum team to create the post-mortem report, case study, lessons learnt and best practices PM update the resource plan and allocation PM inform the client/onshore PM for the project to closed and move to maintenance & support phase if needed.
- 50. Software Development Tools • Tool to plan, track, manage and release • Tool to organize, create documents, and discuss works • Tool for source code version control • Tool for development (IDE) • Tool for analysing source code • Tool for Continuous Integration (CI)
- 51. Software Development Tools (Cont.) • Tool to plan, track, manage and release: Microsoft Project Jira https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira
- 52. Software Development Tools (Cont.) Reporting In Jira Tool: Velocity Chart, Burndown Chart, Sprint Report, Release Burndown, …
- 53. Software Development Tools (Cont.) • Tool to organize, create documents, and discuss works Microsoft SharePoint Confluence https://www.atlassian.com/software/confluence
- 54. • Tool for source code version control SVN (Subversion) TFS (Team Foundation Server) GitHub • Tool for development (IDE) For MS .Net: MS Visual Studio For Java: Eclipse • Tool for analysing source code: For MS .Net: FxCop, StyleCop For Java: Eclipse • Tool for Continuous Integration (CI) For MS .Net: TFS, TeamCity For Java: Jenkins, TeamCity Software Development Tools (Cont.) Branching strategy
- 55. Appendix • User Story Template • Definition Of Ready • Definition Of Done • Sprint Acceptance Criteria • Team Values • Hierarchy (epic, story, task) • Scrum vs Kanban vs Scrumban • Disadvantages Of Scrum
- 56. User Story Template • User Story: describe details of user role, user goal and business value of user story. As a <user role> I want to be able to <user wish/goal>, so that I can <business value> Example: As a registered user I want to log in so that I can access subscriber-only content • Business Acceptance Criteria: describe details of any business acceptance criteria that are associated with this user story • Current and Suggested Mock-up Screens: screens (if any) showing the current and suggested layout for the system or function • Workflows: provide workflows (if any) that supports more details to User Story Acceptance Criteria ID Description <e.g. BRUL1> <e.g. In a contracting market, it shall only be possible to confirm or get approval on an order with order type = "sold" if the order is associated with a contract> <e.g BRUL … > <…. >
- 58. Use Case Template (Cont.)
- 59. Use Case Template (Cont.)
- 60. Definition Of Ready I Independent The user story should be self-contained, in a way that there is no inherent dependency on another user story. N Negotiable User stories, up until they are part of an iteration, can always be changed and rewritten. V Valuable A user story must deliver value to the end user E Estimable The development team has to be able to estimate the size of a user story. S Small User stories should not be so big as to become impossible to plan/task/prioritize with a certain level of certainty. T Testable The user story or its related description must provide the necessary information to make test development possible (business acceptance criteria).
- 61. Definition Of Done • User Story User story is provided or approved by Product Owner and they have to be based-line Selected User Story for the sprint is completed and understood by the team Tasks for selected user stories have been identified and estimated by the team (with consult by Technical lead) Technical Design Document is completed with respect to product theme and understood by the team (depends on user story) Technical Design Document is approved by Technical Lead (and stakeholders) and it have to be based-line (depends on user story) Code meets Coding Standard (e.g. as defined in Code Review Check list) Code is peer reviewed (or Technical lead reviewed) and checked in to SVN Code checked in there's no build errors on build server and not break any others existing code Code merged to another branch in case of enhancement or bug fix (depends on development process and source control tool used)
- 62. Definition Of Done (Cont.) Unit tests are written and executed to make sure that the code is covered and all unit test cases are passed (defined by the team in sprint planning) All test cases of the User Story are executed and passed Integration tests of the affected areas are conducted and passed All acceptance tests of the User Story are met Non-functional requirement fulfilled (browser capabilities, scalability, reliability, security etc..). All Tasks and sub tasks are set to done or removed Remaining hours for story set to zero Necessary documentation is updated and completed such as design document, installation guide, ...
- 63. Definition Of Done (Cont.) • Sprint Installed demo system for review The Acceptance Criteria for the Sprint is met The sprint must be accepted by the product owner Release package is based-line Release documentation is updated and completed such as Release note, Product installation guide, User manual, ...
- 64. Sprint Acceptance Criteria • All test cases of each user story are passed • There are no Critical or Major bugs • Define number of opened bugs before release to client Type of Defect Description Sprint N Blocker/ Critical Showstopper - An error that makes the whole or a significant part of the application inoperable or otherwise has a significant effect upon Customer's business. Tester cannot proceed with any tests e.g. system crash 0 Major An error that has a material effect upon the functionality, performance or user experience of the application function upon which Customer relies for the efficient conduct of its business. Tester can-not proceed with any tests in a functional area 0-1 Normal A major error (as defined above) that has an acceptable work around OR An error that has a nominal effect upon the functionality or performance of the application function upon which Customer relies for the conduct of the business. Does not stop testing - but limits it e.g. data validation wrong 0-2 Minor A minor or cosmetic error that and that causes a minimal effect upon the Customer's business. e.g. screen spelling or error message wrong 0-3
- 65. Team Values • Trust communication • Respect team mate and do not take critic personal • Think careful before saying something • Respect lunch time • Teamwork and support, sharing knowledge • On time for meeting, delivery • Never do deployment on Friday or before holidays • Questions and open discussion for un-clear things • Quality and performance • Work progress and tasks information updated
- 66. Hierarchy (epic, story, task)
- 67. Scrum vs Kanban vs Scrumban SCRUM KANBAN SCRUMBAN Board / Artifacts simple board mapped on the process board mapped on the process board product backlog sprint backlog product increment burndown chart Ceremonies daily scrum none required daily scrum sprint planning other scrum related ceremonies IF needed sprint review sprint retrospective Prioritization Part of backlog grooming, done by PO. Out of the process. Backlog should be prioritized. Out of the process. Backlog should be prioritized. Who feeds the work in progress (“brings new work”)? PO Depends on defined roles and necessities Depends on defined roles and necessities Iterations yes (sprints) no (continuous flow) not mandatory (continuous flow); could have sprints
- 68. Scrum vs Kanban vs Scrumban (Cont.) SCRUM KANBAN SCRUMBAN Estimation yes (ID, SP,…) no (similar size work items) (a) no (similar size work items) (a) Teams Recommended cross functional cross functional / specialized cross functional / specialized Roles Product Owner as needed Team + needed rolesScrum Master Team Teamwork collaborative based on pull approach based on pull approach WIP (work-in-progress limit) planned for the duration of the sprint controlled by workflow state controlled by workflow state Changes to work scope should wait for next sprint added as needed (JIT) added as needed (JIT) Product backlog prioritized list of user stories (estimated) no (JIT) no (JIT) Impediments addressed immediately addressed immediately (b) addressed immediately (b) When does it fit? Product development Support/ Maintenance work (operational level) Product development (unclear vision) Small value adding increments development possible Evolving requirements (no clear roadmap) Requirements in good shape Need to include support/ maintenance (event driven) work in the process
- 69. Disadvantages Of Scrum • Scope creep; Lack of definite end date • Daily meetings at times can go too strict and frustrating • Team Members : not experienced, not committed, leaving … • Task can be spread over several sprints • Big team, Big project are the challenges • Trust communication and management must have for project • Quality is hard to implement (Testing process should be well defined) • Difficult for the Scrum master to plan, structure and organize a project that lacks a clear definition • Frequent changes, frequent product delivery and uncertainty regarding the precise nature of the finished product make for a rather intense project life cycle for everyone involved